Hackernoon
4d
329
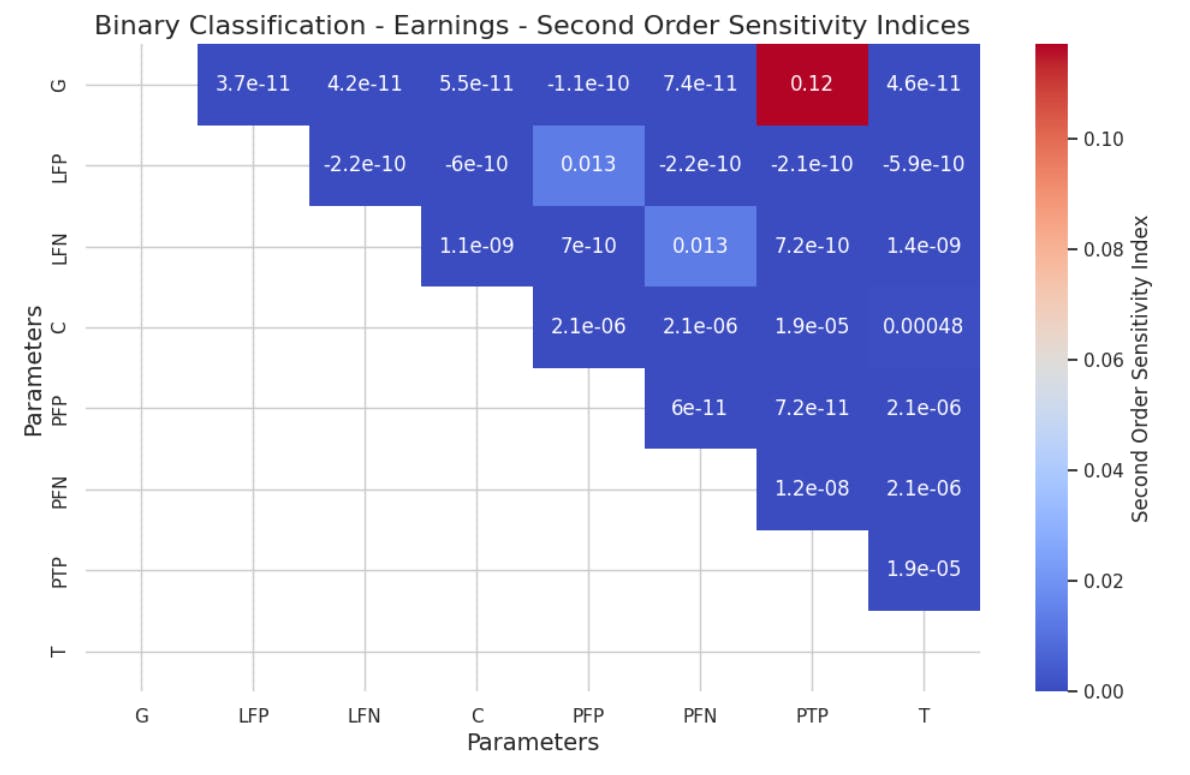
Image Credit: Hackernoon
Exploring Local and Global Sensitivity in Binary Decision Modeling
- Binary classification involves predicting which of two classes a particular instance belongs to, often represented as 0 and 1, 'yes' and 'no', or 'true' and 'false'.
- Binary classification outcomes are typically represented in a confusion matrix, detailing true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives.
- Local sensitivity analysis involves examining partial derivatives, while global sensitivity analysis using the Sobol method provides insights into overall model performance.
- The research delves into understanding the costs associated with binary classification operations and emphasizes the importance of considering different cost scenarios for accurate model evaluation.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app