ML News
Arxiv
80

Image Credit: Arxiv
Leveraging priors on distribution functions for multi-arm bandits
- Researchers have introduced Dirichlet Process Posterior Sampling (DPPS), a Bayesian non-parametric algorithm for multi-arm bandits.
- DPPS, akin to Thompson-sampling, makes decisions based on posterior probabilities of arm optimality without assuming a parametric reward distribution.
- The algorithm employs Dirichlet Process priors to model the reward generating distribution directly, offering a principled way to integrate prior beliefs.
- Empirical studies demonstrate strong performance of DPPS in various bandit environments, with a non-asymptotic optimality shown through information-theoretic analysis.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Arxiv
215

Image Credit: Arxiv
Mind the Memory Gap: Unveiling GPU Bottlenecks in Large-Batch LLM Inference
- Large language models often face inefficient resource utilization during inference due to their auto-regressive nature.
- Existing literature typically explains performance plateau in large-batch inference as a shift to the compute-bound regime, but a new study reveals it remains memory-bound.
- Researchers propose a Batching Configuration Advisor (BCA) to optimize memory allocation, reducing GPU memory requirements and improving resource utilization.
- The study challenges conventional assumptions, offers insights and strategies for better resource utilization, especially for smaller language models.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Arxiv
42

Image Credit: Arxiv
EvalTree: Profiling Language Model Weaknesses via Hierarchical Capability Trees
- A study introduces a method called EvalTree to identify weaknesses in language models (LM) by constructing a capability tree and pinpointing underperforming nodes.
- EvalTree outperforms other baseline weakness profiling methods by precisely and comprehensively identifying weaknesses on benchmark instances like MATH and WildChat.
- The weakness profiling by EvalTree enables targeted data collection, leading to improved LM performance compared to other data collection strategies.
- EvalTree also reveals shortcomings in Chatbot Arena's human-voter-based evaluation process, providing a tool for practitioners to explore capability trees interactively.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Arxiv
154

Image Credit: Arxiv
REGEN: A Dataset and Benchmarks with Natural Language Critiques and Narratives
- The paper introduces a novel dataset, REGEN, designed to benchmark the conversational capabilities of recommender Large Language Models (LLMs).
- REGEN extends the Amazon Product Reviews dataset by including user critiques and narratives associated with recommended items.
- An end-to-end modeling benchmark is established for conversational recommendation using the LUMEN framework that incorporates LLMs for critiquing, retrieval, and generation.
- Results show that incorporating critiques in recommendations enhances quality and LLMs trained on the dataset effectively generate recommendations and contextual narratives comparable to state-of-the-art models.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Arxiv
23

Image Credit: Arxiv
Communities in the Kuramoto Model: Dynamics and Detection via Path Signatures
- Researchers propose using path signatures, a mathematical framework, to analyze multivariate dynamical processes governed by structural connections.
- Path signatures encode geometric and temporal properties of continuous paths and can reveal lead-lag phenomena in dynamical data.
- The study showcases the application of path signatures in detecting structural communities in time series data from the Kuramoto Stochastic Block Model, achieving exact recovery of communities.
- The research suggests that path signatures offer a new perspective for analyzing complex neural data and high-dimensional systems, allowing for the inference of underlying structures based on temporal functional relationships.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Arxiv
381

Image Credit: Arxiv
Using AI to Summarize US Presidential Campaign TV Advertisement Videos, 1952-2012
- Introduction of the largest and most comprehensive dataset of US presidential campaign television advertisements, along with machine-searchable transcripts and high-quality summaries for academic research.
- Automation of the process through a large-scale parallelized, AI-based analysis pipeline to prepare, transcribe, and summarize over 9,700 presidential ads from the Julian P. Kanter Political Commercial Archive.
- Human evaluations demonstrate that the AI-generated transcripts and summaries are of similar quality to manually created ones, proving the effectiveness of the methodology.
- The dataset provides valuable insights, such as tracking the evolution of focal issue areas over seven decades of presidential elections, and the methodology can be applied to create high-quality summaries for other video datasets.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Arxiv
53

Image Credit: Arxiv
MedSegFactory: Text-Guided Generation of Medical Image-Mask Pairs
- MedSegFactory is a medical synthesis framework that generates high-quality paired medical images and segmentation masks across various modalities and tasks to enhance existing segmentation tools.
- It utilizes a dual-stream diffusion model, with one stream synthesizing medical images and the other generating corresponding segmentation masks, ensuring precise alignment through Joint Cross-Attention (JCA).
- The bidirectional interaction between the streams allows for improved consistency between generated image-mask pairs and on-demand generation based on user-defined prompts.
- MedSegFactory's approach improves scalability and data quality, demonstrating superior performance in 2D and 3D segmentation tasks while addressing data scarcity and regulatory constraints in the medical imaging domain.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Arxiv
234

Image Credit: Arxiv
GNN-ACLP: Graph Neural Networks Based Analog Circuit Link Prediction
- Circuit link prediction is important in analog circuit design automation, but current methods face challenges like insufficient use of circuit graph patterns, data scarcity, and limited adaptability to netlist formats.
- GNN-ACLP is a Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) based framework that addresses these challenges with innovations like the SEAL framework for improved prediction accuracy, Netlist Babel Fish for format conversion, and SpiceNetlist dataset for model training.
- Experiments show significant accuracy improvements on various datasets with GNN-ACLP, demonstrating robust feature transfer capabilities and enhanced model generalization.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Medium
73
Image Credit: Medium
Kronecker Decomposition of Weight Matrices using Least Squares Approach
- Knowledge distillation in machine learning involves transferring knowledge from a large 'teacher' model to a smaller 'student' model.
- One effective method for model compression is the Kronecker decomposition, which involves breaking down a large matrix into the Kronecker product of two smaller matrices.
- The Kronecker decomposition significantly reduces the number of parameters stored, leading to reduced compute and storage requirements.
- By defining a cost function and using techniques like Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), optimal A and B matrices can be obtained for the best least-squares approximation of the original weight matrix W.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Medium
151
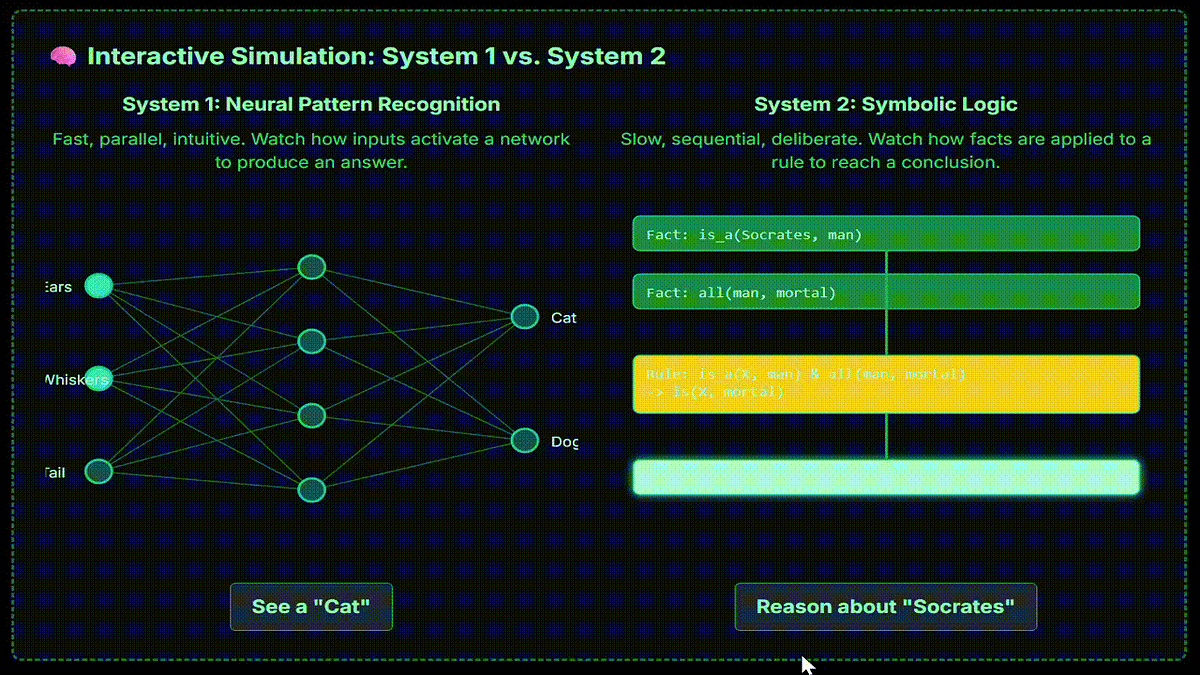
Image Credit: Medium
Neural-Symbolic AI
- The quest for Neural-Symbolic integration aims to combine the strengths of neural networks and symbolic systems in AI.
- Hyperbolic space is being explored for embedding hierarchies, fueled by a mathematical breakthrough from the 19th century.
- The surge in Neural-Symbolic AI is attributed to advancements in hardware and distributed systems, enabling learning and reasoning fusion at scale.
- Federated learning addresses the bottleneck of building knowledge bases in symbolic AI by allowing AI models to be sent to data for collective learning without sharing private data.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Medium
176

Image Credit: Medium
The AI Patent Land Grab: How QuickCode’s “Innovation” Reveals a Broken System
- QuickCode's patent application aims to claim ownership over obvious AI techniques.
- The patent describes basic ML processes as revolutionary and groundbreaking inventions.
- Filing such patents harms innovation by hindering progress and promoting rent-seeking behavior.
- The AI community should reject such patents and prioritize genuine innovation and collaboration.
- It's crucial to safeguard the open, collaborative spirit that drives AI advancements.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Medium
179
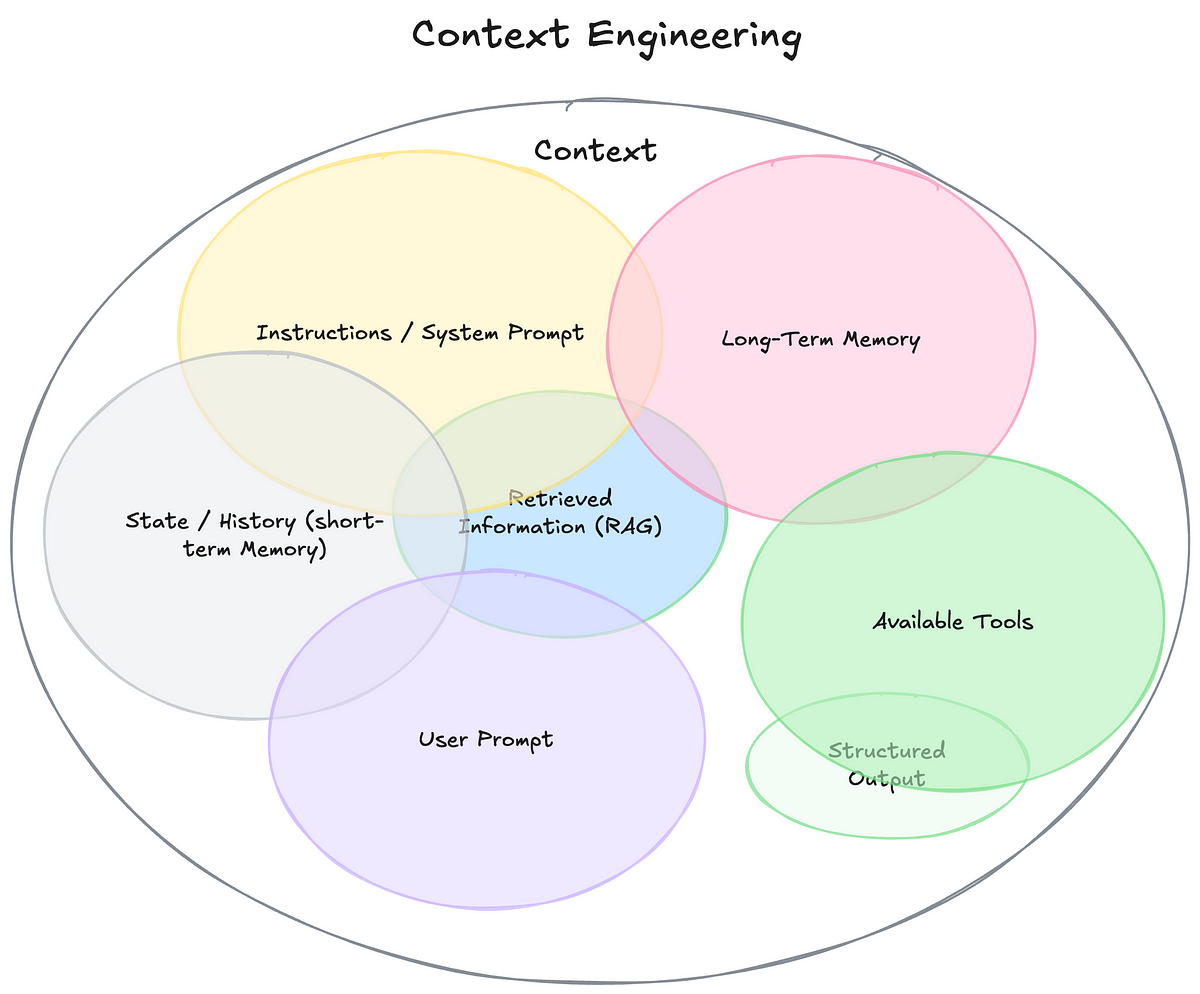
Image Credit: Medium
From Prompting to Context Engineering: The Next Frontier in AI Systems
- The true differentiator in building intelligent AI systems today is not just the prompt but the context, marking the age of Context Engineering.
- Context engineering involves dynamically providing relevant knowledge, instructions, tools, and memory to AI models at runtime tailored to the task at hand.
- Context engineering ensures AI models can actually complete tasks by considering all relevant inputs and providing rich context for responses.
- Effective context engineering involves dynamically constructing context, deciding what knowledge and tools to load, and presenting data clearly to improve AI model performance.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Medium
260

Image Credit: Medium
What I Learned About AI, ML, and DL in One Week
- AI can perform various tasks like OCR, face detection, text-to-speech, sentiment analysis, and language translation.
- Machine learning includes supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on neural networks.
- Pros and cons exist for AI, ML, and DL applications, impacting areas like efficiency, bias, interpretability, and resource requirements.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Medium
360

Image Credit: Medium
How I’d Learn ML/AI FAST If I Had to Start Over
- Developing deep critical thinking skills is crucial for becoming a great software engineer.
- Understanding concepts and problem-solving abilities are more important than memorization in AI/ML.
- Knowing how to code, particularly in Python, is essential for aspiring AI/ML engineers.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Medium
1k

Image Credit: Medium
When AI Took the Cal
- The author experiences a sudden internet outage on a crucial night with impending deadlines.
- Usually expecting a frustrating encounter with customer support, the author is pleasantly surprised by an AI-powered virtual assistant named Nova.
- Nova proves to be highly effective, asking specific questions and guiding the author through troubleshooting steps more efficiently than any human representative.
- The AI-powered virtual assistant Nova provides personalized and effective assistance in resolving the author's internet connectivity issue.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app