Physicsworld
3w
163
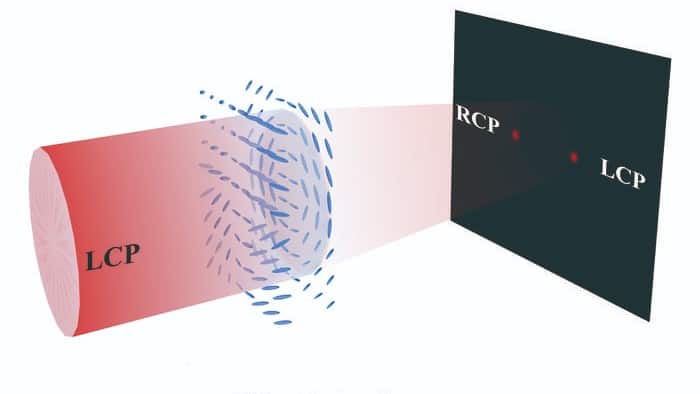
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Liquid-crystal bifocal lens excels at polarization and edge imaging
- Researchers at China's Hunan University have developed a bifocal lens with adjustable focal points using liquid crystal materials.
- The lens features a bilayer structure that responds differently to an applied electric field, splitting incoming light into oppositely polarized beams.
- The lens demonstrated excellent performance in polarization imaging and edge imaging experiments.
- Further research is underway to reduce manufacturing costs and explore potential applications in optical systems.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app