Bioengineer
3d
326
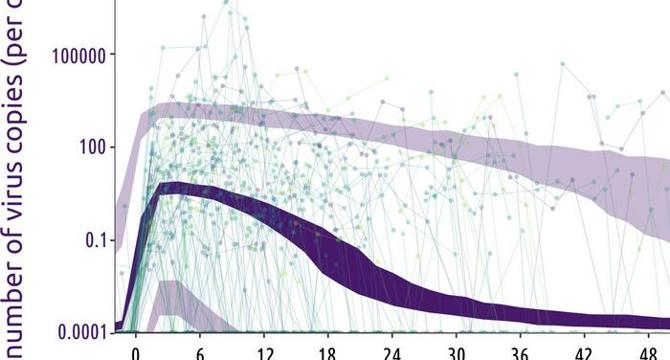
Image Credit: Bioengineer
New Longitudinal Study Uncovers Dynamics of Human Papillomavirus Infection Kinetics
- A longitudinal study conducted by researchers from CNRS in France has revealed significant dynamics in viral load and immune response during human papillomavirus (HPV) infections.
- The study focused on understanding the transition of acute HPV infections into chronic conditions and identified a prolonged plateau phase after the initial viral load increase.
- The research highlighted the correlation between HPV viral load and specific immune cell populations, suggesting the potential for targeted immune modulation as a clinical intervention.
- The findings emphasize the need for longer-term studies to understand the differences between chronic and acute infections and the importance of public health strategies encompassing education and vaccination efforts.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app