Medium
1M
41
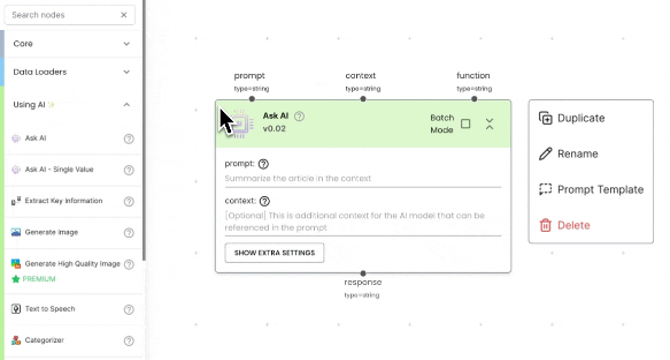
Image Credit: Medium
How Deep Tech Founders Turn LLMs Into Infrastructure
- LLMs have become accessible and widely utilized in creating products, posing challenges in differentiation.
- Distinguishing between using LLMs as products versus infrastructure is crucial for defensibility and functionality.
- AI startups often fall into two categories based on their approach to leveraging LLMs.
- Real-world examples like Perplexity and Cursor demonstrate innovative uses of LLMs as infrastructure.
- Perplexity's architecture incorporates real-time web crawling and document retrieval for fresh and verifiable information.
- Cursor integrates LLMs into coding workflows, facilitating both developers and non-technical users in software creation.
- Gumloop's drag-and-drop interface enables users to create AI-driven workflows, offering flexibility and adaptability.
- The rise of LLMOps architectures emphasizes the importance of structure and operationalization in AI product development.
- The layered leverage in AI product development includes grounding models with external data, structuring logic, and optimizing speed and responsiveness.
- Successful AI product development requires a blend of product thinking and technical architecture to translate capabilities into user experience effectively.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app