Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
31
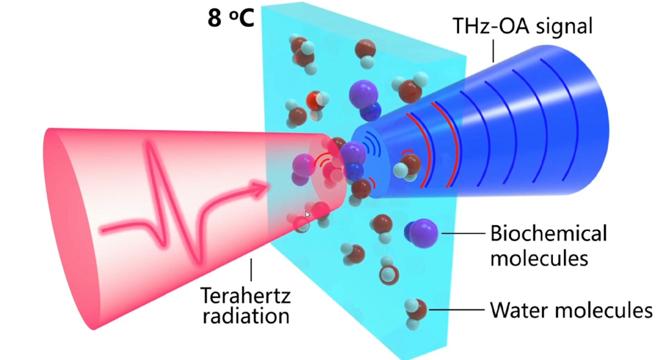
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Terahertz optoacoustics allows real-time monitoring of blood sodium levels
- Researchers have developed terahertz optoacoustic technology to measure blood ion concentrations non-invasively.
- Combining terahertz spectroscopy with optoacoustic detection allows for real-time monitoring of blood sodium levels.
- The method overcomes challenges by utilizing temperature-dependent optoacoustic response to detect ions present.
- The team successfully demonstrated detection of sodium ions in human blood and living mice.
- Future plans involve applying the approach to detect neural ion activity without labeling.
Read Full Article
1 Like
COSMOS
195

Image Credit: COSMOS
Uncovering the cosmic dawn from the far side of the Moon
- Astronomers plan to launch a spacecraft to the far side of the Moon to uncover secrets of the early universe's 'Cosmic Dawn.'
- The mission aims to listen for ancient signals using the Moon as a shield against Earth's interference.
- The proposed spacecraft, CosmoCube, will orbit the Moon with radio equipment to detect faint signals from the early universe.
- The mission could provide insights into cosmological mysteries such as the Hubble tension and the interactions between dark matter and normal matter.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Netflixtechblog
264

Image Credit: Netflixtechblog
Netflix Tudum Architecture: from CQRS with Kafka to CQRS with RAW Hollow
- Tudum.com enriches Netflix fan experience with exclusive content and interactive features.
- Initially leveraging CQRS with Kafka, Tudum faced delays in reflecting live edits.
- Introducing RAW Hollow, an in-memory database, significantly reduced data propagation time and latency.
- The shift to RAW Hollow resulted in faster request times, improved caching, and enhanced scalability.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Physicsworld
149

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Acoustic rainbows emerge from novel sound-scattering structure
- Researchers at Danmarks Tekniske Universitet have created an acoustic rainbow structure that decomposes sound into its component frequencies in free space.
- This structure, mimicking optical rainbows, could enable the design of devices tailored to emit or receive specific frequencies of sound.
- The breakthrough was achieved using computational morphogenesis and topology optimization techniques, allowing for the creation of complex sound-scattering structures.
- This advancement opens up possibilities for developing new acoustic materials, lenses, and complex spatio-spectral sound field control in the future.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Physicsworld
223

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Muon g-2 achieves record precision, but theoretical tensions remain
- Muon g-2 Experiment achieves record precision in measuring muon anomalous magnetic moment.
- Experiment at Fermilab in Chicago confirms the experimental value of muon g-2.
- Theoretical tensions persist between prediction and measurement, hinting at new physics possibilities.
- Recent data and lattice QCD simulations align with Fermilab result, challenging previous discrepancies.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Knowridge
262
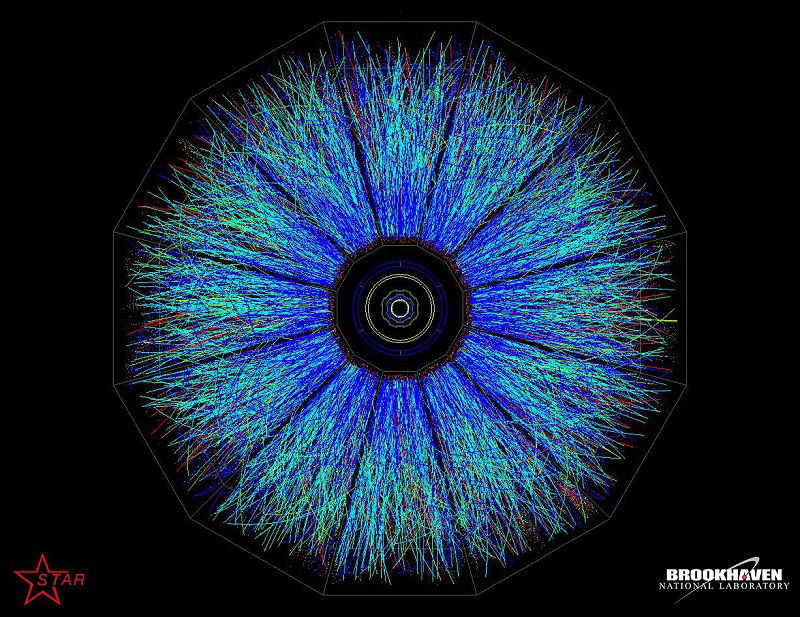
Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists unlock secrets of matter under extreme conditions
- Researchers studied how heavy particles containing charm and bottom quarks behave under extreme conditions similar to those after the Big Bang.
- By analyzing collisions at particle accelerators like the LHC and RHIC, temperatures hotter than the Sun's center are generated, creating a quark-gluon plasma state.
- The transition of this plasma into hadronic matter helps in understanding the evolution of matter from the chaotic early universe to its structured form today.
- The study reveals the importance of the cooling phase post-plasma for observing heavy hadron interactions, providing insights into the fundamental properties of matter under extreme conditions.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Hackernoon
83
Image Credit: Hackernoon
Understanding Quantum Mechanics: A Tour Through Its Most Bizarre Interpretations
- Richard Feynman simplified quantum mechanics through the double-slit experiment's perplexing results.
- Electrons exhibit wave-like behavior, forming interference patterns, challenging conventional understanding of matter.
- Quantum mechanics leads to technological advancements, quantum computers, and perplexing interpretations like superdeterminism.
- Various interpretations exist, from Many-Worlds Theory to retrocausality, delving into consciousness and free will.
- Quantum mechanics poses deep philosophical questions and challenges our fundamental understanding of reality.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Medium
359
Image Credit: Medium
Is Math Overrated? Famous Physicist Views Simply Put
- Famous physicists critique math-heavy approach in physics and emphasize intuition and simplicity.
- Richard Feynman valued conceptual understanding over calculations. Carlo Rovelli sought beauty in physics.
- Lee Smolin and Julian Barbour challenge string theory and time perception theories.
- Ernst Mach and Albert Einstein's evolving views on math and intuition discussed.
- Contrast with David Deutsch's math-centric approach. Scientists explore other dimensions for theory unification.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Nytimes
59

Daniel Kleppner, Physicist Who Brought Precision to GPS, Dies at 92
- Daniel Kleppner, an experimental physicist known for his work in developing an atomic clock essential for GPS, passed away at the age of 92 in California.
- During the mid-1950s, Kleppner learned about building precise clocks capable of detecting gravity's effects on time, leading him to work with renowned physicist Norman Ramsey at Harvard University.
- Dr. Ramsey's research on measuring atomic frequencies laid the foundation for nuclear magnetic resonance and modern MRI technology, enabling the development of atomic clocks that keep incredibly precise time.
- Kleppner's contributions to physics and his role in the development of atomic clocks have had a lasting impact, especially in the field of global positioning systems.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Knowridge
7
Image Credit: Knowridge
Are we in a giant void that would help explain the Hubble Tension
- Hubble Tension, a major cosmological mystery, revolves around inconsistent universe expansion measurements.
- Research suggests a giant void near the Milky Way accelerates the local cosmic expansion.
- Presentation at NAM 2025 supports the theory, proposing a solution to Hubble Tension.
- Baryon acoustic oscillations and local void concept could potentially resolve cosmological inconsistencies.
- Local void theory challenges standard cosmological models and requires further study for confirmation.
Read Full Article
Like
Physicsworld
0
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Physics meets fashion as bioluminescent dress debuts at Paris Haute Couture Week
- Fashion designer Iris van Herpen debuts a bioluminescent dress featuring 125 million living algae at Paris Haute Couture Week.
- The dress is a collaboration with designer Chris Bellamy and biophysicists Nico Schramma and Mazi Jalaal from the University of Amsterdam.
- The bioluminescent dress is made of a gel material incorporating millions of bioluminescent algae, Pyrocystis lunula, known for emitting light as a defense mechanism.
- The garment emits light upon deformation and movement, keeping the algae alive, and is part of van Herpen's new fashion collection - Sympoiesis.
Read Full Article
Like
Hobbieroth
327

Image Credit: Hobbieroth
David Cohen: The Father of MEG
- Gary Boas recently published a short biography of David Cohen, known as the father of magnetoencephalography (MEG).
- The book delves into Cohen's childhood in Canada, his college days, and graduate studies at the University of California, Berkeley, highlighting his contributions to the field.
- Cohen's groundbreaking work in combining the SQUID magnetometer with a shielded room led to clear and unambiguous signals of magnetic fields produced by human organs, marking the launch of a new field of study called biomagnetism.
- David Cohen, now 97 years old, remains active in the field of biomagnetism, and Boas's biography of him is available for free for those interested in learning more about his contributions.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Physicsworld
195
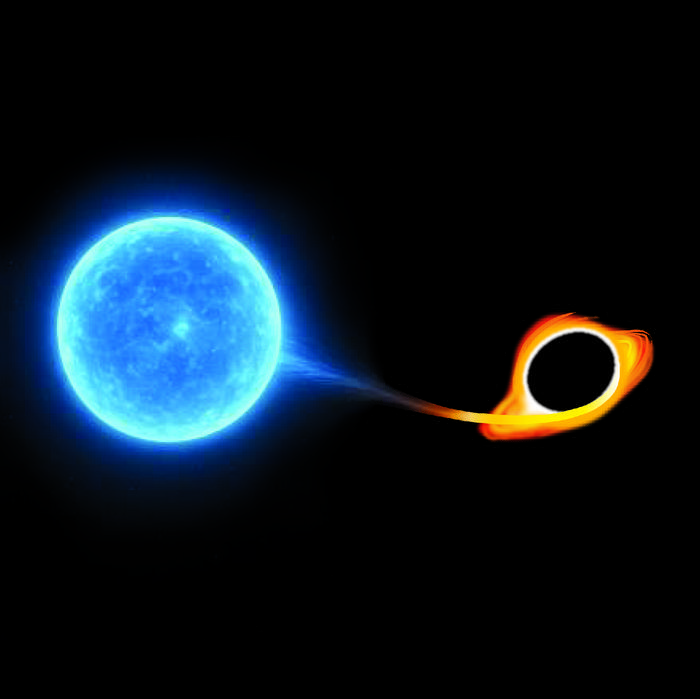
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Astronomers observe the biggest booms since the Big Bang
- Astronomers detect most energetic cosmic explosions known as extreme nuclear transients (ENTs).
- ENTs occur when massive stars are shredded by supermassive black holes, releasing huge energy.
- New discoveries have energy output surpassing even the brightest supernova explosions.
- They provide insights into high-energy physical processes, offering a new tool for studying black holes.
- Astronomers anticipate detecting several ENTs per year with new survey instruments.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Brighter Side of News
52
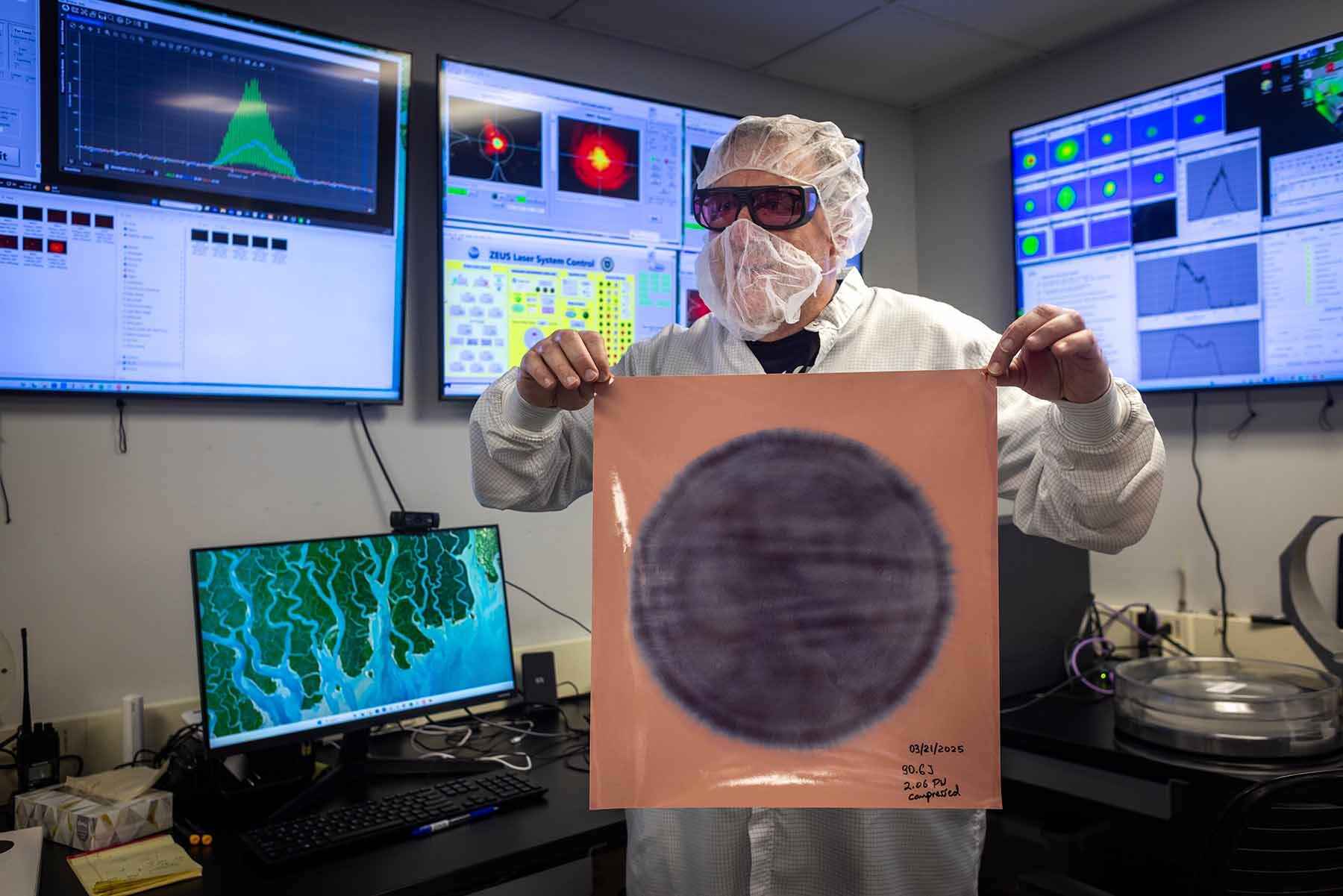

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Scientists fire most powerful US laser ever—100 times Earth’s total energy usage
- University of Michigan's ZEUS laser achieves record 2 petawatt peak power, 100x Earth's usage.
- ZEUS explores quantum physics, plasma science, and astrophysics, reshaping high-intensity laser research.
- Facility aims for 3 petawatts, invites national and international scientists for experiments.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
125
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Glimpses of Coronal Rain
- A new adaptive optic technique has provided detailed images of the sun's corona, which is usually difficult to observe due to its faintness.
- The images, captured at the Big Bear Solar Observatory, show plasma from solar prominences and coronal rain with unprecedented detail.
- Over 2,200 adjustments per second were made to the telescope's mirror to counter atmospheric distortions and improve resolution to 63 kilometers.
- There are plans to implement this technology on the 4-meter Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope for even finer imagery of the sun's corona.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app