Eletimes
2M
330
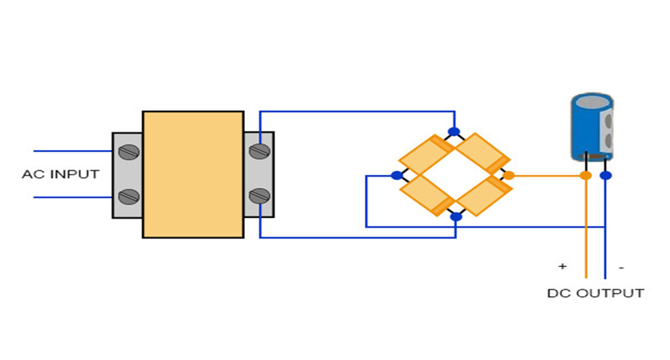
Image Credit: Eletimes
AC to DC Converter Types, Formula and Examples
- AC-DC converters transform alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) which is essential for the operation of electronic devices like computers, televisions, and smartphones.
- The use of AC-DC converters is driven by the fact that AC is the standard power supply provided by utility companies, while many electronic devices are designed to function with DC power.
- AC-DC converters provide a stable and reliable DC power supply for the consistent performance of electronic devices and are composed of essential components like transformers, switching devices, passive filters, and the load they supply.
- Several types of AC-DC converters can be classified based on control, components, and application needs - Uncontrolled Rectifiers, Controlled Rectifiers, Linear AC to DC Converters, Switch-Mode AC to DC Converters (SMPS), Special-Purpose Rectifiers, and Modern Integrated Converters.
- AC to DC conversion is achieved through rectification and filtering, and various formulas like the peak voltage, DC voltage output, ripple voltage, ripple factor, efficiency, and filtered DC voltage are used.
- AC to DC converters are used in various applications ranging from small household devices to industrial systems, renewable energy systems, telecom and IT infrastructure, medical equipment, and many more.
- Examples of AC to DC converters include phone chargers, laptop power supplies, televisions, on-board AC to DC converters for electric vehicles, power supplies for control systems, imaging systems, and servers amongst others.
- AC to DC converters have enabled optimized power delivery, reduced energy losses, efficient performance, and compact form factor, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages.
- AC-DC converters and their various types are essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable performance of the electronic devices that have become an integral part of our daily lives.
- The article on AC to DC Converter Types, Formula and Examples concludes that the choice of a specific AC-DC converter type depends on factors like the required voltage and current output, the desired efficiency and reliability, and the application needs, amongst others.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app