Neural Networks News
Hackernoon
1M
4
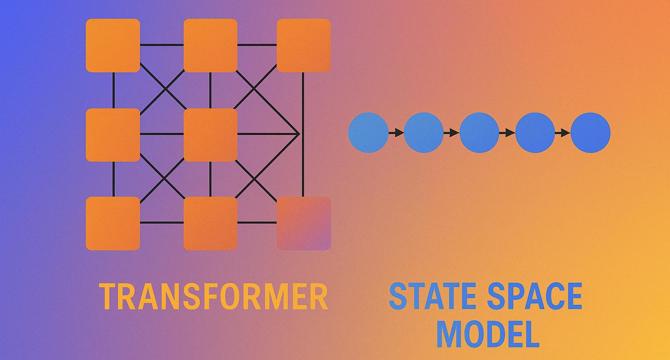
Image Credit: Hackernoon
The AI Industry's Obsession With Transformers Might Finally Be Waning
- The AI industry's focus on Transformers seems to be diminishing, with State Space Models (SSMs) gaining favor among practitioners prioritizing speed and efficiency.
- Transformers, though powerful, face challenges with scalability, memory usage, and latency, especially with lengthy inputs.
- SSMs offer advantages like linear scaling, steady memory usage, faster inference, and easier deployment on constrained hardware.
- The implementation of SSMs, such as the Mamba model, has shown improvements in latency, memory efficiency, and performance in real-world projects.
- Choosing between Transformers and SSMs depends on the product's requirements, with SSMs being more efficient for handling long-form documents and real-time interactions.
- The shift towards SSMs signifies a move towards more product-focused AI infrastructure design, considering factors like speed, cost, and long-term efficiency.
- While Transformers will still have their place, SSMs offer a viable alternative for products needing quick feedback and operating within moderate system constraints.
- This shift highlights a transition from research-driven decisions to product-driven decisions, emphasizing practical results over pure performance metrics.
- Adapting to these changes can benefit AI products by prioritizing functionality and operational efficiency, enhancing the overall product development process.
- The evolution in AI model selection reflects a maturation in the industry's approach, showcasing a shift towards more thoughtful and pragmatic decision-making.
Read Full Article
Like
Medium
2M
399

Image Credit: Medium
The Silicon Soul: How NPUs Are Quietly Rewiring the Future of Personal Computing
- Neural Processing Units (NPUs) are quietly revolutionizing personal computing by enabling on-device AI capabilities in laptops.
- The NPU, integrated into processors like the Intel Core Ultra 9 185H, allows for tasks such as noise cancellation, facial recognition, and live transcription to be performed on the device without the need for cloud processing.
- NPUs mimic the human brain's functioning, making computers more intuitive and personal by enabling them to learn and adapt with users.
- These NPUs are becoming more affordable and will soon be omnipresent in various devices, transforming how technology interacts with users and raising questions about privacy and control.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Medium
2M
59

Image Credit: Medium
ML Foundations for AI Engineers
- Intelligence boils down to understanding how the world works, requiring an internal model of the world for both humans and computers.
- Humans develop world models by learning from others and experiences, and computers learn similarly through machine learning.
- Traditional software development involves explicit instructions, while machine learning relies on curated examples for training models.
- Machine learning consists of training (learning from curated examples) and inference (applying the model to make predictions).
- Deep learning and reinforcement learning are special types of machine learning that enable computers to learn about the world.
- Deep learning involves training neural networks to learn optimal features for tasks, surpassing traditional model limitations.
- Training deep neural networks involves complex non-linearities and requires algorithms like gradient descent for parameter updates.
- Reinforcement learning allows models to learn through trial and error, with models improving based on rewards rather than explicit examples.
- Good data quality and quantity are crucial for training machine learning models, as bad data can hinder model performance.
- Machine learning provides a way for computers to align models to reality using data and mathematics, revolutionizing how tasks are learned and performed.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Minis
1y
1.5k

Image Credit: Minis
Elon Musk thought Parag Agrawal was not the 'fire-breathing dragon' the platform needed
- Elon Musk and then-Twitter CEO Parag Agrawal got dinner together in March 2022.
- Musk came away from the meeting describing Agrawal as a nice guy, but not the"fire-breathing dragon" Twitter needed.
- That's according to an excerpt published in The Wall Street Journal from Walter Isaacson's forthcoming biography of Musk.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Minis
2y
1.5k

Image Credit: Minis
If we use Elon Musk's Neuralink, we'll be Avengers: Enam Holdings exec
- Enam Holdings Director, Manish Chokhani, believes that integrating Neuralink into our spinal cords, as proposed by Elon Musk, could lead us to possess abilities akin to the Avengers, making us superhuman.
- Chokhani sees AI as the ultimate frontier in human evolution, suggesting that as we continue to enhance our abilities, we are progressively moving towards becoming more superhuman.
- Chokhani highlights the potential of robotics, sensors, and computing power to replicate and enhance our limbs, effectively extending our nervous system and augmenting human capabilities.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Minis
2y
1.2k
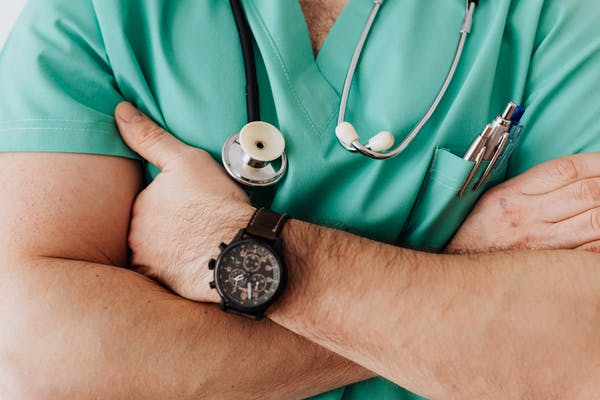

Image Credit: Minis
Science competes with Neuralink with launch of new platform for accelerating medical device development
- Science Foundry, a new platform by Science, offers access to over 80 tools to help companies develop medical devices more easily.
- The cost of developing medical devices can be prohibitive for startups, but Science Foundry aims to reduce barriers to innovation.
- Science is part of the growing brain-computer interface industry and is working on a visual prosthesis called the Science Eye to restore visual input to patients with serious blindness.
- It aims to support other neurotechnology, medical technology, and quantum computing startups at a cost comparable to academic facilities but with added benefits.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Minis
2y
405

Image Credit: Minis
Wall Street bets millions on new class of psychedelic drugs
- Wall Street investors are investing tens of millions of dollars in psychedelic drugs that could treat mental illness for a fraction of the cost of traditional therapy.
- Transcend Therapeutics, Gilgamesh Pharmaceuticals, and Lusaris Therapeutics have raised over $100 million since November to develop drugs for treating PTSD and depression.
- The companies' focus on more cost-effective psychedelic therapy coincides with a selloff in biotech stocks last year that dampened enthusiasm for hallucinogens' commercial potential.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Minis
2y
813

Image Credit: Minis
Bezos and Gates-funded brain implant startup tests mind-controlled computing on humans
- Synchron is one of several companies working on brain-computer interface technology.
- The system developed by Synchron is implanted through blood vessels and enables patients to control technology with their thoughts.
- Synchron CEO Tom Oxley has stated that the technology helps patients engage in activities that they may have previously been unable to do.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Minis
2y
677

Image Credit: Minis
Man in US developed 'uncontrollable' Irish accent after cancer diagnosis
- A man in North Carolina developed an uncontrollable Irish accent after being diagnosed with prostate cancer.
- The man had never visited Ireland and had no immediate family from there.
- The case was jointly studied and reported by Duke University and Carolina Urologic Research Center.
- FAS is a rare condition that occurs due to a neurological disorder, brain injury, or psychological disorder.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Minis
2y
583
Image Credit: Minis
New brain chips may bend your mind in strange & troubling ways: Study
- Neuralink, a neurotech startup founded by Elon Musk, is working on implanting its skull-embedded brain chip in humans.
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are being developed to facilitate direct communication between human brains and external computers for medical use cases such as helping paralyzed people communicate.
- BCIs are still in their infancy, and there are ethical concerns and potential negative effects to consider, such as dependency on the devices and changes to the sense of self.
- BCIs have surpassed their early sci-fi depictions and are attracting significant private and military funding for medical and non-medical uses.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Minis
2y
472
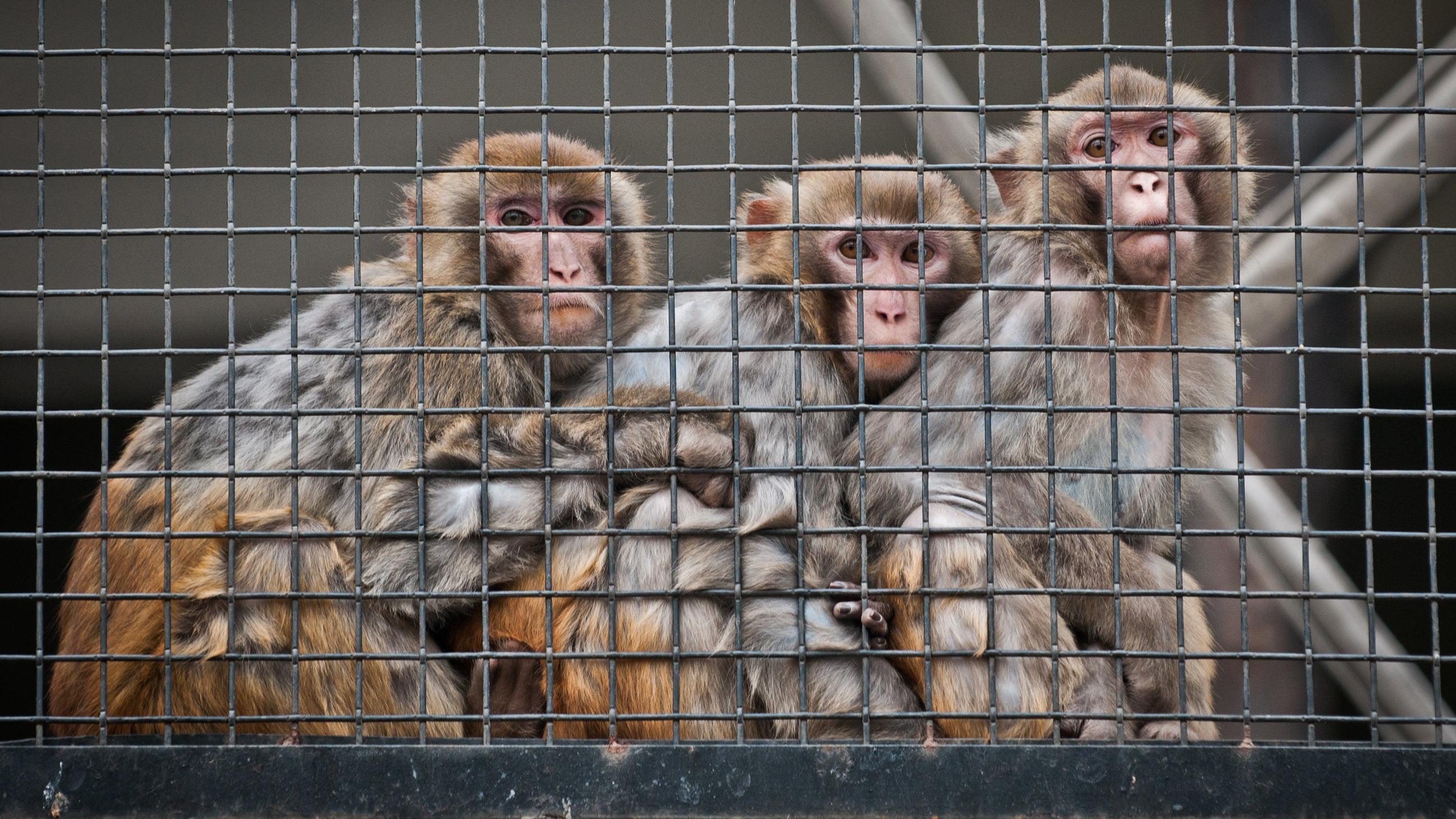

Image Credit: Minis
Musk's Neuralink may have illegally transported pathogens, animal advocates say
- The Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) has announced its intention to request a government investigation into Neuralink, a brain-implant firm owned by Elon Musk.
- The group claims to have evidence suggesting that the removal of brain implants from monkeys, which may have carried infectious diseases, was conducted unsafely.
- PCRM alleges that these incidents occurred in 2019.
- The animal welfare group is calling for the government to investigate these claims and ensure that proper safety protocols are in place to protect both animals and human health.
Read Full Article
28 Likes
Minis
2y
1k

Image Credit: Minis
Brain implant communication sets new record of 62 words per minute
- Researchers at Stanford University claim a new record for communicating thoughts to words through brain implant.
- A 67-year-old woman with ALS was able to communicate at a rate of 62 words per minute through the implant, 3.4 times faster than previous record.
- The study was conducted at Stanford University in the US.
Read Full Article
30 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app