Medium
1M
288
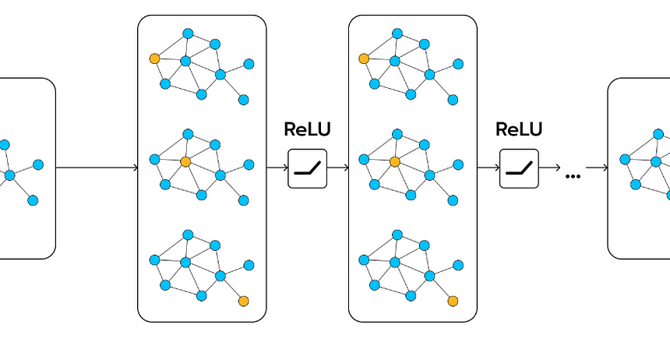
Image Credit: Medium
The Brain-Inspired Framework for Understanding Connections : Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
- Neural networks mimic the brain's ability to learn and process data using interconnected artificial neurons.
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) focus on understanding relationships between data points, not just the data itself.
- Graphs, with nodes connected by edges, represent relationships and are vital for modeling complex systems.
- Traditional neural networks struggle with irregular graph-structured data, leading to the rise of GNNs.
- GNNs analyze both node attributes and edge connections, making them ideal for interconnected data analysis.
- GNNs excel in scenarios involving interconnected entities like social networks and chemical structures.
- GNNs provide a holistic view of systems by considering nodes and relationships, overcoming limitations of traditional neural networks.
- One of the strengths of GNNs is their capacity to handle irregular and dynamic graph structures effectively.
- GNNs are adept at capturing the contextual relationships between data points, enhancing their analysis of complex networks.
- The explainability of GNNs, due to their explicit connections, allows for tracing decision-making processes.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app