Medium
17h
88
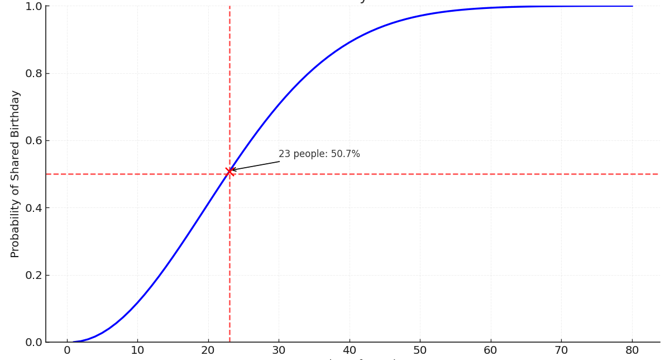
Image Credit: Medium
The Birthday Paradox: Why 23 People Are All You Need for a 50% Chance of Shared Celebration
- In a group of 23 people, there is a 50% chance of at least two people sharing the same birthday.
- The Birthday Paradox arises from comparing every possible pair of people against all 365 potential dates, leading to an explosion in the number of comparisons.
- This paradox has significant implications in computer science and cryptography, setting limits on collision probabilities for hash functions and aiding in testing the quality of random number generators.
- Understanding the principles behind the Birthday Paradox showcases the limitations of human intuition in probability and highlights the importance of precise mathematical analysis in various fields.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app