Medium
4h
54
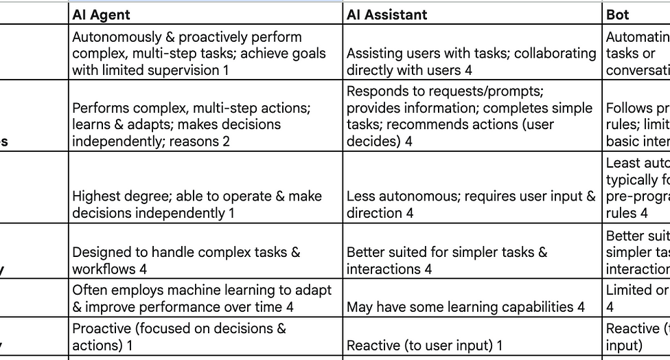
Image Credit: Medium
Google Gemini Deep Research on Enterprise AI Agents Scale, Security
- Enterprise AI agents represent a fundamental shift towards autonomous decision-making and proactive task execution, promising significant productivity benefits by automating repetitive tasks.
- Successful adoption of AI agents hinges on addressing scalability, security, and ethical governance challenges, emphasizing integration, oversight, and alignment with organizational values.
- AI Agents operate autonomously, making decisions independently to achieve complex goals, differing from AI Assistants and Bots in their level of autonomy and decision-making capabilities.
- The emergence of enterprise AI agents signifies a strategic move towards proactive problem-solving and autonomous decision-making, reshaping human-AI collaboration within organizations.
- Multi-agent systems leverage diverse capabilities and roles, simulating human behaviors and enabling collaborative problem-solving across complex enterprise challenges.
- Enterprise AI agents boast multimodal processing and advanced reasoning, empowering them to interpret diverse information types and make informed, adaptive decisions.
- To ensure effective decision-making, AI agents need access to a comprehensive view of organizational information, requiring integration with existing systems and deep contextual understanding.
- Robust architectural designs, like Layered and Blackboard architectures, enable scalable deployment and resilience of complex AI systems in enterprise environments.
- AI agents require high-performance computing resources, distributed architectures, and modular design for scalability, fault tolerance, and efficient resource utilization.
- Implementing fault tolerance, dynamic resource allocation, and proactive security measures are essential for ensuring the reliability, scalability, and security of AI agent systems.
- Privacy, data protection, algorithmic bias mitigation, and AI explainability are critical considerations for enterprises deploying AI agents to maintain compliance and ethical standards.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app