Bioengineer
1M
205
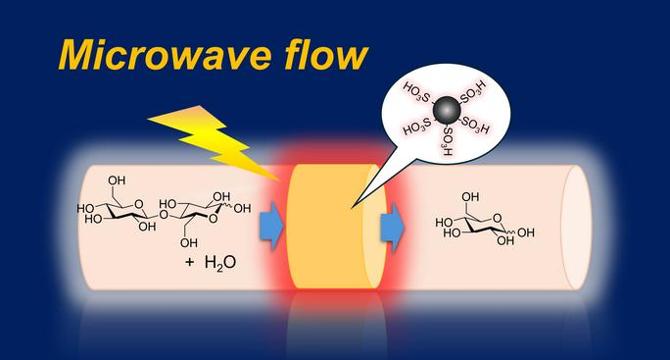
Image Credit: Bioengineer
Utilizing Microwave Flow Reactions to Transform Biomass into Valuable Sugars
- Researchers at Kyushu University in Fukuoka, Japan have developed an innovative technology that harnesses the power of microwave flow reactions combined with solid acid catalysts, thus creating a device that efficiently converts complex polysaccharides into simpler monosaccharides..
- This technology promises sustainable production of valuable sugars with immense applications in the food, pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing industries.
- The team utilized a continuous-flow hydrolysis process featuring microwaves that generate localized high-temperature effects.
- The innovations applied in the creation of this device represent a vast improvement over traditional methods.
- The team reported operating conditions involving microwave temperatures of approximately 100-140 degrees Celsius, which illustrates the energy-efficient nature of the system.
- This technology could lead to less energy consumption in industrial processes, aligning with the growing demand for sustainability in chemical production.
- The team’s work opens avenues for exploring the hydrolysis of additional polysaccharides and potentially even proteins, creating a rich field of inquiry around amino acid and peptide production.
- Leveraging advancements in technology will be vital in addressing the world’s pressing challenges surrounding climate change and resource management.
- Their extensive findings have been documented in the scientific journal APS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
- Ultimately, as institutions and researchers collaborate and share insights, the potential to convert waste into valuable resources becomes increasingly feasible, driving a new era of sustainable practices across various sectors.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app