Dev
2d
172
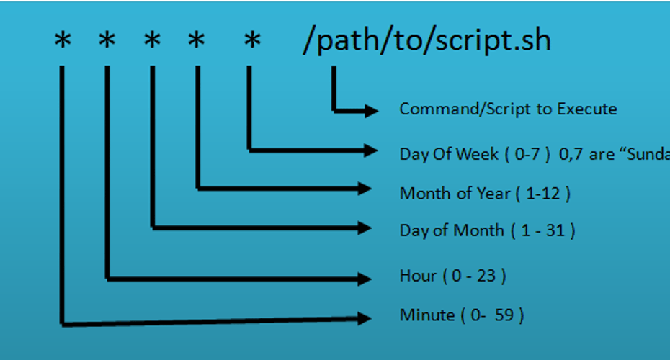
Image Credit: Dev
Mastering Crontab: A Comprehensive Guide to Automating Tasks in Linux
- Crontab is a configuration file that defines cron jobs, allowing Linux users to automate repetitive tasks and reduce manual intervention.
- Crontab files have a specific format for defining schedules, using five fields for time intervals, followed by the command to execute - Minute, Hour, Day of the month, Month, and Day of the week.
- Crontab files use special characters like * for any value, , for specifying multiple values, - for specifying a range, and / for step values.
- Users can edit their crontab file using the crontab -e command, and view scheduled cron jobs using the crontab -l command.
- Crontab provides shortcuts for commonly used schedules, such as @daily, @weekly, @monthly, @yearly, @reboot, and @hourly.
- Environment variables can be defined in the crontab file, which is helpful if your job relies on specific configurations.
- Crontab best practices include using full paths, capturing output in logs for debugging, scheduling jobs carefully to avoid performance bottlenecks, and testing jobs before production.
- Troubleshooting crontab issues include checking syntax errors, verifying cron daemon is running, and checking logs for error messages.
- Real-world examples of tasks that can be automated with crontab include automated backups, database cleanup, server health checks, and restarting services if they go down.
- By understanding the syntax and scheduling options of crontab, users can leverage its automation capabilities for a variety of tasks in Linux.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app