Bioengineer
3d
298
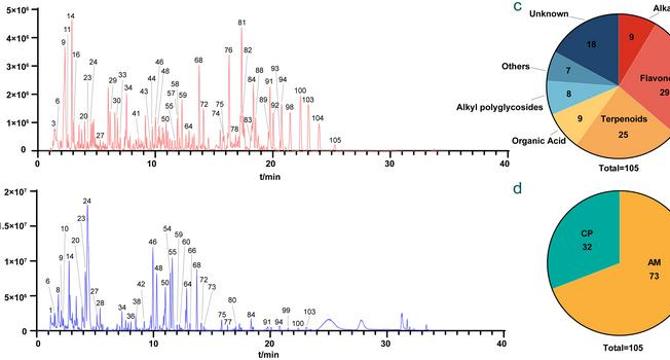
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Unveiling the Chemical Composition and Blood-Absorbed Components of Shenqi Fuzheng Extract Through UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS Analysis
- Shenqi Fuzheng (SQ) is a traditional Chinese medicine formula known for its ability to bolster immune function and replenish Qi, a concept deeply rooted in Chinese health philosophy.
- A recent study has taken this challenge head-on, utilizing advanced analytical techniques to unravel the complexities of SQ’s chemical makeup and its absorption mechanisms.
- From the SQ extract, an impressive array of 105 compounds was identified, 40 of which were detected in rat plasma following oral administration.
- Notably, organic acids and amino acids were found to have higher concentrations within the bloodstream. This result underscores the importance of these classes of compounds in the pharmacological activity of SQ.
- Flavonoids presented another class of compounds of interest, as they were observed to be absorbed more slowly compared to Astragalosides.
- Understanding these time-dependent absorption patterns is vital for elucidating the comprehensive pharmacological profile of SQ.
- The findings of this study not only illuminate the pharmacokinetics of SQ but also emphasize the broader implications of traditional herbal medicine research.
- The significance of this research transcends SQ itself—it serves as a model for how advanced analytical methodologies can be employed to dissect other complex herbal formulas.
- The dialogue between traditional knowledge and scientific validation is essential for developing effective therapeutic strategies that incorporate both realms.
- By dedicating efforts to unravel the complexities of herbal medicines, researchers can enhance the therapeutic arsenal available to modern medicine.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app