Universe Today
2M
156
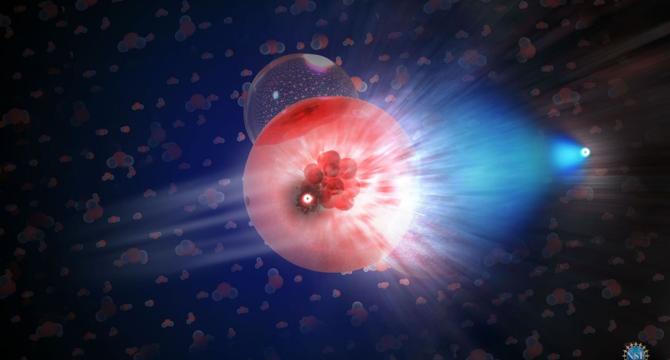
Image Credit: Universe Today
An Unfinished Detector has Already Spotted the Highest-Energy Neutrino Ever Seen
- The KM3NeT neutrino telescope, still under construction, detected the highest-energy neutrino ever recorded before completion.
- Neutrinos are challenging to detect due to their elusive nature and only interact through gravity and the weak nuclear force.
- Neutrinos are often referred to as 'ghost particles' as they have no electric charge and minimal interactions with matter.
- A recent observation by KM3NeT in the Mediterranean Sea marked a milestone in detecting cosmic neutrinos.
- The detected neutrino was associated with a muon with an energy level of 120 (+110/-60) petaelectronvolts.
- High-energy neutrinos like these may originate from distant cosmic sources, providing insights into astrophysical phenomena.
- The detection indicates the possibility of observing cosmogenic neutrinos resulting from interactions of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.
- The KM3NeT Collaboration aims to enhance detector positioning to improve source direction accuracy for future detections.
- Potential sources for the detected neutrino include active galactic nuclei like blazars, as suggested by researchers.
- Neutrinos are valuable in understanding the Universe, with this detection offering significant insights into neutrino astrophysics.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app