Knowridge
5d
221
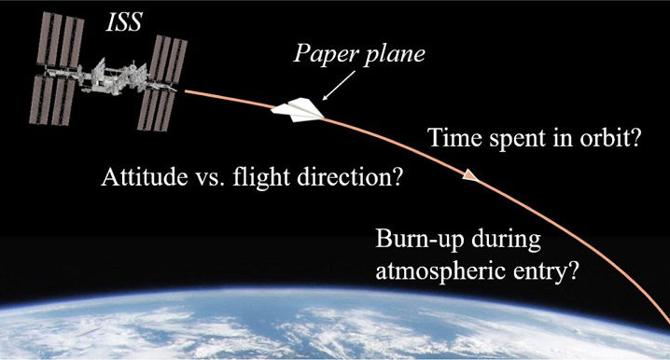
Image Credit: Knowridge
What if you threw a paper airplane from the space station
- A study from the University of Tokyo explored what happens when a paper airplane is thrown from the International Space Station (ISS).
- The paper airplane was made from a standard A4 sheet of white paper, resembling a basic origami design but with aerodynamic modeling.
- Simulations showed that when the paper airplane was launched from the ISS at 400 km with a speed of 7800 m/s, it descended relatively stable until reaching around 120 km altitude.
- At 120 km altitude, increased air density induced uncontrollable tumbling, leading to an uncontrolled flight path similar to traditional paper airplanes. Experimental testing in a wind tunnel showed the paper airplane could withstand high winds but would eventually burn up in the atmosphere.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app