RealPython
2w
210
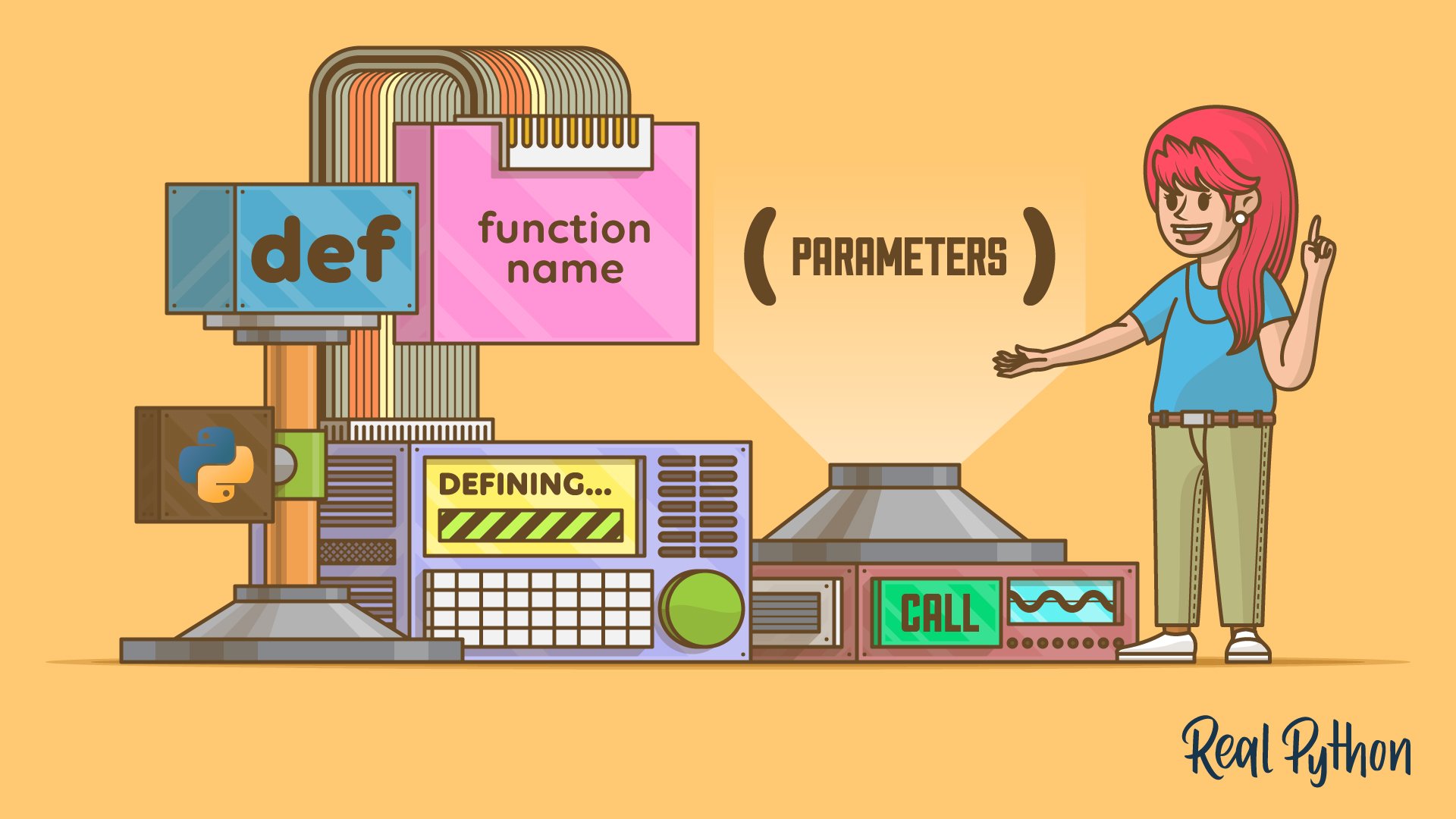
Image Credit: RealPython
Defining Your Own Python Function
- A Python function is a named block of code that performs specific tasks and can be reused in other parts of your code.
- To define a function in Python, you use the def keyword, followed by the function name and an optional list of parameters enclosed in a pair of parentheses.
- Functions help organize code, make it more modular, reusable, and easier to maintain.
- You can call a function using its name and necessary arguments.
- Functions in Python are self-contained blocks of code designed for specific tasks, improving code readability and efficiency.
- Defining and using functions is essential for managing complexity in Python programming.
- Functions in programming are analogous to mathematical functions, mapping inputs to outputs.
- Python supports user-defined functions along with built-in functions.
- User-defined functions in Python allow developers to create custom functions with specified arguments and internal logic.
- The article provides examples of Python built-in functions like id() and len().
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app