Qualys
3w
171
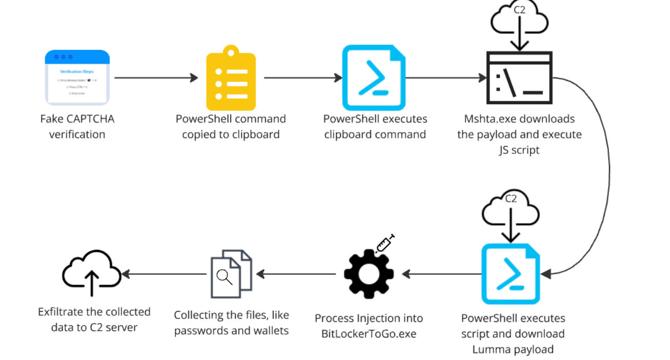
Image Credit: Qualys
Unmasking Lumma Stealer : Analyzing Deceptive Tactics with Fake CAPTCHA
- Lumma Stealer is a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) used for stealing sensitive data like passwords, browser information, and cryptocurrency wallet details, using advanced deceptive methods like fake CAPTCHA verification.
- The Qualys Threat Research Unit (TRU) has monitored this active malware campaign. Recently, fake CAPTCHA pages trick unsuspecting users into payload execution, using muti-stage fileless techniques.
- The malware uses PowerShell, mshta.exe and fileless methods to deliver payloads, exploiting common tools and process injection to carry out its operations.
- Qualys EDR identifies and prevents fileless malware attacks at the pre-execution stage, stopping the download of malicious payloads. For instance, it can terminate PowerShell instances to break the chain of initial attack and prevent further payloads' download.
- The IOCs include C2 server domains with the '.shop' top-level domain (TLD) and files like K1.zip, K2.zip and .exe files VectirFree.exe and Voyuer.pif.
- Qualys EDR also allows the viewing of executed obfuscated scripts' de-obfuscated code and detects early prevention crucial in protecting against sensitive data leakage and exfiltration.
- The investigation revealed an evolving threat landscape characterized by the malware’s ability to adapt and evade detection and employs a variety of tactics.
- Analysts can incorporate some threat detection and hunting queries into their playbooks to detect and prevent such threats in real-time effectively.
- The investigation showed Lumma Stealer to be a persistent challenge for security teams, utilizing legitimate software and deceptive delivery methods, and is an ever-evolving threat.
- Qualys EDR detects fileless malware attacks during pre-execution stages and allows for detection and hunting queries to investigate such threats effectively.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app