Prodevelopertutorial
3w
420
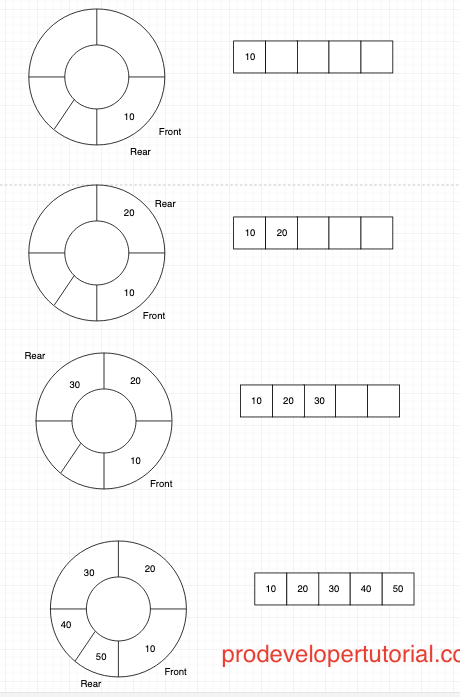
Image Credit: Prodevelopertutorial
Data structure tutorial 9: Circular Queues Data structure introduction and Implementation using arrays.
- Circular Queue uses a data structure (array or linked list) to allow insertion and removal of elements from both the ends (front and rear end).
- In this article, we understand the introduction to Circular Queue Data Structure, Formula to calculate to insert elements, Understanding inserting elements with an example, and Implementation of Circular Queue using arrays.
- In Circular Queue, the front will be pointing at 0 and rear pointer will be pointing at the maximum index size of the queue.
- When an element is inserted at the rear end, rear_end = (rear_end + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; similarly, when an element is deleted from front_ end front_end = (front_end + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; are the formula to calculate the index.
- Depending upon the result, the rear pointer will update accordingly.
- Circular queue, we will be utilizing the space efficiently.
- Data structure uses an array with operations Insert(), Delete(), Display().
- The Insert() function adds an element at the rear end and Delete() function deletes element from the front end.
- Display() function shows the content of the queue.
- Code implementation of Circular Queue using arrays includes InsertQueue(), DeleteQueue(), and DisplayQueue() functions.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app