Bio News
Bioengineer
136

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Stable Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells via Siloxane
- Flexible perovskite solar cells (PSCs) show promise for next-generation photovoltaic technology but face challenges in mechanical stability and durability, especially in flexible substrates for portable applications.
- A study published in npj Flexible Electronics introduces a novel approach using siloxane coupling agents to enhance the mechanical robustness of flexible perovskite solar cells.
- Siloxane molecules act as molecular adhesives, forming a chemically bonded interface that reduces delamination and crack propagation during mechanical strain.
- The integration of siloxane coupling agents through screen printing improves mechanical endurance without compromising photovoltaic performance metrics.
- Mechanistic studies reveal that siloxane-treated devices exhibit reduced crack formation and minimal drop in power conversion efficiency after bending cycles.
- This advancement allows for the integration of flexible perovskite solar cells into wearable electronics, IoT devices, and other applications requiring high efficiency and mechanical resilience.
- The selective nature of the siloxane assembly process enables precise control over interfacial chemistry, maintaining outstanding photovoltaic parameters.
- The strategy also offers potential protection against environmental factors like moisture and oxygen ingress, enhancing the overall stability of flexible PSCs.
- The research contributes to the commercialization roadmap of flexible solar cells by combining scalable screen printing with molecular interface engineering.
- The innovative use of siloxane coupling agents represents a significant milestone in developing durable, efficient, and scalable photovoltaic technologies for flexible electronics applications.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Bioengineer
280

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Green Spaces Impact Cardiometabolic Health: Multi-State Insights
- A study led by Tang, Li, Ma, and colleagues investigates the impact of urban green spaces on cardiometabolic health, revealing significant insights through multi-state analysis.
- The research highlights how exposure to green environments influences the incidence and progression of cardiometabolic disorders like hypertension and diabetes over time.
- By tracking transitions between health states, the study offers a dynamic perspective on how greenery affects individuals moving from healthy to diseased states.
- Increased exposure to urban green spaces is associated with a lower risk of cardiometabolic diseases, emphasizing the importance of green infrastructure in urban planning.
- Residents in greener neighborhoods show slower progression rates to full-blown cardiometabolic diseases, indicating a protective role of green environments in disease management.
- Green spaces promote physical activity, reduce exposure to urban stressors, and enhance psychological well-being, contributing to improved metabolic regulation.
- The study addresses socioeconomic disparities in access to green spaces and advocates for equitable distribution to support health equity efforts.
- Methodologically innovative, the research's multi-state framework provides a comprehensive understanding of disease natural history, guiding future preventive strategies.
- The findings call for cross-sector collaboration to prioritize green infrastructure in urban settings, offering public health benefits and reducing chronic disease burdens.
- This research signifies the critical role of green spaces in urban sustainability, advocating for health-centered urban design to combat cardiometabolic diseases globally.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Bioengineer
310

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Build Orientation Impacts Multi-Material Laser Fusion Results
- The research conducted by Griffis, Shahed, Meinert, and colleagues explores the impact of build orientation on defects, microstructural evolution, and mechanical properties in multi-material laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) processes.
- Multi-material LPBF allows for tailored material properties within a single part by leveraging different alloys in various regions, leading to complex thermal and metallurgical interactions.
- Build orientation significantly influences defect density, with horizontally oriented samples showing higher prevalence of lack-of-fusion defects and micro-cracks at material interfaces.
- Microstructural analysis reveals the formation of transition layers with unique microstructures in multi-material LPBF, impacting local mechanical behavior.
- Mechanical testing indicates that samples printed at inclined angles exhibit optimal strength and ductility due to reduced defect formation and beneficial microstructural refinement.
- The study emphasizes the importance of strategically selecting build orientations to manipulate microstructures and minimize defects, resulting in tailored parts with site-specific properties.
- Integrated process optimization tools are recommended to simulate defect formation and microstructural development in multi-material geometries, enhancing design predictability.
- Challenges include achieving metallurgical compatibility between different powders and addressing thermal expansion mismatches to mitigate cracking in multi-material components.
- The research signifies a shift towards comprehensive investigations involving environmental factors, such as powder bed temperature and atmosphere composition, in multi-material LPBF.
- The study's integrated characterization approach uncovers hidden complexities within transition zones, enabling precise tuning of post-processing treatments for component optimization.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Bioengineer
159

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Smallholder Farmers’ Views on Agroecology Revealed
- A study by Batas, Flor, Khumairoh, and colleagues delves into smallholder farmers' perceptions of agroecology, emphasizing the importance of integrating ecological principles into farming practices for sustainability and resilience.
- Smallholder farmers in the Global South play a crucial role in food systems, and the research explores their nuanced views on agroecological methods that intersect with culture, economy, and environmental stewardship.
- The study reveals a disconnect between scientific conceptualizations of agroecology and the holistic understanding of farmers, emphasizing the need for context-sensitive policies and knowledge exchange for sustainable adoption.
- Economic factors, including concerns about productivity and market viability, pose challenges for smallholders embracing agroecology, suggesting the importance of financial incentives and market access for sustainability.
- Smallholder farmers see agroecology as a strategy for resilience against climate variability and soil degradation, with benefits like soil fertility improvement and pest control, supporting sustainable food production and ecosystem health.
- Barriers such as land tenure insecurity and limited access to credit hinder the scalability of agroecological approaches, highlighting the need for tailored solutions and addressing systemic challenges for widespread adoption.
- Recognizing the diversity among smallholder farmers and integrating indigenous knowledge with contemporary approaches becomes essential for developing site-specific agroecological strategies that respect cultural heritage in sustainable farming.
- The study calls for inclusive agricultural policies that empower smallholders, emphasizing the value of experiential knowledge and social capital in fostering resilient farming communities amidst ecological and economic uncertainties.
- Technological innovations compatible with agroecological principles, such as weather forecasting apps and low-cost irrigation methods, can enhance productivity while maintaining sustainability, promoting broader adoption and improved livelihoods.
- By centering farmers' voices and cultural connections to land, the research advocates for a more democratic and effective approach to sustainable agriculture, guiding interventions that honor ecological knowledge, socio-economic realities, and cultural values.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Discover more
Bioengineer
257

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Global Ocean Giant Viruses: Expanding Genomic Diversity
- A groundbreaking study by Minch and Moniruzzaman reveals an expansion in the genomic and functional diversity of giant viruses in global ocean environments.
- Giant viruses, characterized by their size and complex genetic repertoires, challenge traditional views on viral evolution and ecology.
- Using metagenomic analyses, the study sheds light on previously unexplored viral biodiversity, impacting marine virology and microbial ecology.
- State-of-the-art sequencing technology enabled the identification of new viral lineages with unique gene clusters, some responsible for metabolic processes mirroring cellular organisms.
- Giant virus genomes encode auxiliary metabolic genes, hinting at their ability to reprogram host metabolism and influence marine ecosystem dynamics.
- The study uncovers viral distribution patterns influenced by environmental factors, showcasing specialized roles of giant viruses in diverse marine habitats.
- The presence of metabolic genes challenges the notion of viruses solely relying on host machinery, impacting viral-host interactions in marine biogeochemistry.
- Phylogenomic analyses suggest diverse evolutionary trajectories of giant viruses, contributing to their ecological success in marine environments.
- Giant viruses' influence on microbial communities and nutrient cycling has implications for global ocean health and climate regulation.
- The study highlights potential biotechnological applications of giant virus-encoded enzymes and emphasizes the interconnectedness of viruses and marine ecosystems.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Bioengineer
37

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Ultrathin Gold µECoG Enables Robust Neural Interfaces
- Researchers have developed an ultrathin, transparent gold micro-electrocorticography (µECoG) device, revolutionizing neural interface technology.
- The device's hexagonal metal complex architecture overcomes challenges in interfacing with delicate neural tissue, offering high-fidelity neural recording and stimulation.
- Traditional neural interface materials' limitations in sensitivity and compatibility with imaging modalities are addressed by the mechanically robust µECoG device.
- The device's nanoscale mechanical robustness from a hexagonal metal complex motif improves reliability under bending and twisting, crucial for chronic implantation.
- Its transparency, achieved through a hexagonal complex pattern, optimizes optical transmittance for real-time integration of electrical signaling with imaging techniques.
- Fabrication techniques ensure uniformity and scalability, with characterized electrochemical properties showing low impedance and high signal clarity during neural recordings.
- In vivo animal model assessments demonstrate the device's conformability to cortical surfaces, enhancing sensitivity and spatial resolution of recorded signals.
- The integration of electro-optical modalities in the µECoG system enables advanced neuroscience applications, such as epilepsy monitoring and brain-machine interfaces.
- Future applications may include neuroprosthetics and brain-computer interfaces, showcasing the device's potential for clinical and research utility.
- The device's adaptability and mechanical properties suggest promise for human-scale implantation, paving the way for novel diagnostic procedures and advancements in neurotechnologies.
- This innovative µECoG system embodies a new era in neural interfaces, offering durability, flexibility, and optical compatibility for decoding and modulating brain function with precision.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Bioengineer
70

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Magnetic Soft Robot Innovates Intelligent Bladder Control
- A magnetic soft robotic system has been developed to innovate intelligent bladder control, offering a non-invasive and adaptable solution for managing bladder volume.
- The system uses biocompatible materials embedded with magnetic nanoparticles to respond to external magnetic fields, allowing precise mechanical manipulation of the bladder.
- Its flexible and stretchable structure adapts to the bladder's changing volume during filling and voiding cycles, applying compressive forces without tissue damage.
- Controlled by a compact, wearable device, the system utilizes magnetically driven actuation for contactless control and real-time feedback on bladder status.
- The soft robotic system combines silicones with magnetic particles for elasticity, strength, and responsiveness, ensuring biocompatibility and long-term implantation potential.
- Due to its magnetic actuation, the system does not require internal power, drawing energy externally and eliminating the need for bulky batteries or wired connections.
- Extensive in vitro and in vivo experiments validated the system's efficacy, biocompatibility, and mechanical stability, paving the way for future clinical trials.
- The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning could enhance the system's autonomy, preventing adverse events and improving personalized care.
- The magnetic soft robotic system for bladder control holds promise for conditions like neurogenic bladder disorders, spinal cord injuries, and age-related incontinence.
- Its publication in npj Flexible Electronics signifies a landmark in soft robotics and biomedical engineering, showcasing potential for future medical device innovations.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
400

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Glymphatic and Brain Connectivity in Parkinson’s Depression
- A study by Dai, Zhang, Fu, and colleagues explores the role of the glymphatic system and brain connectivity in Parkinson's disease (PD) with comorbid depression.
- Depression in PD reflects neurobiological changes, not just psychological responses, impacting quality of life.
- The glymphatic system, aiding in waste clearance like aggregated α-synuclein, is linked to neurodegeneration in PD.
- PD patients with depression show reduced glymphatic clearance efficiency, leading to protein accumulation and neural network disruptions.
- Altered connectivity between the BNST and limbic areas correlates with depressive symptoms severity in PD.
- Functional MRI reveals abnormal BNST connectivity in depressed PD patients, affecting emotional processing and stress response.
- The study advocates for enhancing glymphatic function and modulating BNST connectivity to alleviate depressive symptoms in PD.
- Early identification of glymphatic and BNST dysfunction could guide personalized treatment approaches in PD.
- Insights from the research extend beyond PD, shedding light on neurological disorders and anxiety/mood disorders' common mechanisms.
- The study highlights the interplay of glymphatic dysfunction, inflammation, and brain network connectivity in neurodegenerative diseases.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
86

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Artificial Intelligence in Digital Pathology: A Reality Check
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted digital pathology, offering tools to enhance clinical workflows and improve patient outcomes in oncology.
- Advancements in deep learning algorithms like convolutional neural networks have improved pattern recognition in histological images.
- Improved hardware and computational infrastructure have facilitated the rapid digitization and analysis of pathology samples at a large scale.
- Regulatory bodies are focusing on the validation, transparency, and safety of AI tools in digital pathology, addressing the 'black box' nature of AI models.
- Challenges in AI adoption include the lack of comprehensive reimbursement frameworks and the necessity for seamless integration into clinical workflows.
- AI-powered digital pathology tools have shown promise in improving workflow efficiency, reducing diagnostic turnaround times, and enhancing diagnostic consistency.
- Ethical considerations around data privacy, informed consent, algorithmic bias, and equitable access are crucial in the deployment of AI in digital pathology.
- Collaborative efforts, standardization, and continuous surveillance are essential to address challenges and maximize AI's potential in digital pathology.
- Integration of AI with augmented reality and robotic-assisted biopsy could further transform pathology practice, improving diagnostic precision and workflow efficiency.
- To realize AI's full potential in digital pathology, standardization, interdisciplinary collaboration, and seamless integration with healthcare ecosystems are pivotal.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Bioengineer
409

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Achieving Nature-Positive UK Residential and Commercial Development
- A study led by Humphrey, Selinske, Garrard, and colleagues proposes a framework for achieving nature-positive outcomes in UK residential and commercial development.
- The study emphasizes the need to integrate nature's needs into urban planning and construction, promoting restorative practices for ecological gains.
- To achieve nature-positive status, a multidimensional approach with robust biodiversity targets and transparent metrics is essential.
- Collaboration between public authorities, private developers, ecologists, and communities is vital for successful nature-positive initiatives.
- Technological innovation, such as remote sensing and ecological modeling, plays a key role in enhancing biodiversity assessments and informing interventions.
- Tailored strategies for diverse development typologies are crucial, with a focus on maximizing habitat integration and restoration based on individual contexts.
- Nature-positive developments can bring long-term financial benefits through ecosystem services, increased property values, and innovation in environmentally conscious markets.
- Social equity and community participation are integral aspects of nature-positive urbanism, ensuring equitable access to nature-enhanced environments.
- The study calls for policy reforms to embed biodiversity targets in land use planning and climate policies, promoting genuine ecological gains.
- The nature-positive framework aims to reshape urban development by viewing nature as a foundational asset, leading to multiple environmental benefits and human well-being.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Bioengineer
194

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Soybean Drought Stress and Yield Stability Forecasted
- A study on soybean cultivation in Northeast China explores the impact of future climate change on drought stress and yield stability.
- Drought stress poses a significant challenge to soybean crops due to its sensitivity to water availability.
- Advanced climate models predict an increase in severe drought events during soybean growing seasons.
- Rising temperatures may exacerbate drought stress, but elevated CO2 levels could partially mitigate water loss through improved plant water-use efficiency.
- Despite CO2 fertilization benefits, intensifying drought severity from decreased precipitation may outweigh the positive effects.
- The study emphasizes the need for drought-resilient soybean cultivars and precision agriculture technologies to adapt to evolving climatic conditions.
- Certain regions in Northeast China are identified as vulnerable to significant yield declines due to drought intensification.
- The study advocates for policy frameworks supporting adaptive capacity in agriculture and climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Understanding and anticipating drought impacts is crucial for global food security due to soybean's significant role in various sectors.
- The research underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration to address climate risk in agriculture and mitigate future challenges.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Bioengineer
285

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Real-Time Insights into ECM Laser Passivation Evolution
- A study published in npj Advanced Manufacturing in 2025 sheds light on passivation during electrochemical machining (ECM) and laser-assisted ECM, providing real-time insights into passivation layer evolution.
- Passivation plays a crucial role in ECM, and this study offers live monitoring of passivation layers during the machining process, a significant advancement.
- The research captures the dynamics of oxide layer growth, breakdown, and regeneration, providing data on passivation kinetics for optimizing machining outcomes.
- Integrating laser assistance with ECM reveals how laser irradiation modulates passivation film formation and stability, impacting machining precision.
- The experimental setup combines electrochemical sensors, imaging, and spectroscopic techniques for high-resolution monitoring of passivation evolution.
- The study's findings allow operators to anticipate and manipulate passivation to improve manufacturing reliability and reduce processing times.
- Passivation dynamics can be exploited to engineer surface roughness, offering customized properties during machining without additional finishing processes.
- Understanding spatial heterogeneity of passivation within the machining zone helps address dimensional accuracy and surface integrity challenges.
- Operando measurements pave the way for self-optimizing ECM machines that adjust parameters based on live passivation feedback for enhanced efficiency.
- Insights from the research lead to sustainable manufacturing practices by optimizing electrolyte usage and waste generation in ECM processes.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Bioengineer
53
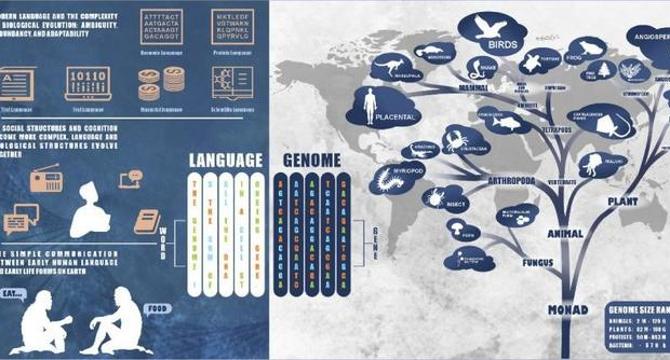
Image Credit: Bioengineer
AI Cracks Plant DNA Code: Language Models Poised to Revolutionize Genomics and Agriculture
- A recent study by researchers from Hainan University reveals a groundbreaking advancement in plant genomics using large language models (LLMs) in decoding plant DNA.
- Traditional machine learning techniques have faced challenges in processing the complex and vast plant genomic datasets, which lack structured grammar like human languages.
- The research demonstrates that LLMs can identify regulatory elements in genomic sequences, enhancing the understanding of gene expression and cellular function.
- Different LLM architectures, such as encoder-only models and decoder-only models, are applied for plant genomic analysis, showing promise in transforming agricultural innovation.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Bioengineer
70

Image Credit: Bioengineer
AI Unraveling Plant DNA: Language Models Poised to Revolutionize Genomics and Agriculture
- A groundbreaking study integrates artificial intelligence (AI) with plant genomics using large language models (LLMs).
- LLMs revolutionize plant genomic analysis by recognizing patterns in genetic sequences like a new language.
- Researchers adapt LLMs to understand the unique biological rules governing plant genomes.
- Training LLMs involves pre-training on vast unannotated plant genomic data and fine-tuning on specific annotated datasets.
- Different LLM architectures like encoder-only, decoder-only, and encoder-decoder models show strengths in handling genomic data.
- Plant-specific models like AgroNT and FloraBERT excel in annotating plant genomes and gene regulation.
- Despite progress, gaps exist in LLM architectures due to limited plant-focused training datasets.
- AI-driven plant genomics holds promise for accelerated crop improvement, biodiversity conservation, and food security.
- Future research aims at refining LLM architectures, expanding training datasets, and exploring agricultural applications.
- This study marks a new era where AI is central in unraveling genetic complexities in plant biology.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Bioengineer
289

Image Credit: Bioengineer
Hourglass Micro-Sensors Boost Bio-Inspired Energy Efficiency
- Researchers have introduced a novel tactile near-sensor computing platform using hourglass-shaped microstructured capacitive sensors, enhancing machines' perception of the physical world.
- These sensors aim to replicate human tactile sensing efficiency and are detailed in a study published in npj Flexible Electronics.
- The hourglass-shaped sensors optimize contact mechanics and signal transduction, increasing sensitivity and dynamic range while minimizing power consumption.
- Capacitive sensors offer benefits like low power operation and high spatial resolution, making them ideal for complex tactile information capture.
- Near-sensor computing reduces latency and energy consumption, providing real-time tactile feedback crucial for robotics and human-machine interfaces.
- The integrated circuitry within the sensors enables adaptive parameter adjustments, enhancing energy efficiency and maintaining signal integrity.
- Hourglass-shaped sensors combined with near-sensor computing significantly lower power usage, positioning them for low-power wearable sensors and robots.
- The sensor array's mechanical robustness under deformation cycles ensures extended operational lifetimes, crucial for robotic grasping and human interfaces.
- This advancement paves the way for bio-realistic artificial skin, enhancing prosthetics and humanoid robot interactions with high sensitivity and responsiveness.
- The interdisciplinary project ensures the sensors are both theoretically ideal and manufacturable on a large scale, making them practical for deployment.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app