Space News
Livescience
6

Image Credit: Livescience
100 undiscovered galaxies may be orbiting the Milky Way, supercomputer simulations hint
- Scientists suggest over 100 unseen galaxies may be circling the Milky Way.
- Predictions based on simulations and mathematical models could support standard cosmology.
- Dark matter halos may hide dwarf galaxies making them hard to detect.
- Advanced telescopes like Vera Rubin Observatory may unveil these hidden galaxies soon.
Read Full Article
Like
TechCrunch
177

Image Credit: TechCrunch
The votes are in: TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 Audience Choice winners revealed for roundtables and breakouts
- The top five roundtables and top five breakout sessions have been selected for TechCrunch Disrupt 2025 after a voting process involving the TechCrunch audience.
- Breakout session winners include topics like AI tools in development, acquisition strategies in tech, AI for national security, AI for a better digital future, and agentic AI for startups.
- Roundtable session winners cover themes such as building trusted and scalable communities, AI safety and usefulness, the future of space economy in low Earth orbit, scaling search and AI, and challenges in real-world AI applications.
- The sessions will feature speakers from notable companies like GitHub, Coinbase, Pinterest, Amazon, and experts from various fields, offering insights and strategies for attendees to navigate the evolving tech landscape at Disrupt 2025.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
262

Image Credit: Nasa
Ax-4 Undocks from Station Inside Dragon for Earth Return
- The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft with the Axiom Mission 4 crew undocked from the International Space Station's space-facing port on the Harmony module.
- The undocking marks the completion of the Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4), the fourth private astronaut mission to the space station.
- Dragon is on an orbital track aiming for a splashdown off the coast of California on July 15, carrying over 580 pounds of cargo, including NASA hardware and data from experiments.
- NASA's coverage of the mission will end soon, with Axiom Space taking over for Dragon's re-entry and splashdown on their website.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
67

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA+ is Live as Ax-4 Prepares to Undock from Station
- NASA+ is live for the undocking of the Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4) from the International Space Station, with coverage available on various platforms.
- Coverage will end 30 minutes after undocking, with Axiom Space resuming coverage of the re-entry and splashdown on their website.
- The hatch between the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and the space station was closed in preparation for the return of private astronauts Peggy Whitson, Shubhanshu Shukla, Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski, and Tibor Kapu.
- The Dragon spacecraft is set to undock at 7:05 a.m. EDT and splashdown off the coast of California on Tuesday, July 15.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
293

Image Credit: Nasa
Ax-4 Boards Dragon and Closes Hatch for Departure
- The hatch between the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and the International Space Station closed at 5:07 a.m. EDT, in preparation for the return of Axiom Mission 4 (Ax-4) astronauts.
- Live coverage on NASA+ will resume at 6:45 a.m. for the scheduled undocking at 7:05 a.m., with the journey home targeting a splashdown off the coast of California on Tuesday, July 15.
- Axiom Space will provide coverage of Dragon's re-entry and splashdown on their website, while NASA's coverage will end around 30 minutes after undocking.
- Follow the space station blog, @space_station, ISS Facebook, and ISS Instagram accounts for updates on station activities.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Livescience
145
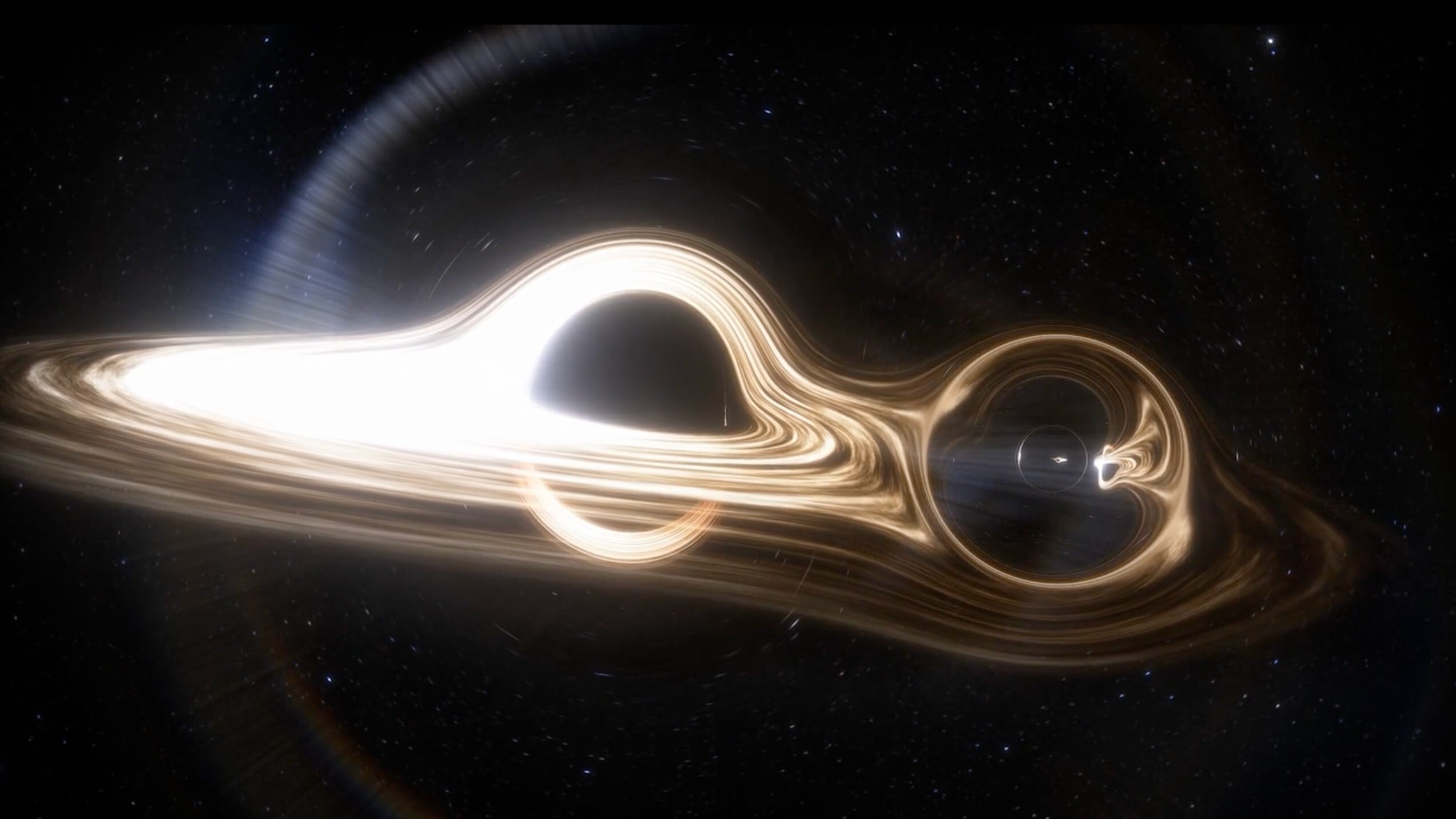

Image Credit: Livescience
Scientists detect most massive black hole merger ever — and it birthed a monster 225 times as massive as the sun
- Scientists have detected the most massive black hole merger, creating a 225-sun black hole.
- The merger challenges conventional theories, as the black holes' masses don't fit usual models.
- The new black hole is 225 times the mass of the sun, double the previous record.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Spaceflightnow
151

NASA, SpaceX target July 31 for Crew-11 launch to the ISS
- Next SpaceX Crew-11 mission to ISS targeting July 31 launch date.
- Crew includes NASA, JAXA, and Roscosmos astronauts for 6-month mission.
- Possible extension to 7 or 8 months under consideration for mission.
- Pre-launch preparations, boost of ISS, and extended Dragon reuse discussed.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Medium
111

Here’s a well-crafted, philosophical and scientific article draft based on My idea that “1 0 1 0”…
- The article explores the concept of the universe's cyclical nature, suggesting a pattern of expansion and contraction represented by the binary code 1 0 1 0.
- It connects this binary code to consciousness, proposing that 1 symbolizes an active mind while 0 represents stillness, creating a cyclical pattern of awareness and rest.
- The article envisions a universe structured as a vibrating binary field in multiple dimensions, suggesting that reality itself may be encoded in the simplest form of 1 0 1 0.
- It invites scientists and philosophers to view the universe as a living wave pulsating with binary awareness, presenting a new perspective on reality as a cosmic symphony governed by the rhythm of on and off.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Medium
320

“THE WAVY UNIVERSE CONSCIOUSNESS CYCLE” A New Perspective on Reality by Prasanth Retnakaran…
- The Wavy Universe Consciousness Cycle proposes a timeless loop where the universe is viewed as a rhythmically repeating flow of energy and structures, indicating that space and time oscillate perpetually.
- Consciousness in this model is seen as fundamental rather than localized or emergent, playing a vital role in observing, influencing, and experiencing universal cycles. It may act as the carrier signal for the wave's propagation, enabling a self-reflective and living universe.
- Black holes are portrayed as compressors in the cycle, condensing information and matter into singularity nodes, while white holes are envisioned as rebirth nodes releasing energy and structure back into the cosmic flow.
- The Wavy Universe Consciousness Cycle merges physics, cosmology, and metaphysical philosophy, portraying the universe as a dynamically oscillating structure with consciousness as a central force, providing new insights into the connections between science and inner awareness.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Nasa
268
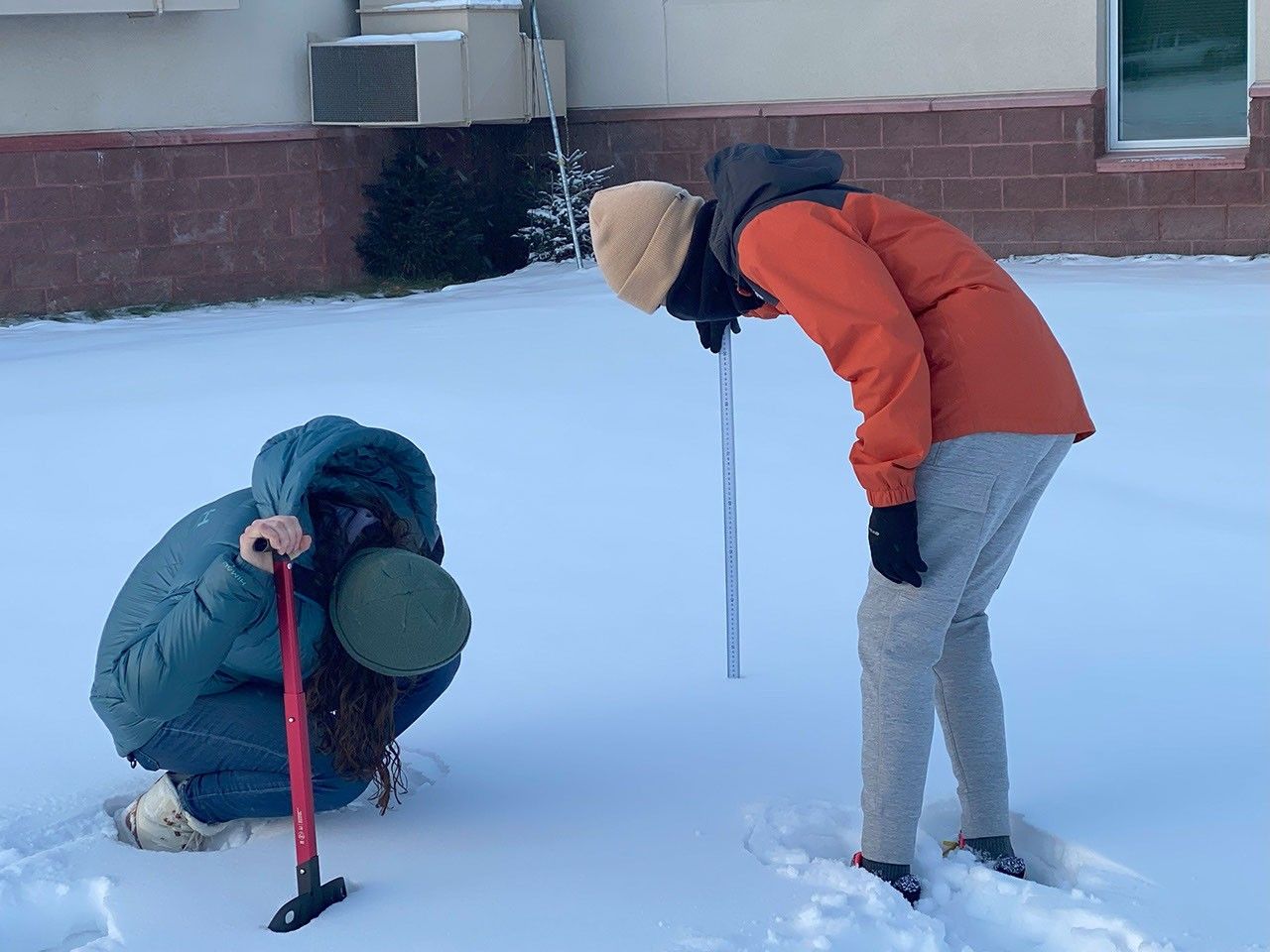

Image Credit: Nasa
Linking Satellite Data and Community Knowledge to Advance Alaskan Snow Science
- Seasonal snow is vital for water and energy cycles globally, affecting billions.
- Alaskan scientists combine satellite data with communal knowledge for studying snow water equivalent.
- NASA project in Interior Alaska merges InSAR, ground data, and student involvement.
- Alaskan youth contribute to snow science research, showcasing collaborative effort's impact.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Earthsky
319

Image Credit: Earthsky
Life on Venus? Exciting new VERVE mission could find it
- VERVE mission concept aims to find evidence of microbial life in Venus' clouds.
- Probe would search for biosignature gases like phosphine and ammonia in Venus' atmosphere.
- Researchers suggest VERVE could hitch a ride on EnVision spacecraft to Venus in 2031.
- Debate continues on the possibility of extremophile microbes living in Venus' clouds.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
The Verge
82

Image Credit: The Verge
Texas governor says his emails with Elon Musk are too ‘intimate or embarrassing’ to release
- Texas Governor Greg Abbott is refusing to release months’ worth of emails sent to Elon Musk and his companies citing a law that prevents the disclosure of 'highly intimate or embarrassing' information.
- The Texas Newsroom requested emails with Elon Musk dating back to last fall but the governor’s office later refused to follow through on the request, claiming the emails contain private and non-public information.
- The language used by the public information coordinator in the governor’s office is based on a common-law privacy exemption, with SpaceX also objecting to the disclosure of its emails due to potential competitive harm.
- Elon Musk has expanded his presence in Texas recently with Tesla, X, and SpaceX all being headquartered there, and public records requests have revealed interactions between Texas officials and SpaceX representatives.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Guardian
671

Starwatch: use the moon to find Saturn before its pirouette in the sky
- This week, the moon can help track down Saturn, the sixth planet in the solar system, as it brightens in the constellation of Pisces.
- Saturn and the Earth will have their closest approach on 21 September.
- The moon can be used as a guide to locate Saturn and observe its retrograde motion in the sky.
- The conjunction between the moon and Saturn will be visible from the southern hemisphere.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Knowridge
248
Image Credit: Knowridge
We may live in a giant cosmic void—and it could solve a big mystery
- Astronomers propose that Earth and the Milky Way galaxy may be situated in a large cosmic void, which could explain the Hubble tension, a discrepancy in measuring the universe's expansion rate.
- The concept suggests that a less dense region like a void could cause nearby matter to move away faster, giving the illusion of a quicker local expansion rate.
- New findings presented by Dr. Indranil Banik indicate that our local universe might be less dense, supporting the idea of a massive void about a billion light-years wide with 20% less matter than average.
- While controversial, recent data on baryon acoustic oscillations (BAOs) favor the void theory over the standard model, providing a statistical edge in favor of the concept.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Nasa
143

Image Credit: Nasa
Chief Training Officer Teresa Sindelar Touches the Future of Human Spaceflight
- Teresa Sindelar's journey to NASA's Johnson Space Center began after meeting astronaut Tom Stafford.
- She became a chief training officer, overseeing astronaut, crew member, and flight controller training.
- Her dedication to mentoring and leading by example has shaped the next generation.
- Sindelar received the 2025 Space Flight Awareness Program Honoree Award for her work.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app