Medium
7d
112
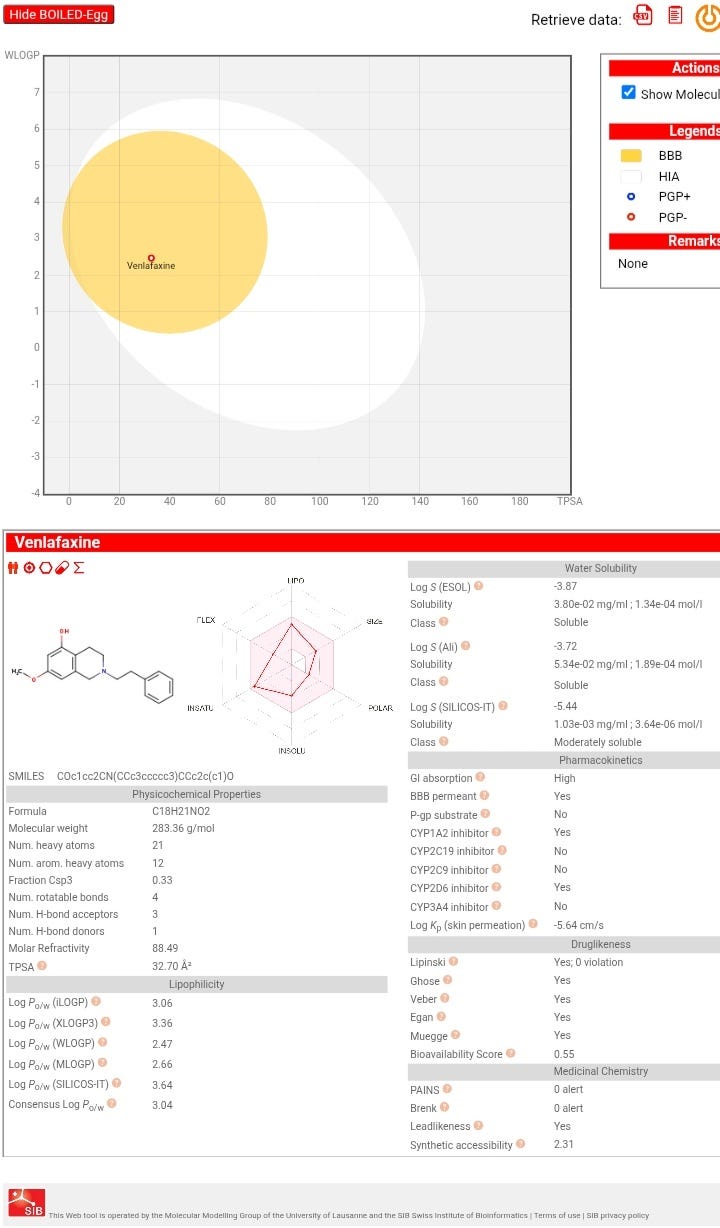
Image Credit: Medium
Venlafaxine: assessing the potential for repurposing.
- Venlafaxine, commonly used for depression and anxiety disorders, is likely a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor with potential CNS activity based on its structure.
- Research to validate its biological targets integrates experimental, computational, and multiomics approaches like computational target prediction and high-throughput screening.
- Machine learning enhances prediction of target druggability by integrating diverse protein features, addressing data imbalance, and predicting drug-target interactions for faster drug discovery.
- ML models can predict side effects, prioritize targets for specific diseases, and improve the efficiency of drug development by scoring and ranking targets based on predicted therapeutic effects.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app