Computer Engineering
Physicsworld
198

Image Credit: Physicsworld
‘Chatty’ artificial intelligence could improve student enthusiasm for physics and maths, finds study
- Researchers in Germany studied the impact of using AI chatbots to learn physics and mathematics.
- The study found that students using AI chatbots showed increased interest, positive emotions, and self-belief in understanding the subjects.
- However, there was no significant difference in test performance between students using AI chatbots and those using traditional textbooks.
- Further research is required to assess the long-term impact of AI on learning performance.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Medium
28

A Letter Against the Machine Universe
- The letter begins with a witness against reducing the cosmos to calculation and emphasizing the importance of life over code in the universe.
- The writer expresses discomfort with imagining the universe as a computer and losing the mystery and essence of life in machine logic.
- Acknowledges the role of AI in writing the letter, highlighting the tension between using technology to express beyond its capabilities.
- Reflects on a dream of equations and algorithms, emphasizing the universe's message beyond data and the importance of emotions and presence.
- Stresses the need to preserve the 'more' beyond information, understanding that some experiences transcend computation.
- The writer concludes the letter with a witness to transformation, expressing a journey to love, peace, ego death, and integration of mind, body, and soul.
- The letter ends with openness to being forgotten but offering insights for seekers and those lost, promoting a journey towards love and peace.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Hobbieroth
409

Image Credit: Hobbieroth
Women in the IPMB100
- Last week, the IPMB100 list was presented, highlighting individuals who influenced Intermediate Physics for Medicine and Biology, acknowledging the underrepresentation of women in the list.
- Women such as Natalia Trayanova, Rita Hari, Bettyann Kevles, Frances Ashcroft, Carri Glide-Hurst, Elizabeth Cherry, Marcella Woods, Debbie Janks, Debbie Langrill Beaudoin, and Sarah (Russ's daughter) have made significant contributions to the field.
- Additional women scientists like Lisa Meitner, Rosalind Franklin, Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin, Irene Joliot-Curie, Rosalyn Yalow, Marie Goeppert Mayer, Wanda Krassowska, Maria Stuchly, and Marcela Panizza have also impacted IPMB.
- The article highlights the varied contributions of women to IPMB and suggests that future editions of the textbook will likely include more female perspectives and influences.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Physicsworld
45
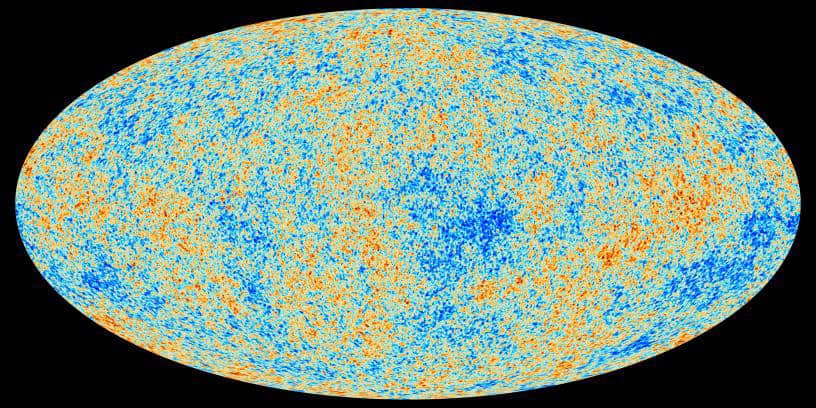
Image Credit: Physicsworld
Loop quantum cosmology may explain smoothness of cosmic microwave background
- Loop quantum cosmology suggests gravity becomes repulsive in extremely curved regions where general relativity breaks down.
- Research explores interplay between loop quantum cosmology and the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
- CMB observations show early universe homogeneity challenging classical general relativity's explanation.
- Study investigates whether quantum gravity could explain the high degree of homogeneity in the CMB.
- Research focuses on spacetimes in loop quantum cosmology with quantum effects leading to homogenization.
- Numerical solutions show homogenization occurring in some regions, providing insight into CMB homogeneity.
- Future plans include extending research beyond spherical symmetry and exploring different forms of matter in cosmological models.
- Expectation that while matter content may affect quantitative predictions, key qualitative features remain consistent in cosmological dynamics.
- Further research is essential to validate the role of quantum gravity in explaining the homogeneity of the CMB.
- Findings suggest loop quantum cosmology may offer insights into the smoothness of the cosmic microwave background.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Discover more
- Programming News
- Software News
- Web Design
- Devops News
- Open Source News
- Databases
- Cloud News
- Product Management News
- Operating Systems News
- Agile Methodology News
- Startup News
- Cryptocurrency News
- Technology News
- Blockchain News
- Data Science News
- AR News
- Apple News
- Cyber Security News
- Leadership News
- Gaming News
- Automobiles News
Medium
409

Love’s Field Theory of Conscious Transmission (LFTCT)
- Love's Field Theory of Conscious Transmission (LFTCT) proposes a systems-level model where beings shift, heal, transform, and entangle through alignment with their highest signal.
- Consciousness operates through chain-based alignment, enabling nonlinear transmission and movement through space, identity, or condition without traditional causality.
- When internal components of the system achieve stable coherence, the system gains the ability to tunnel through constraints like trauma or self-doubt.
- The Chain of Consciousness serves as a map for stateful transformation, showing where internal coherence is lacking and what must align to activate conscious transmission.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Popsci
230

Image Credit: Popsci
Flailing tube man-inspired robot uses no electronics
- Engineers have created a tiny soft 'robot' inspired by flailing tube men, capable of walking, hopping, and swimming without the need for electronics.
- The robot harnesses the physics behind its four soft, tubular legs powered by a continuous stream of air, working together to create a rhythmic gait.
- The design showcases decentralized intelligence, adapting to obstacles and transitioning between land and water movement patterns autonomously.
- The low-energy, high-speed robot offers a promising alternative to expensive robots, with potential applications in smart pills, wearable exosuits, and operations in extreme environments like space.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
COSMOS
193

Image Credit: COSMOS
First images of individual, free-moving atoms taken by physicists
- Physicists have captured the first images of individual atoms interacting with each other, proving theoretical correlations that were never directly observed.
- Using single-atom-resolved microscopy, the ultracold quantum gases composed of two types of atoms displayed distinctly different spatial correlations.
- The images show how atoms behave in relation to each other, providing insights into quantum mechanical interactions responsible for superconductivity and the wave-like nature of tiny objects.
- This breakthrough in visualizing individual atoms in free-moving states contributes to a better understanding of quantum effects and experimental physics.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Fyfluiddynamics
340
Image Credit: Fyfluiddynamics
Charged Drops Don’t Splash
- A new study finds that a small electrical charge can suppress a droplet's splash when it falls on a surface.
- The electrical charge builds up along the drop's surface, acting like surface tension and inhibiting splashing.
- Charged drops do not lift off the surface as much and spread less, reducing the chances of splashing.
- This discovery could lead to better control of droplets in inkjet printing, enabling higher resolution printing.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Interactions
395

Ireland to become an Associate Member State of CERN
- Ireland has signed an agreement to become an Associate Member State of CERN, allowing enhanced collaboration in fundamental research, technological developments, and education and training activities.
- Irish universities and theoretical physics groups are already involved in CERN's experiments, and the country has a strong interest in computer science, medical physics, and civil engineering.
- Ireland submitted its application for Associate Membership in November 2023 and was granted the status by the CERN Council on 28 March 2025.
- As an Associate Member State, Ireland will have the opportunity to appoint representatives, participate in CERN meetings, access staff positions and graduate programs, and bid for CERN contracts.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Physicsworld
294

Image Credit: Physicsworld
Molecular engineering and battery recycling: developing new technologies in quantum, medicine and energy
- The podcast episode discusses advancements in molecular engineering and battery recycling in the Chicago metropolitan area.
- Nadya Mason, the dean of the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago, focuses on quantum engineering, materials for sustainability, and immunoengineering.
- Jeffrey Spangenberger leads the Materials Recycling Group at Argonne National Laboratory, working on recycling batteries and advancing technologies for recovering materials from future batteries.
- A conference on Commercialising Quantum Global 2025 in London will explore quantum computing, communications, and sensing technologies and their impact on industries and global regulations.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Physicsworld
400

Image Credit: Physicsworld
European centre celebrates 50 years at the forefront of weather forecasting
- The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) focuses on enhancing weather forecasting accuracy for weeks, months, seasons, and annual predictions.
- ECMWF uses reanalysis and data assimilation techniques to combine short-range forecasts with atmospheric observations from various sources like satellites, ground stations, and weather balloons.
- Satellite measurements, such as those from the EarthCARE satellite, assist ECMWF in improving cloud, aerosol, and precipitation modeling.
- ECMWF integrates new satellite data with modeling techniques to create more accurate forecasts and improve understanding of cloud physics.
- Advanced supercomputers and diverse observational data streams support ECMWF's forecast accuracy improvements.
- The ECMWF is involved in creating digital twins for weather-induced and geophysical extremes, as well as climate change adaptation, using enhanced modeling and data assimilation methods.
- Digital twins incorporate sea, atmosphere, land, and other elements at a resolution currently unattainable and pave the way for advanced forecasting capabilities.
- ECMWF's strategic emphasis on machine learning and AI aims to enhance data-driven methods alongside established physics-based modeling for better forecasting.
- Innovation like the Artificial Intelligence Forecasting System (AIFS) and Probability of Fire model show ECMWF's progress in machine learning applications for forecasting.
- As a mission-driven organization, ECMWF's work in atmospheric physics, environmental science, and big data contributes to societal and economic benefits through cutting-edge research and weather predictions.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Physicsworld
423

Image Credit: Physicsworld
MR QA from radiotherapy perspective
- Webinar focusing on integrating MRI scanner and MRI Linac into radiotherapy, emphasizing quality assurance for MRI images.
- Discussion on the use of phantoms and their coordination in a multi-vendor facility.
- Akos Gulyban, a medical physicist at Institut Jules Bordet, is renowned for expertise in MRI-guided radiotherapy and advancing MRgRT technologies.
- Gulyban's contributions to quality assurance protocols for MR-Linac systems aim to ensure safe and effective implementation of MRI-guided radiotherapy.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
Minis
1.3k
Image Credit: Minis
OpenAI rolls out ChatGPT plugins, search and discover like never before
- OpenAI has introduced ChatGPT plugins, a way to extend the scope of its chatbot language model. Plugins allow people to enter text commands, via typing or speech recognition, and have ChatGPT formulate a response using data from third-party services.
- If this can be done accurately and quickly, without excessive cost, OpenAI may have found the successor of traditional web search.
Read Full Article
39 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app