The Register
3d
326
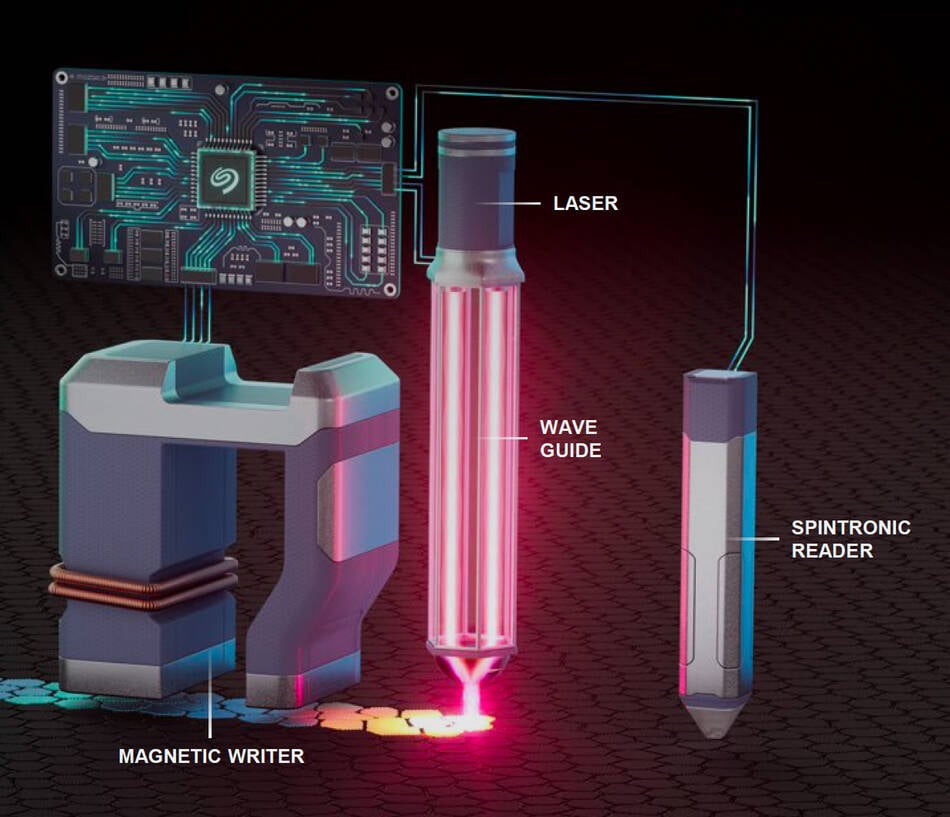
Image Credit: The Register
Seagate still HAMRing away at the 100 TB disk drive decades later
- Seagate continues to work towards achieving 100 TB disk drives using HAMR technology with Mozaic 3+ HAMR tech currently supporting 3-3.6 TB per platter in their drives.
- Competitors like Western Digital and Toshiba are also moving towards HAMR tech for increased areal density in disk drives but are lagging behind Seagate's development progress.
- Seagate has faced challenges in mass production and qualification of HAMR drives, leading to delays in introducing higher capacity models to the market.
- Seagate aims to introduce 40-plus TB drive samples in the near future with plans to reach a capacity range of 12-44 TB and further advancements in subsequent generations.
- Despite previous setbacks, Seagate is optimistic about achieving 100 TB disk drives by around 2033, leveraging evolving HAMR technology for increased areal density.
- The company anticipates that over 40% of its disk drive exabytes will be supported by HAMR technology by the end of fiscal 2026, with further growth expected in fiscal 2027.
- Seagate's strategy involves leveraging HAMR technology to reduce production costs by reinventing lower capacity drives with fewer platters and sliders, aiming for a 10-15% cost reduction.
- The delays in HAMR productization have allowed competitors to catch up in terms of capacity, with Seagate opting for a ten-platter design compared to Western Digital and Toshiba's eleven-platter approach.
- Analysts believe that HAMR technology is reaching maturity, with expectations of wide-scale adoption by early 2026.
- Seagate's vertically integrated laser approach aims to enhance cost efficiency in production, while ongoing investments in HAMR technology indicate a strong commitment to achieving higher disk drive capacities.
- The prolonged challenges in HAMR technology development may give Seagate a competitive advantage in the market, potentially leading to increased market share and revenue over competitors.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app