Physicsworld
2w
297
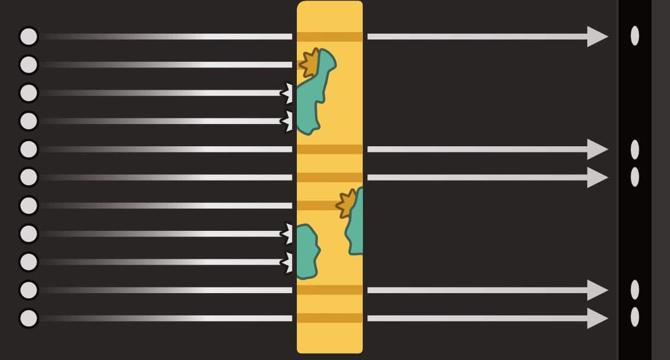
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Neutrons differentiate between real and fake antique coins
- Neutrons can differentiate between real and fake antique coins by passing easily through the metallic regions of genuine coins but being blocked by hydrogen-bearing compounds formed due to corrosion.
- Researchers in the US and South Korea used a neutron beam to identify authentic antique coins based on the presence of hydrogen-rich corrosion inclusions, which resulted in a unique 2D pattern when neutrons were fired through the coins.
- The team utilized neutron tomography to examine the deeper corrosion in genuine coins compared to replicas, as well as neutron grating interferometry to analyze the pores on the coin surfaces, distinguishing between authentic and fake coins based on pore sizes.
- This innovative technique could help in verifying the age of coins, protecting corroded areas, and benefit coin collectors, historians, and economists, with further studies planned to include more coins and metallic artefacts.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app