Medium
1M
202
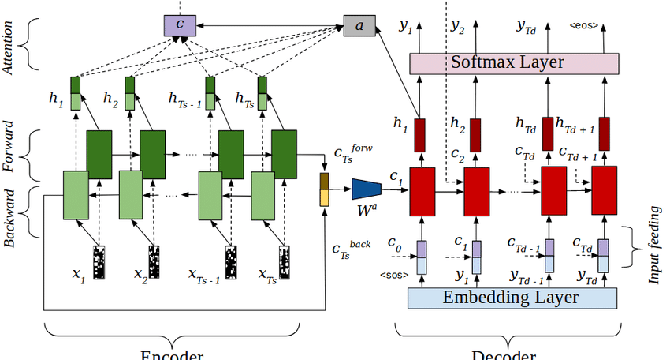
Image Credit: Medium
Neural Machine Translation: Unveiling the Encoder-Decoder Architecture
- Neural Machine Translation employs deep learning techniques, utilizing extensive datasets of translated sentences to train models capable of translating between various languages.
- The Encoder-Decoder structure is a traditional and well-established version of NMT, consisting of two recurrent neural networks (RNN) that work together to form a translation model.
- The encoder processes the input sequence to generate a set of context vectors, which are then used by the decoder to produce an output sequence.
- The incorporation of attention mechanisms in the encoder-decoder architecture enables the model to focus on specific parts of the input for better translation accuracy, especially in longer sentences.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app