Bioengineer
3d
87
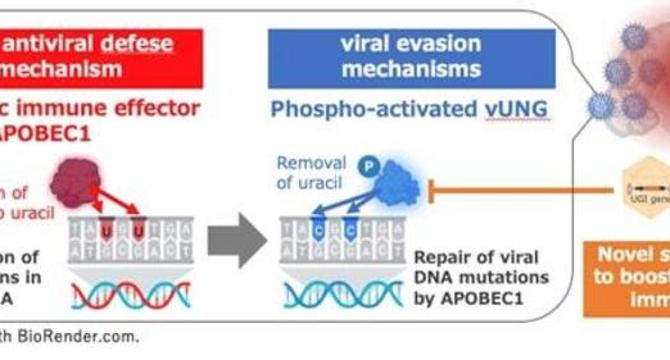
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Boosting Brain Immunity Against HSV-1 by Targeting Viral Enzymes
- A study led by Professor Yasushi Kawaguchi reveals insights into how HSV-1 evades the host immune system in the brain by targeting APOBEC1 with the vUNG enzyme.
- The vUNG enzyme counteracts APOBEC1's mutagenic activity, preserving viral genome integrity and enabling viral proliferation in the brain.
- Research shows that vUNG enzymatically excises uracil bases induced by APOBEC1, preventing mutations that hinder viral replication.
- By inhibiting vUNG through gene therapy with AAV-UGI, APOBEC1's antiviral function is restored, reducing viral replication and enhancing survival rates.
- The study highlights the importance of APOBEC1 in mediating antiviral immunity and proposes a novel approach to combat viral immune evasion.
- Targeting the vUNG enzyme's immunosuppressive function via gene therapy could offer a safer and more sustainable strategy for managing viral encephalitis.
- The use of AAV vectors for gene delivery shows promise in suppressing viral infection in the brain, paving the way for future clinical trials.
- Precision drug design based on vUNG phosphorylation specificity may lead to adjunctive therapies for neurotropic viral infections.
- The study sheds light on the complex interplay between HSV-1 and the host immune system and presents a potential avenue for treating herpes simplex encephalitis.
- Harnessing the body's intrinsic antiviral defenses offers hope for more effective, durable, and less toxic treatments against neurotropic viral infections.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app