Educba
7d
208
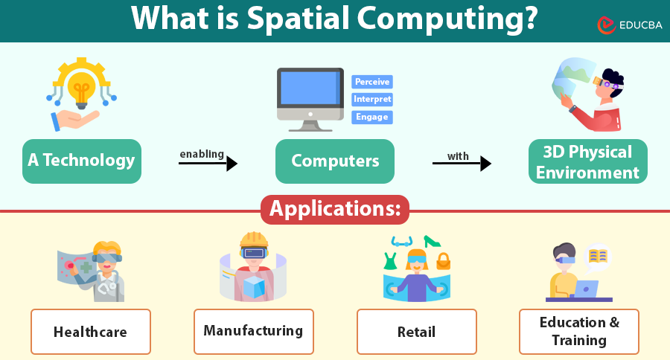
Image Credit: Educba
Spatial Computing
- Spatial computing involves computers perceiving, interpreting, and engaging with the physical environment in 3D space, blending digital content into real environments for natural interaction.
- Core technologies behind spatial computing include AR, VR, MR, 3D mapping, computer vision, AI, sensors, and spatial audio.
- Spatial computing combines sensing, spatial mapping, contextual understanding, interaction, rendering, and feedback for immersive experiences.
- Benefits of spatial computing include enhanced interaction, improved decision-making, cost reduction, increased engagement, and remote collaboration.
- Real-life applications of spatial computing span healthcare, manufacturing, retail, education, construction, and architecture, offering improved efficiencies and experiences.
- A case study on Apple's Vision Pro spatial computing headset showcases features like eye and hand tracking, spatial audio, and real-time rendering, driving mainstream adoption.
- Challenges in spatial computing include hardware cost, privacy concerns, technical complexity, and user experience considerations.
- Spatial computing is revolutionizing interactions with technology and physical spaces, offering vast potential across various industries and everyday life.
- As spatial computing adoption grows and hardware accessibility increases, it is poised to become an essential technology, shaping the future of human-machine interaction.
- Spatial computing market is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rising demand and interest in this transformative technology.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app