Chargedevs
4w
80
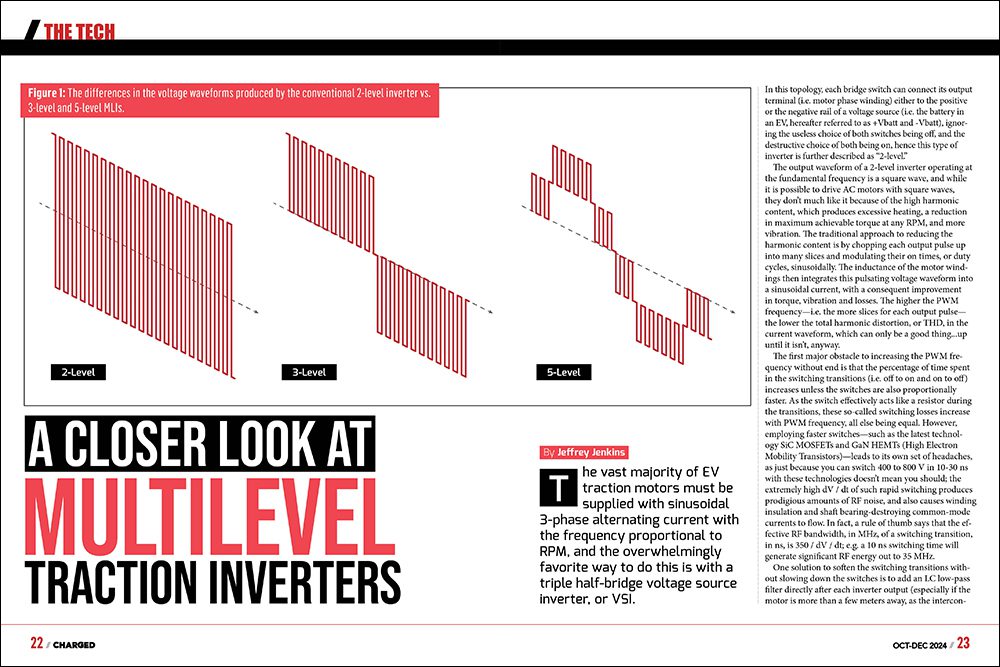
Image Credit: Chargedevs
A closer look at multilevel traction inverters
- Most EV traction motors require sinusoidal 3-phase AC with frequency proportional to RPM, typically supplied by triple half-bridge VSIs.
- Traditional 2-level inverters produce square waveforms with high harmonic content that can lead to heating, torque reduction, and vibration.
- Increasing PWM frequency to reduce harmonic content leads to higher switching losses, requiring faster switches like SiC MOSFETs and GaN HEMTs.
- High-speed switching in inverters causes RF noise and common-mode currents, necessitating the use of dV/dt filters to mitigate these issues.
- Multilevel inverters (MLIs) offer lower THD and common-mode currents by generating output voltage levels with additional steps.
- MLIs require separate voltage sources for each level or use capacitive voltage dividers to create voltage levels indirectly.
- Neutral Point Clamped and Flying Capacitor are 3-level MLI types that offer different methods of generating the 0 V output level.
- Active Neutral Point Clamped and T-type MLIs balance charge on divider capacitors and handle loads with a wide power factor range.
- MLIs present challenges in terms of complexity, component count, and development costs compared to 2-level VSIs.
- While MLIs offer advantages, such as reduced noise and common-mode currents, the argument for their adoption in EVs is challenging.
- Consideration of filter addition to existing inverters may be a more straightforward solution for reducing noise in EV applications.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app