Brighter Side of News
1M
355
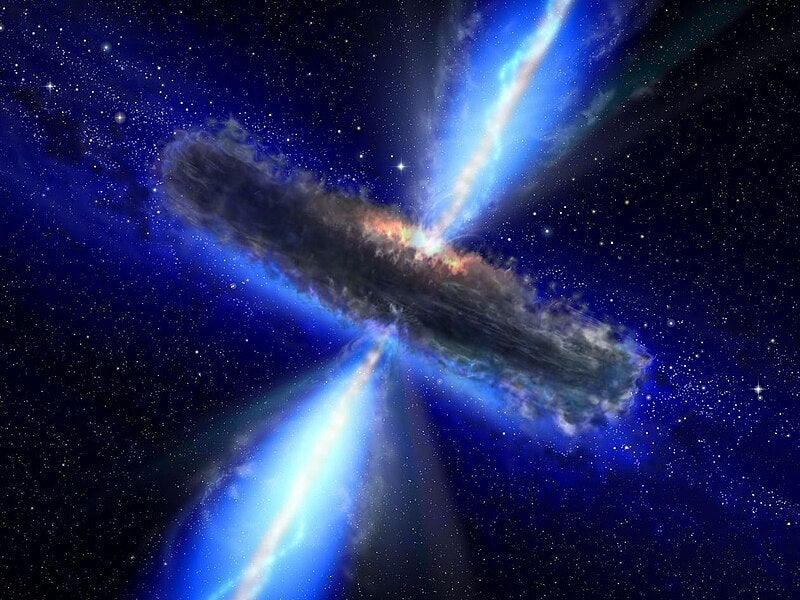
Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Astronomers discover cosmic water source 140 trillion times larger than Earth’s oceans combined
- Astronomers have uncovered the largest and most distant water reservoir ever detected in the universe, enveloping a quasar more than 12 billion light-years away.
- The water reservoir is equal to 140 trillion times the volume of Earth’s oceans and surrounds the quasar APM 08279+5255, which hosts a black hole 20 billion times the mass of the sun.
- Water vapor plays a crucial role in understanding the conditions around the quasar, heating gas to unusual levels and making it far denser than typical interstellar environments.
- The discovery offers insights into the future of the quasar, with the available gas potentially sustaining the black hole's growth until it becomes larger or collapsing into new stars.
- Astronomers detected the water reservoir using instruments like Z-Spec and the Plateau de Bure Interferometer, revealing the vast quantity of water in the region.
- Water in the universe can be found in interstellar clouds, protoplanetary disks, comets, asteroids like Ceres, planetary atmospheres, surfaces, and even exoplanets like K2-18b.
- The formation of water primarily occurs through chemical reactions between hydrogen and oxygen, leading to water ice in space that eventually coalesces into larger bodies containing water.
- This remarkable discovery showcases the pervasiveness of water throughout the universe and provides valuable insights into the extreme environments surrounding quasars.
- Understanding the presence of water in various cosmic objects enhances our knowledge of planetary formation processes and the distribution of water in different regions of the universe.
- The immense scale of the water reservoir around the quasar APM 08279+5255 challenges previous assumptions about the distribution of water in deep space and highlights the unique conditions in that region.
- The research team's observations shed light on the role of water vapor in shaping the environment around quasars and contribute to the ongoing exploration of water sources across the cosmic landscape.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app