Electronics News
Knowridge
57

Image Credit: Knowridge
Replying to the wrong text could cost you, data security expert says
- U.S. consumers lost $470 million to scam text messages in 2021, a fourfold increase from 2020, according to the Federal Trade Commission.
- Data privacy expert Murat Kantarcioglu warns that AI technologies could make text scams more convincing and realistic by using publicly available information from social media.
- Scammers may use advanced techniques like incorporating realistic images and synthetic audio to manipulate individuals into falling for scams, Kantarcioglu cautions.
- Proactive measures smartphone users can take include being cautious of unsolicited text messages, avoiding clicking on links, verifying messages from separate trusted channels, and reporting scams to prevent further harm.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Knowridge
207

Image Credit: Knowridge
Are ad blockers backfiring? New study finds they may show you worse ads
- A new study suggests that ad blockers may not be as effective as users think and could even lead to worse ads being shown.
- The study focused on Adblock Plus' 'Acceptable Ads' feature, which aims to balance ad support for websites with providing users a better browsing experience.
- Users with the Acceptable Ads feature turned on saw 13.6% more problematic ads than those without any ad blockers, including ads with inappropriate content and misleading claims.
- The study raises concerns about ad platforms potentially targeting users with ad blockers with lower-quality or riskier ads, posing privacy risks. The research will be presented at the Privacy Enhancing Technologies Symposium on July 15, 2025.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Insider
153

Image Credit: Insider
The Pentagon is taking a big stake in a rare earth mining company, sending the stock up 60%
- MP Materials Corporation surged as much as 60% on news that the Defense Department is acquiring a stake in the only rare earth mine in the US, located in Mountain Pass, California.
- The Defense Department has agreed to purchase $400 million of the company's preferred shares, with the potential for conversion to common stock, making it MP's largest shareholder.
- The Pentagon's investment represents a roughly 15% stake in MP Materials, showing a strategic shift towards strengthening the domestic critical mineral supply chain and reducing reliance on Chinese imports.
- This move signifies a broader effort by the US government to secure essential resources and decrease dependency on foreign nations for key materials used in electronics, defense systems, and robotics.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Livescience
48

Image Credit: Livescience
Quantum materials with a 'hidden metallic state' could make electronics 1,000 times faster
- A new method of changing electronic states on demand could make electronics 1,000 times faster and more efficient, according to researchers.
- Controlled heating and cooling of a quantum material named 1T-TaS₂ allows it to switch between insulating and conducting electricity at different temperatures.
- Using the technique of thermal quenching, scientists could achieve a stable 'hidden metallic state' in 1T-TaS₂ at practical temperatures, potentially replacing silicon components in electronics.
- This advancement in quantum materials has the potential to revolutionize electronics by increasing processing speeds exponentially and reducing the space needed for components.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Medium
346
Image Credit: Medium
Lenovo Hybrid USB-C Dock (UK Plug) — The Secret to a Seamless Workspace
- The Lenovo Hybrid USB-C Dock is a versatile docking solution designed to expand laptop capabilities with a hybrid interface supporting both USB-C and USB-A connections.
- It is compatible with various laptop brands like Lenovo, Dell, HP, and MacBook, offering ports, display outputs, and power management tools for a seamless workstation experience.
- The dock supports dual 4K displays at 60Hz, comes with a USB-C cable and USB-C to USB-A adapter, and includes a 135W AC power adapter for charging laptops and other devices.
- The Lenovo Hybrid Dock simplifies connectivity with enterprise features for easier IT management in corporate and education environments.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Knowridge
382
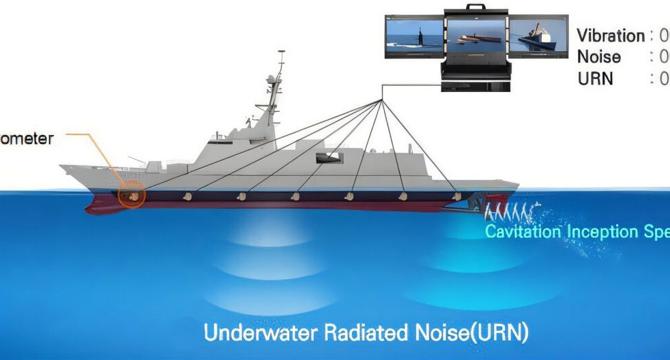
Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists build smart sensor system to quietly monitor ships underwater
- South Korean researchers have developed a real-time sensor system to predict underwater noise generated by ships without expensive equipment.
- The system attaches to a ship's hull to monitor underwater radiated noise, crucial for naval stealth operations.
- The smart algorithm in the system calculates ship noise accurately, detects anomalies, and helps in early fault detection.
- The system, tested on real naval ships, not only aids in naval stealth but also offers benefits for commercial ships in maintenance and noise control.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Knowridge
71

Image Credit: Knowridge
What is the optimal setting for your air conditioner
- Air conditioners operate on the principle of moving heat from a cold area to a high-temperature area, requiring electricity to power compressors.
- The optimal temperature setting for an air conditioner is around 80 degrees Fahrenheit, slightly lower than body temperature, to allow efficient radiation transfer of excess heat from the body.
- Large temperature differences between indoor and outdoor environments cause stress on the body, requiring energy for temperature balance.
- The efficiency of air conditioners depends on building insulation; it is better to adjust usage based on insulation quality, with considerations for natural airflow and sunlight management.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Knowridge
413
Image Credit: Knowridge
Ultra-stretchy smart foam could power the future of wearable tech
- Scientists in China have developed a highly sensitive and durable stretchable foam that can revolutionize how we track body movement and interact with technology.
- The foam, functioning as a sensor, can detect pressure and stretch changes by measuring electrical resistance, thanks to its piezoresistive strain sensor technology.
- Created using a special foaming technique called supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO₂) foaming, the foam can stretch up to 952% of its original length while maintaining its functionality.
- The production method is environmentally friendly, making the foam not only effective but also sustainable, with potential applications in wearable tech, soft robotics, health monitoring devices, and more.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Knowridge
331

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists discover eco-friendly way to make electronics using proteins
- Scientists have discovered a cleaner, eco-friendly method to produce semiconductors essential for electronic devices using water and specially designed proteins at room temperature.
- The new method, developed by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University and Princeton University, could make semiconductor production cheaper and safer in the future by eliminating the need for harmful chemicals and high heat.
- The breakthrough involves using custom-designed proteins, inspired by natural biomineralization processes, to guide the formation of quantum dots without toxic chemicals, marking a significant advancement in high-tech material production.
- The research, led by Dr. Leah Spangler and Dr. Michael Hecht, offers promising possibilities for creating cleaner, safer materials for electronics and improving the manufacturing process, potentially reducing the environmental impact of technology.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
352

Image Credit: Knowridge
New smart sensor could sniff out indoor pollution—and heals itself
- Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have developed a new formaldehyde sensor for indoor use with a special polymer coating that extends its life and allows it to regenerate.
- The sensor is based on MXene, known for its electrical properties and gas detection abilities, but typically vulnerable to air and humidity exposure.
- A nano-scale polymer coating made using Chemical Vapor Deposition protects the sensor, extending its effectiveness to over five months, compared to only two months without the coating.
- The coating not only protects the sensor but also helps it regenerate. When its performance fades, introducing humidity revives its sensitivity by about 90%—making it a sustainable and reliable solution for monitoring indoor air quality.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Knowridge
0

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists 3D print electronics with plant-based plastic and pencil graphite
- A team from the Singapore University of Technology and Design has developed a breakthrough 3D printing method using biodegradable materials to create electrically conductive components for electronics.
- They use cellulose acetate, a plant-based plastic, and graphite particles to make a custom ink capable of conducting electricity, solving the challenge of handling high heat in traditional 3D printing.
- By printing the ink into water using direct ink writing at room temperature, the researchers achieved clean, precise prints that are highly conductive (up to 60% graphite by weight) and flexible for applications like bendable circuits and sensors.
- This environmentally friendly method shows promise for creating sustainable electronics, and the team aims to further explore eco-materials for everyday use in the future.
Read Full Article
Like
Knowridge
204
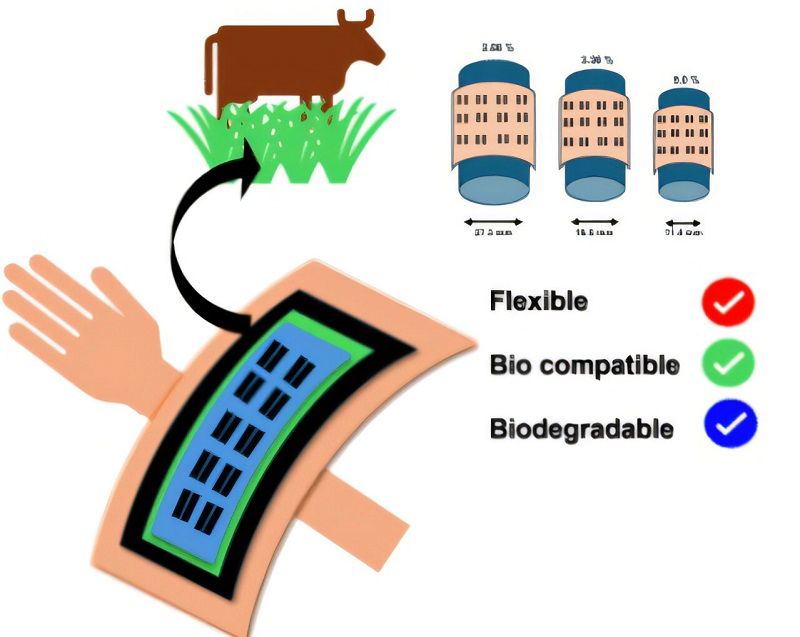
Image Credit: Knowridge
The next big thing in wearable tech? It biodegrades when you’re done
- Canadian scientists have developed a biodegradable wearable technology using collagen and semiconducting polymers.
- The material is flexible, safe for the human body, and environmentally friendly, designed to eventually break down to avoid pollution.
- This innovation could lead to practical applications like stretchable devices for plant growth tracking and potential life-changing uses such as implants to aid vision loss.
- Published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, the research aims to create effective, safe wearable devices with minimal environmental impact.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Dev
41

Image Credit: Dev
Debugging a Washed-Out TFT Display: A Real-World RGB Interface Mismatch
- A client faced color distortion issues with their TFT LCD display due to an RGB interface mismatch.
- The problem stemmed from connecting an 18-bit RGB TFT display to a 24-bit RGB output without proper signal mapping.
- By mapping the correct bits and grounding unused lines, the display showed accurate colors, resolving the issue.
- The incident highlights the importance of addressing RGB interface differences to prevent color inaccuracies in TFT displays.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Knowridge
326

Image Credit: Knowridge
New Japanese tech makes drone surveillance smarter and cheaper
- Researchers at the University of Tsukuba in Japan have developed a new method, SPADE, to assist in designing and testing drone-based video surveillance systems.
- SPADE, which stands for Simulator-assisted PerformAbility Design methodology for UAV-based Systems, allows engineers to simulate drone flights and video data processing in a virtual environment.
- By using SPADE, designers can assess system performance, video quality, object detection, and energy usage before physically implementing the drone surveillance system.
- The new approach aims to save time, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with building advanced drone surveillance systems, potentially leading to more efficient and reliable designs for both small-scale and large-scale projects.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
84
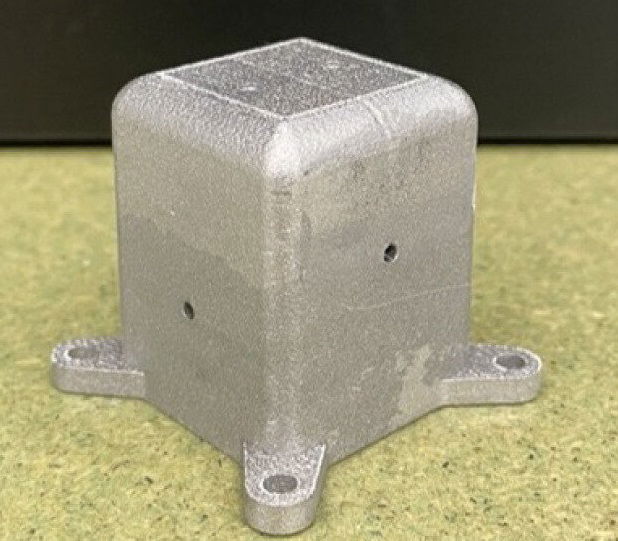

Image Credit: Knowridge
Wax-powered cooling system could keep space electronics from overheating
- Researchers are using wax-filled heat sinks to manage heat in space to prevent electronics from overheating in the absence of air circulation.
- The wax-based phase change material in the heat sinks melts at the electronics' operating temperature, absorbing and storing heat to prevent rapid overheating.
- Experiments conducted on a CubeSat orbiting Earth have shown promising results in extending electronics' operational time before overheating, unaffected by microgravity.
- The ongoing research aims to simplify cooling systems for future space missions based on the performance of the wax cooling technology, potentially saving time and resources in prototype development.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app