Bioengineer
1w
164
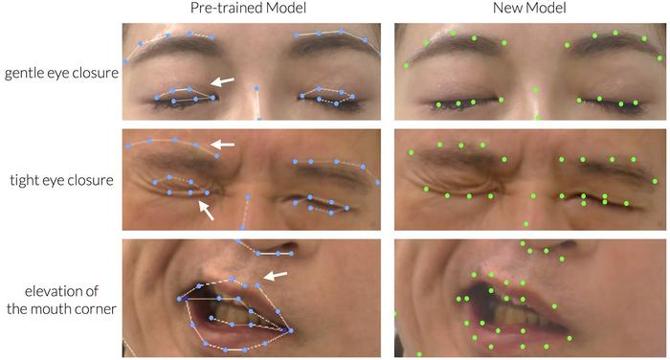
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Automated Facial Palsy Assessment Powered by Innovative AI Tool, Reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®
- A recent study led by Dr. Takeichiro Kimura explores using AI for facial palsy assessment, aiming to refine automated evaluations with the 'fine-tuning' method.
- Facial palsy presents challenges due to the need for precise assessments, with traditional methods showing inconsistencies among practitioners.
- The study identified shortcomings in previous AI facial recognition models like 3D-FAN, which struggled to detect asymmetrical features of facial palsy accurately.
- By fine-tuning the AI model with a diverse dataset of clinical video images, the team improved the detection of facial keypoints, particularly in sensitive areas.
- The enhanced AI model showed reduced error rates in assessing key points, showcasing significant improvements in facial analysis accuracy.
- The study suggests that this AI tool could be applied to other medical conditions with rare disorders, leading to advancements in AI-assisted diagnostics.
- The refined AI tool aims to establish reliable methodologies for objective evaluations in clinical settings and may enhance treatment outcomes for facial palsy patients.
- Integrating AI into clinical assessments could provide a more thorough understanding of patient conditions, ultimately improving treatment interventions.
- The use of fine-tuned AI in facial palsy evaluation represents a significant advancement in medical diagnostics, with the potential for broader applications in healthcare.
- This research underscores the transformative impact of AI technology in healthcare, offering a more scientific approach to patient care and management.
- Overall, the study highlights the promising future of AI-assisted medical evaluations, indicating the potential for more reliable and objective patient assessment approaches.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app