Bio News
Bioengineer
25

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Stage of B-Cell Development Influences Effectiveness of Leukemia Treatments
- Study shows B-cell developmental stage impacts pediatric B-ALL treatment outcomes.
- Research explores cellular origins of leukemia, aiding risk stratification and therapy targeting.
- Insights reveal diverse leukemia developmental paths challenging existing concepts on treatment resistance.
- Identification of multipotent leukemic cells suggests potential treatment evasion mechanism.
- Novel multipotency score predicts patient response, paving the way for personalized therapies.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
116
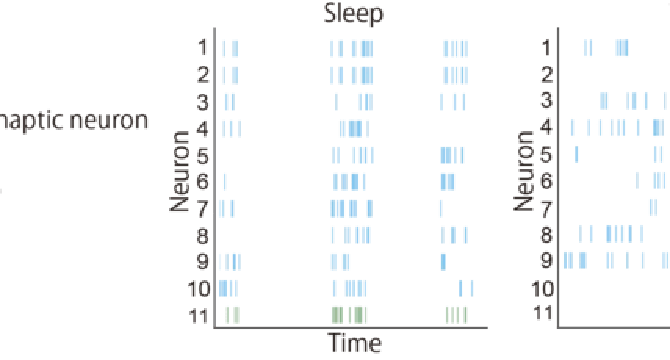
Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Scientific Insights Reveal Conditions for Effective “Sleep Learning”
- New scientific insights reveal how synaptic connections in the cerebral cortex dynamically change during sleep.
- Conditions for effective 'sleep learning' include specific neural activity thresholds and synaptic potentiation.
- The study bridges the roles of synaptic downscaling and strengthening during sleep cycles.
- Abnormalities in sleep-related synaptic plasticity could contribute to cognitive disorders like Alzheimer's.
- The research combines computational neuroscience with empirical neurobiology, pushing the frontier of systems neuroscience.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Bioengineer
350

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Diverse Genetic Profiles and Treatment Disparities in HER2-Mutated NSCLC Across Brazil
- Groundbreaking study in Oncotarget delves into HER2-mutated NSCLC in Northeastern Brazil.
- Reveals genetic complexity, clinical challenges, and treatment disparities in underrepresented population.
- Highlights diverse HER2 mutations and therapeutic potential, emphasizing need for inclusive research.
- Proposes tiered diagnostic framework and calls for equitable access to targeted therapies.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Bioengineer
341

Image Credit: Bioengineer
St. Jude Algorithm Harnesses Water Dynamics to Accelerate Drug Discovery
- St. Jude scientists unveil ColdBrew algorithm illuminating water's role in drug discovery.
- ColdBrew refines protein-ligand interactions by predicting water displacement in binding sites.
- Tool corrects cryo-induced artifacts, aids rational ligand design, democratizes water displacement insights.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
191

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Lab-Grown Breast Tissue Sheds New Light on Lactation Science
- Groundbreaking study from ETH Zurich revolutionizes understanding of lactation science.
- Researchers develop 3D breast tissue replicas to mimic milk production environment.
- Innovative bioprinting technique shows promise for studying lactation and female health research.
- Platform allows exploration of milk synthesis, disease modeling, and therapeutic development opportunities.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
383

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How Pesticide Exposure Alters Gut Microbiome Composition
- Groundbreaking study reveals how pesticides interact with human gut bacteria, leading to metabolic changes.
- Research uncovers specific bacterial species mitigating pesticide-induced toxicity, offering potential probiotic therapies.
- Findings highlight nuances in pesticide effects on gut microbes, reprogramming metabolism and lipid profiles.
- Discovery signifies gut bacteria's role in modulating inflammation from pesticide exposure, shaping future interventions.
- Study underscores importance of understanding pesticide-microbiome dynamics for human health protection.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Bioengineer
150

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How a Malfunctioning Brain Transport Protein Sparks Severe Epilepsy
- Study reveals the role of SLC13A5 transporter in severe epilepsy related to citrate dysfunction.
- Mutations in SLC13A5 gene disrupt citrate transport leading to developmental epileptic encephalopathy.
- Research employs deep mutational scanning to identify critical mutations affecting transporter function.
- Understanding SLC13A5 variants aids in rare disease mechanism elucidation for potential targeted therapies.
- Findings highlight importance of functional mapping for membrane proteins in neurological disorders.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Bioengineer
233

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Regional rollout of therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy
- Researchers introduce active therapeutic hypothermia in regional neonatal transport network for encephalopathy.
- This approach enhances neonatal critical care, addressing logistical challenges during infant transfers.
- Precision cooling devices and standardized protocols improve neurologic outcomes and reduce brain injury.
- Parental communication, consent, and future telemedicine integration are pivotal components of this initiative.
- The study sets a new standard in neonatal care, extending neuroprotection beyond NICUs.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
408

Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Study Uncovers Uneven Land Subsidence in New Orleans, Heightening Flood Risk Concerns
- New Orleans faces land subsidence leading to elevated flood risk concerns.
- Research reveals sinking rates, impacting infrastructure like flood protection systems.
- The study highlights causes such as soil compaction and anthropogenic activities.
- Urgent attention needed to monitor and maintain critical flood defenses in city.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
241

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Innovative Urine-Based Tumor DNA Test Promises Personalized Bladder Cancer Therapy
- A groundbreaking study introduces urine-based tumor DNA analysis for personalized bladder cancer therapy.
- The research utilizes utDNA to predict recurrence risk in high-risk NMIBC patients undergoing atezolizumab.
- Positive utDNA after immunotherapy indicates higher recurrence risk, guiding treatment escalation decisions.
- This innovative approach offers potential for tailored treatments and improved patient outcomes in bladder cancer.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Bioengineer
300

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Roberto Morandotti Honored with IEEE Photonics Society Quantum Electronics Award
- Professor Roberto Morandotti honored with 2025 IEEE Photonics Society Quantum Electronics Award.
- Recognition celebrates his pioneering work in quantum optics and photonics at INRS, Canada.
- His research focuses on entangled photons, quantum communication, and advancing quantum technologies.
- Award highlights Morandotti's leadership, mentoring, and significant contributions to quantum photonics.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
379

Image Credit: Bioengineer
CABI Study Highlights Need for Improved Access to Parthenium Weed Information Among Women in Pakistan
- CABI study in Pakistan explores women's access to parthenium weed information.
- Parthenium weed threatens agriculture, biodiversity, and health in over 50 countries worldwide.
- Research highlights gender disparities and advocates for biological control for sustainable management.
- Economic analysis shows benefits of integrating biological control to alleviate financial burdens.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Bioengineer
29

Image Credit: Bioengineer
How the Brain Makes Decisions: Insights into the Science of Choice
- Recent research sheds light on how the brain forms indirect associations between stimuli.
- Mice study shows brains can link unrelated scents and tastes through indirect associations.
- Findings reveal the role of amygdala and entorhinal cortex in encoding these associations.
- Understanding indirect associations may aid in treating mental health conditions and improving decision-making.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
29

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Precursors to Bone Marrow Cancer May Halt Their Own Progression
- Groundbreaking research sheds light on how precursor cells in bone marrow cancer halt progression.
- Senescent plasma cells create a protective state by inducing dormancy in surrounding cells.
- This discovery opens avenues for early intervention and potential prevention of multiple myeloma.
- Understanding senescence and immune interactions may lead to novel therapeutic strategies.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Bioengineer
250

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Wafer Lens Magnifies X-Ray Beam Size by Over 3,400 Times
- Researchers at Nagoya University develop a deformable mirror using lithium niobate wafer.
- Innovative mirror technology can flexibly adjust X-ray beam size over 3,400 times.
- Achievement allows for enhanced X-ray imaging capabilities in various industrial applications.
- Technology offers precise control for real-time analysis and observation of samples.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app