Medium
15h
219
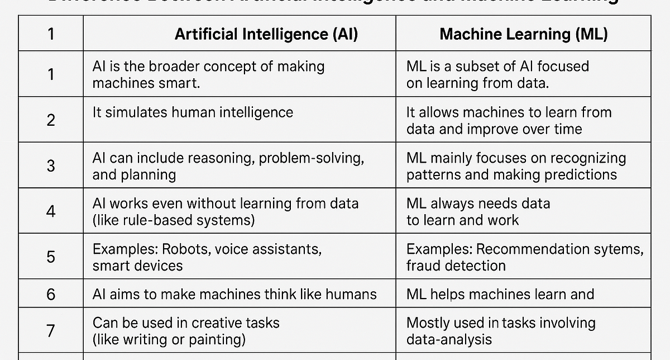
Image Credit: Medium
Difference Between Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines capable of performing tasks requiring human intelligence.
- AI systems simulate human intelligence and can be rule-based or data-driven.
- Examples of AI include voice assistants like Siri, self-driving cars, and chatbots.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of AI that focuses on developing algorithms allowing computers to learn from data and make predictions without explicit programming.
- Key characteristics of ML include learning from historical data, improving accuracy over time, and requiring large datasets for training.
- Examples of ML include email spam filters, movie recommendations on Netflix, and product recommendations on Amazon.
- Real-life examples of AI vs. ML include a robot vacuum planning its cleaning path (AI) and predicting prices of used cars based on data (ML).
- Differences between AI and ML include the approach to problem-solving and the focus on learning from data.
- Understanding the distinctions between AI and ML is crucial for further advancements and application development in modern computing.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app