Physicsworld
1M
181
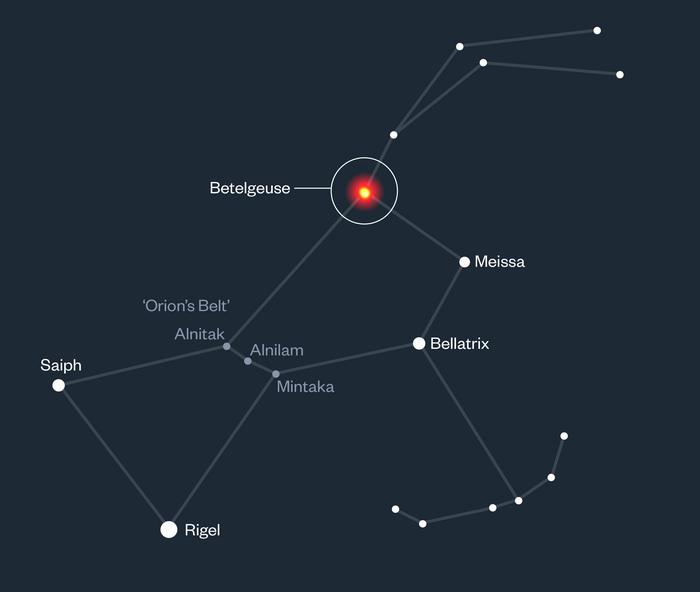
Image Credit: Physicsworld
‘Buddy star’ could explain Betelgeuse’s varying brightness
- Betelgeuse, the red supergiant star, experiences a cycle known as the long secondary period (LSP).
- Low-mass companion star named Alpha Ori B or 'Betelbuddy' may be responsible for the recent 'Great Dimming' of Betelgeuse.
- A team of researchers analysed direct-observation data and combined it with advanced computer models to simulate Betelgeuse's activity.
- Research hypothesis suggests the brightness of Betelgeuse varies when Betelbuddy displaces light-blocking dust.
- Betelgeuse is the 10th brightest star in the night sky located 548 light-years away, in the constellation Orion.
- Studies have shown that LSPs in red giants could be due to an orbiting companion star displacing cosmic dust, changing the amount of starlight reaching earth.
- Advanced computer models revealed that the companion star could remove dust from its vicinity, resulting in the brightest phase of the star.
- Observing space telescopes can provide direct evidence of this companion star’s existence.
- The research may have far-reaching implications have more targets out there and potentially a need for more detailed models on how companions and dust clouds may interact.
- The study has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app