Physicsworld
6d
202
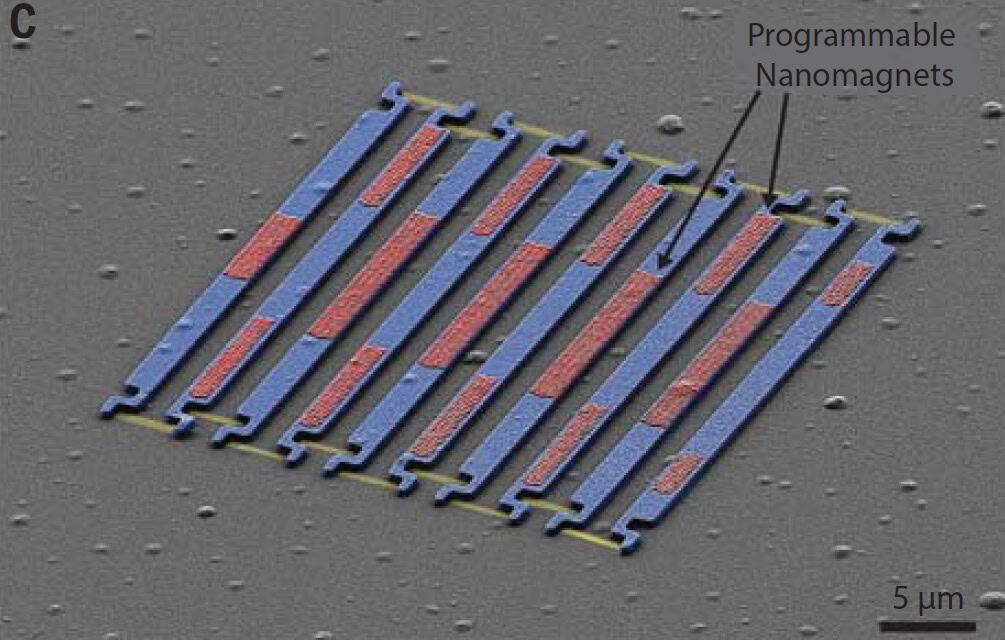
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Magnetically controlled microbots are small enough to diffract visible light
- Researchers at Cornell University have developed magnetically controlled microbots that are small enough to diffract visible light.
- The microbots utilize nanoscale hinges made using atomic layer deposition (ALD) and nanomagnet arrays for magnetic actuation.
- The ability to control light at the microscale offers new possibilities for imaging and probing the microscopic world.
- Potential applications include endoscopic imaging, high-resolution microscopy, and sensing magnetic fields and current in integrated circuits.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app