Bioengineer
1w
290
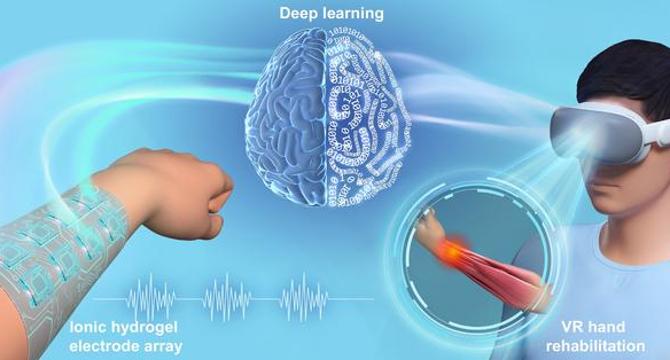
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Non-Hand-Worn, Load-Free VR Rehabilitation System Enhances Hand Recovery Using Deep Learning and Ionic Hydrogel Technology
- A revolutionary non-hand-worn, load-free VR hand rehabilitation system has been developed by researchers at Zhengzhou University, combining deep learning and ionic hydrogel technology to enhance hand recovery for conditions like stroke and osteoarthritis.
- The system utilizes flexible electrodes to capture electromyographic signals, eliminating the need for bulky mechanical gloves traditionally used in hand rehabilitation and enabling users to engage in exercises comfortably and freely.
- Ionic hydrogel electrodes with self-healing properties are applied on the forearm to accurately capture EMG signals during hand movements, offering extended usability and efficiency in the rehabilitation process.
- A trial showcased the system's 97.9% accuracy in recognizing 14 hand rehabilitation gestures, facilitated by advanced deep learning algorithms like Convolutional Neural Networks for decoding movements into virtual actions.
- The VR platform integration enriches the rehabilitation experience, providing interactive virtual environments for practicing movements that enhance engagement and motivation, crucial for physical and emotional recovery aspects.
- This innovative system empowers patients to perform rehabilitation exercises at home without the constraints of clinical supervision, potentially improving the quality of life for individuals undergoing hand rehabilitation by offering a personalized, load-free therapy solution.
- The research team aims to further enhance gesture recognition accuracy and expand the system's capabilities, with potential applications beyond hand recovery in fields like stroke rehabilitation, musculoskeletal therapy, and geriatric care.
- The utilization of ionic hydrogels in this non-hand-worn VR rehabilitation system represents a significant advancement in biomedical technology, promising versatile and effective solutions for diverse medical conditions and heralding a new era in rehabilitation devices.
- This interdisciplinary approach in healthcare technology exemplifies the transformative potential of deep learning, material science, and rehabilitation collaborations, signifying a crucial step towards improving patient outcomes and broadening medical treatment accessibility.
- In conclusion, the introduction of this VR hand rehabilitation system signifies a remarkable progression in rehabilitation therapies, offering innovative, patient-centered designs that promise enhanced recovery experiences across a wide range of therapeutic applications.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app