Medium
1M
31
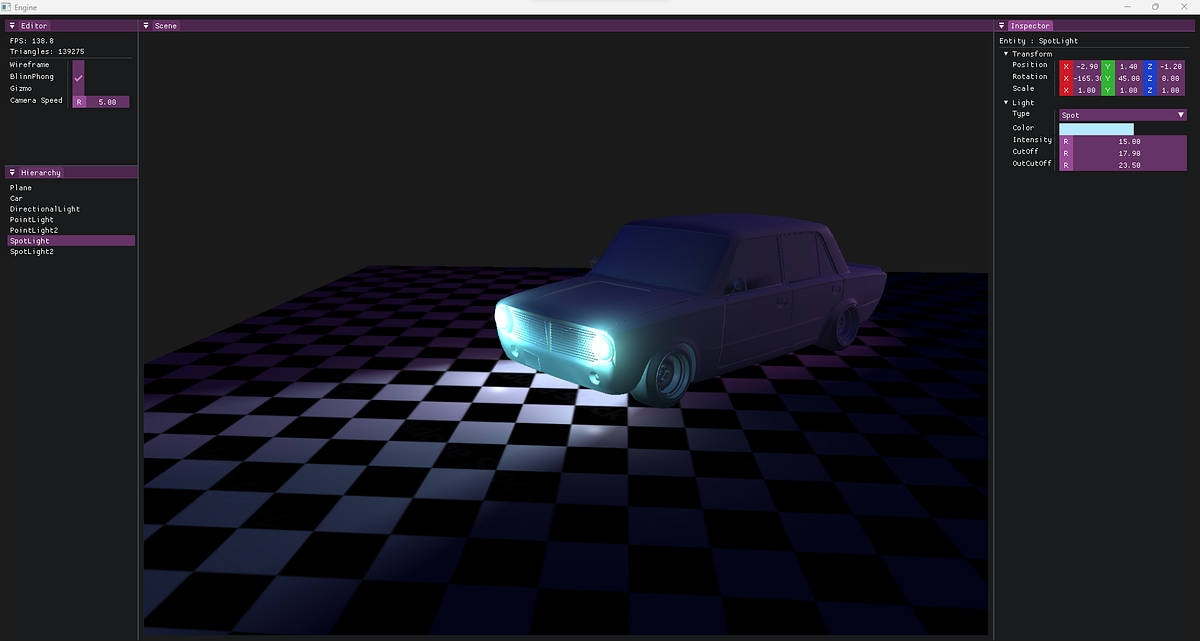
Image Credit: Medium
How to pick a 3D object using raycasting in C++
- In the journey of developing a 3D viewer in C++, the focus shifted to making object selection user-friendly by implementing raycasting for picking objects.
- The process involves detecting mouse click input, converting 2D mouse position to the 3D world, and determining the ray direction based on camera position.
- Intersecting the ray with bounding boxes of entities involves utilizing a struct to encapsulate intersection logic and performing intersection tests.
- The work involves methods like EditorRaycast for intersection tests and transforming the ray from world space to local space of entities for accurate collision detection.
- The bounding box of entities is described with two 3D vectors and models initialize their bounding box during the initialization phase.
- RayAABoxIntersection method effectively checks for intersections between the ray and bounding box, providing data in the HitInfo struct.
- The process overview involves looping through entities, projecting rays, checking intersections, and outlining the steps to achieve object selection using ray/bounding box intersection.
- The article concludes by discussing the pros and cons of using bounding boxes for object picking, highlighting solutions and offering assistance in game/3D development.
- This article aims to aid in understanding the process of raycasting for object selection and encourages engagement through comments and GitHub project exploration.
- For further clarification or inquiries, the author welcomes contact and wishes the readers a productive day.
Read Full Article
1 Like
For uninterrupted reading, download the app