Earthsky
1M
322
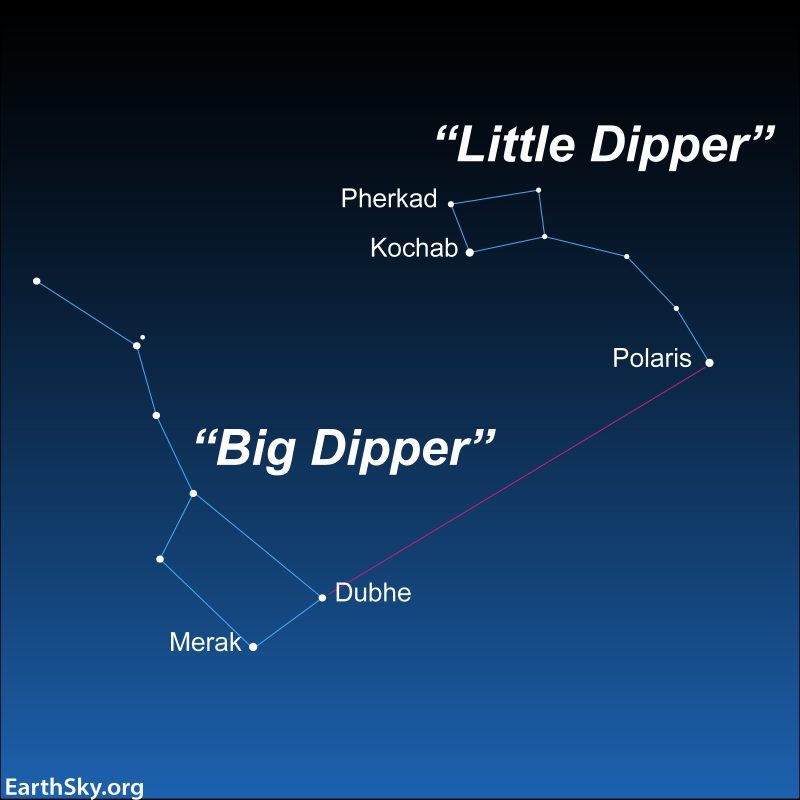
Image Credit: Earthsky
Use the Big Dipper to find Polaris, the North Star
- An imaginary line drawn from the 2 outermost stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper always points to Polaris.
- The two outer stars in the bowl of the Big Dipper, known as Dubhe and Merak, point to Polaris, making it easy to find.
- Polaris, also known as the North Star, appears fixed in the northern sky and is moderately bright, making it easily visible at night.
- The Big Dipper is not a constellation itself but an asterism within the constellation Ursa Major. It is best seen in the spring and can be used to find directions in the Northern Hemisphere.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app