Bioengineer
2w
82
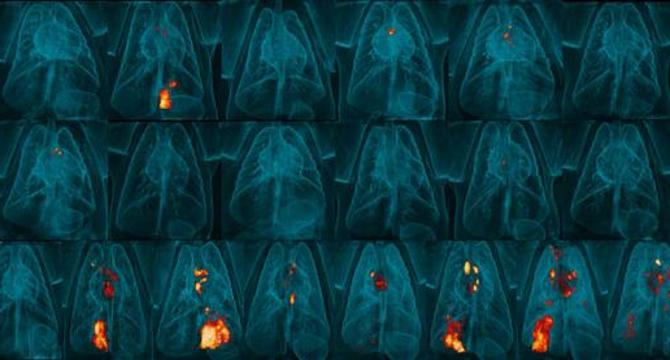
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Revolutionary Self-Destructing Vaccine Shows Improved Tuberculosis Protection in Monkeys
- A self-destructing strain of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) has shown promise in combating tuberculosis (TB) among macaque monkeys according to a study from the University of Pittsburgh. The methodology of delivering the BCG vaccine can lead to partial protection and an elevated risk of adverse immune reactions, so the self-destructing strain provides greater safety and may eliminate the possibility of vaccine-derived infections, especially in weakened populations. The Kill-Switch BCG vaccine was found to effectively protect against TB and to be as or more effective than conventional BCG methods.
- The team, who collaborated with scientists from Cornell University and the National Institutes of Health, engineered a safety switch, allowing the vaccine to trigger biodegradation upon the presence of doxycycline, an antibiotic. In mouse models, the Kill-Switch BCG strain demonstrated comparable immunity to standard BCG injections and rapid elimination from the subject's systems. The study's results highlight a significant development in the field of TB vaccination strategies.
- Intravenous administration of the standard BCG vaccine resulted in a remarkable bacterial load reduction within the lungs of macaques. Eight weeks following exposure, none of the monkeys displayed any detectable levels of lung inflammation, and six of the eight were devoid of recoverable live bacteria. The researchers believe this intravenous vaccination approach could become a staple in preventive healthcare, given its promise for safe administration.
- The results of the study build upon preliminary findings from the same collaborating team that established the effectiveness of intravenous administration of a standard BCG vaccine in reducing bacterial load within macaque monkey lungs. With rigorous investigation, this avenue of research could have an important impact on public health policy, particularly among populations most at risk due to compromised immune systems.
- The unique approach to TB prevention represented by the self-destructing BCG vaccine represents a significant breakthrough in biotechnology and immunology. As the world continues to grapple with infectious diseases like tuberculosis, innovative vaccine technology is needed to develop preventative treatments that are effective and sustainable.
- The study was published in the journal of Nature Microbiology on 10 January 2025 and detailed the efficacy of the self-destructing BCG strain and its potential for safe intravenous administration. Researchers suggest that this new frontier of vaccine development could represent a vital future strategy in the fight against tuberculosis, and it could help the public health industry develop more resilient and effective public health strategies.
- Tuberculosis has been designated the deadliest disease worldwide by the World Health Organization in 204, with this research providing a potential solution to this crisis. The study's findings may help to shift perspectives on vaccination as a proactive and preventative global health strategy, particularly among the most vulnerable members of society.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app