Nasa
1M
53
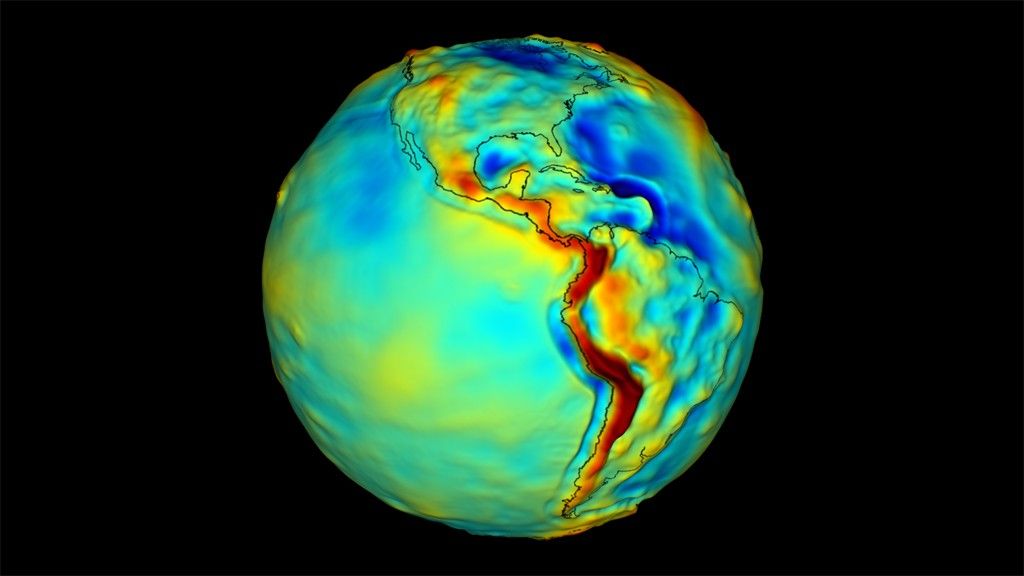
Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Aims to Fly First Quantum Sensor for Gravity Measurements
- Researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, private companies, and academic institutions are developing the first space-based quantum sensor for measuring gravity.
- The mission aims to pave the way for groundbreaking observations of everything from petroleum reserves to global supplies of fresh water.
- The sensor, called Quantum Gravity Gradiometer Pathfinder (QGGPf), uses ultra-cold rubidium atoms as test masses to measure differences in gravitational strength and locate gravitational anomalies.
- This technology validation mission, scheduled to launch near the end of the decade, aims to test the novel technologies for manipulating interactions between light and matter at the atomic scale.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app