Dev
4w
168
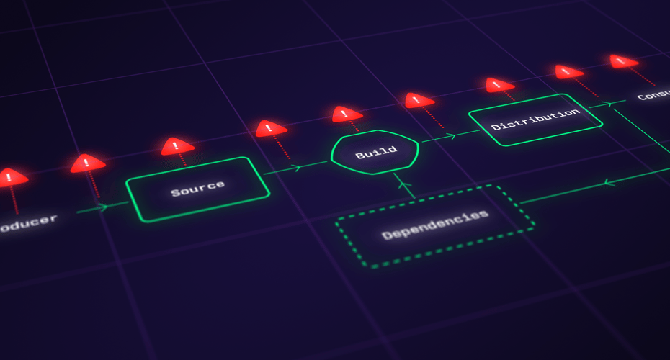
Image Credit: Dev
Understanding the SLSA framework
- The Software Supply Chain Levels for Software Artifacts (SLSA) framework has emerged to fortify software supply chains against threats, evolving to address new risks.
- SLSA is an open-source framework developed by Google, stewarded by OpenSSF, offering a structured approach to securing software delivery pipelines.
- It provides guidelines, automated tools, and documentation to evaluate software artifact security levels and dependencies independently.
- SLSA tracks include levels for different aspects of the supply chain, with the 1.0 release focusing on the 'Build' track with four levels.
- Core principles of SLSA include trusting platforms, verifying artifacts, validating code over individuals, and preferring attestations over inferences.
- The framework aims to address threats like build process compromise, malicious artifact injection, chained dependency and code injection, and malicious code injection.
- SLSA can be used to assess internal infrastructure, audit software vendors, and suppliers, and highlight security gaps.
- Companies may self-assess or run audits using SLSA without a formal certification process, while OSS software and industry insiders document compliance levels.
- To get started with SLSA, companies can educate themselves, self-evaluate artifacts, and aim to implement the guidelines incrementally.
- Buildkite Package Registries provides support for SLSA provenance, aiding in adopting and enhancing security efforts using the framework.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app