Bioengineer
6d
375
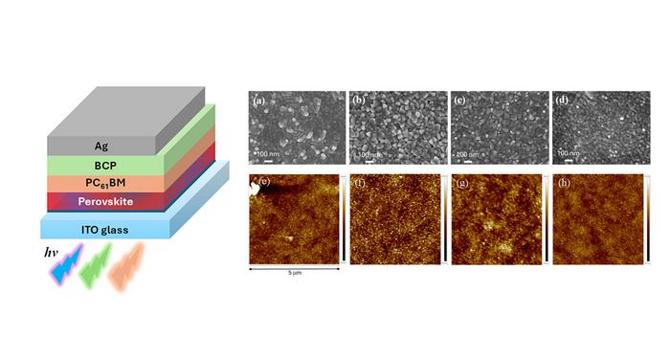
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Harnessing Indoor Lighting to Power Devices
- Perovskite solar cells (PeSCs) represent a groundbreaking innovation in solar technology, with unique adaptability to indoor lighting environments.
- Research highlights the efficiency of PeSCs in converting indoor fluorescent and LED light into electrical energy.
- Bandgap engineering in PeSCs allows for optimized spectral absorption of artificial indoor lighting, surpassing traditional silicon cells in low-light conditions.
- A defect passivation technique enhances the efficiency and stability of PeSCs, crucial for commercialization efforts.
- Under typical indoor lighting levels, PeSCs achieve exceptional power conversion efficiency, hinting at diverse application possibilities.
- PeSCs offer potential for powering smart homes, wearable tech, and IoT devices through ambient indoor lighting, reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
- The lightweight and flexible nature of PeSCs enables integration in unconventional settings like energy-generating windows and displays.
- Optimization for indoor performance addresses the growing need for renewable energy solutions in automated indoor environments.
- Improved device stability and resistance to environmental degradation further support the practical deployment of PeSCs in real-world settings.
- The study signifies a significant advancement in perovskite technology, offering a sustainable and versatile approach to indoor energy harvesting.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app