Space News
Arstechnica
183
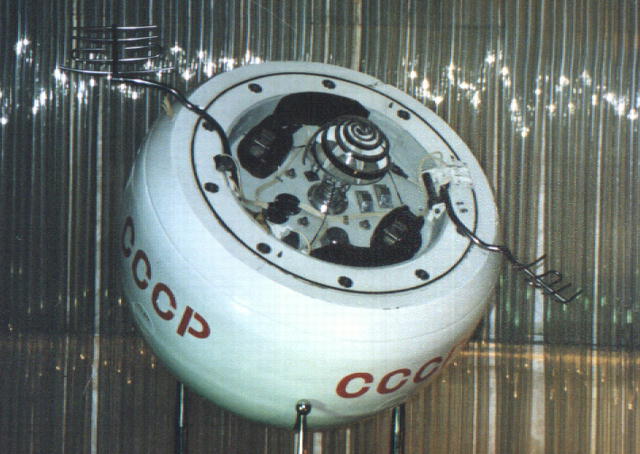

Image Credit: Arstechnica
A Soviet-era spacecraft built to land on Venus is falling to Earth instead
- Soviet-era spacecraft Kosmos 482, meant to land on Venus, is set to reenter Earth's atmosphere after a misfire over 50 years ago.
- Kosmos 482, about a half-ton in mass, was designed with a titanium heat shield to survive Venus' extreme conditions and now faces reentry into Earth.
- The spacecraft has a good chance of surviving the plunge through Earth's atmosphere, as its design is meant to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
- Although most space debris burns up during reentry, the European Space Agency predicts that Kosmos 482 is likely to reach Earth's surface intact.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Brighter Side of News
324
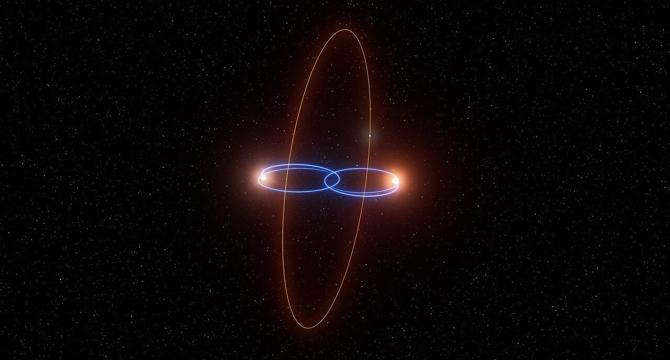
Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Astronomers find rare planet orbiting at 90 degrees around twin brown dwarf stars
- A planet named 2M1510 (AB) b has been confirmed to orbit at a 90-degree angle around twin brown dwarf stars, challenging traditional ideas of planetary formation and orbit.
- The planet's orbit is nearly perpendicular to the orbital plane of its host stars, making it a rare and unique discovery in the cosmos.
- The system consists of two brown dwarfs forming an eclipsing binary, with the planet following a polar orbit around them, adding complexity to the system.
- This planetary system is only the second known to contain an eclipsing pair of brown dwarfs and the first to host a planet with a polar orbit.
- The discovery raises questions about planet formation and stability in such unconventional positions, providing valuable insights into planetary evolution.
- The two brown dwarfs, collectively known as 2M1510, are of similar mass and are part of the Argus moving group, adding to the system's complexity.
- Researchers used the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile to detect the irregularities in the orbits of the brown dwarfs, leading to the identification of the planet.
- The planet, 2M1510 (AB) b, follows a polar orbit, contrary to the coplanar orbits typically observed for circumbinary planets, making it a groundbreaking find in planetary science.
- The presence of the planet was deduced based on subtle effects on the binary stars' orbits, providing evidence of its influence on the system.
- The discovery challenges existing models of planetary formation that assume planets form in coplanar discs, highlighting the diversity and complexity of planetary systems.
- This unexpected finding showcases the importance of curiosity-driven research and the advancements in astronomical techniques that enable the discovery of unconventional planets like 2M1510 (AB) b.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
The Verge
219

Image Credit: The Verge
The US is reportedly encouraging countries to adopt Musk’s Starlink in tariff trade talks
- The US government is promoting Starlink adoption in tariff trade talks with other countries, including India, Somalia, Lesotho, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Vietnam.
- US embassies and the State Department are encouraging countries to allow US satellite internet services like Starlink without promising lower tariffs in return.
- India rushed to secure regulatory approval for Starlink to potentially enhance trade deals with the US.
- White House spokesperson emphasized that the US is prioritizing American companies' success, and SpaceX did not immediately respond to requests for comment.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
TechCrunch
278

Image Credit: TechCrunch
Starlink’s launch in India now a matter of when, not if
- Starlink, Elon Musk's satellite-based broadband project, has received state approval in India to begin compliance procedures in the country.
- The Indian Department of Telecommunications granted approval for Starlink, and now the company needs to adhere to licensing requirements and security guidelines set by New Delhi.
- Starlink's connectivity in India is expected to take six to nine months to roll out, targeting the market of over 1.4 billion people with limited internet access.
- Starlink will face competition in India from other satellite internet providers like OneWeb, Airtel, Jio SpaceFiber, and Amazon's Kuiper.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
78

Image Credit: Nasa
Biotech and Health Research Top Thursday’s Workday, Crew Completes Training
- Biotechnology work and health research were the main focus on Thursday aboard the International Space Station, with crew members also conducting training and experiment cleanup duties.
- The CIPHER investigation studied how the human body reacts to spaceflight, examining adaptation of various body systems to longer missions.
- NASA crew members conducted biotechnology work to understand in-space manufacturing of nanomaterials, with experiments aiming to mimic DNA in space.
- Crew members also participated in cardiovascular system investigation, emergency training, veggie facility cleanup, and orbital plumbing duties on the station.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Digitaltrends
267

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
Soar through the famous Cosmic Cliffs in this stunning NASA visualization
- NASA has released a 3D visualization of the Carina Nebula, known as the Cosmic Cliffs, featuring data from multiple space telescopes.
- The visualization showcases the nebula in different wavelengths of light, from visible light to X-ray to infrared, exploring the intricate structures of dust and gas within.
- Stars within the Carina Nebula contribute to its unique shape by emitting stellar winds that sculpt the surrounding material, leading to the formation of new stars.
- The region of the nebula referred to as the Cliffs, technically called Gum 31, exhibits cliff-like formations carved out by stars in the NGC 3324 cluster.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Medium
166
Image Credit: Medium
Going to Space
- The fascination with space travel dates back to childhood for many, including the author who was born into an Air Force family in England in 1956.
- Exposure to short films, TV shows, and literature about space exploration fueled the author's passion for human space travel since an early age.
- Humanity's dream of venturing into space became a reality through the launch of satellites, such as the Voyager probes, and culminated in historic events like landing on the Moon.
- The author's personal connection to space exploration includes watching the manned missions to the moon take off from Florida, where their father was involved in installing communication arrays for tracking these missions.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
4

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA’s Hubble Pinpoints Roaming Massive Black Hole
- NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has discovered a massive black hole roaming 600 million light-years away, consuming stars in a tidal disruption event (TDE).
- The new TDE, named AT2024tvd, revealed a wandering supermassive black hole that is offset from the center of the galaxy, a rare find among TDE events.
- This offset black hole weighs one million solar masses and coexists with a 100 million solar mass central black hole within the same galaxy.
- The TDE phenomenon involves a star being ripped apart by a black hole's gravitational forces, leading to the formation of a disk around the black hole and the emission of high-temperature radiation.
- The flare from the TDE was detected by ground-based telescopes and confirmed by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, with Hubble pinpointing the event's location within the galaxy.
- The black hole responsible for the TDE is suspected to have been ejected from the galaxy's center due to three-body interactions or may be a remnant from a past galaxy merger.
- Future telescopes like the Vera C. Rubin Observatory and NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will aid in further understanding transient events like TDEs.
- This discovery opens up possibilities for uncovering more wandering black holes and sheds light on the dynamics of supermassive black holes in galaxies.
- The collaborative efforts of telescopes like Hubble and Chandra enable scientists to study and track rare celestial events, enhancing our knowledge of the universe.
- Hubble's continued operation and groundbreaking discoveries underscore its vital role in advancing astrophysical research and understanding the cosmos.
Read Full Article
Like
Nasa
249

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Stennis Tool Enables Unified Collection of Test Data
- NASA has developed the NASA Data Acquisition System (NDAS) at NASA's Stennis Space Center to collect hot fire data across test facilities in a standardized way, ensuring consistent performance.
- Before NDAS, contractors used various tools for data collection, making cross-collaboration difficult, but now NDAS provides a one-size-fits-all approach for NASA.
- NDAS was developed by a blended team of NASA personnel and contractors starting in 2011, and the software system is designed to work with any test hardware, supporting hot fire requirements for both NASA and commercial customers.
- The system utilizes LabVIEW, a graphical platform, which allows for modular components and future adaptability.
- NDAS captures high-speed and low-speed sensor data during propulsion tests and also monitors facility systems for general health and safety.
- The system was first demonstrated in 2014 and has been used for various engine tests, supporting SLS Green Run testing for Artemis missions.
- NDAS provides a common user experience, driving consistency across test complexes and centers, and has expanded beyond Stennis to other NASA centers and beyond, attracting interest from government agencies.
- The software's ongoing updates have provided growth opportunities for the NASA Stennis teams, and it is seen as an ever-evolving solution for data acquisition needs.
- Designed for the RPT office at NASA Stennis, NDAS is now being adopted in aerospace, defense, research institutions, and other areas requiring reliable and scalable data acquisition systems.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
170

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Stennis Releases First Open-Source Software
- NASA's Stennis Space Center has released its first-ever open-source software, a peer review tool to facilitate more efficient and collaborative creation of systems applications for rocket propulsion tests.
- The new NASA Data Acquisition System Peer Review Tool simplifies the collaborative review process, allowing developers to build better software applications.
- Developed over several years, the tool aims to improve efficiency, save time, and address issues earlier during software code reviews.
- The tool, designed to work with National Instruments LabVIEW, enhances the peer review process by allowing developers to post comments, pictures, and other elements for more effective discussions.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Medium
236
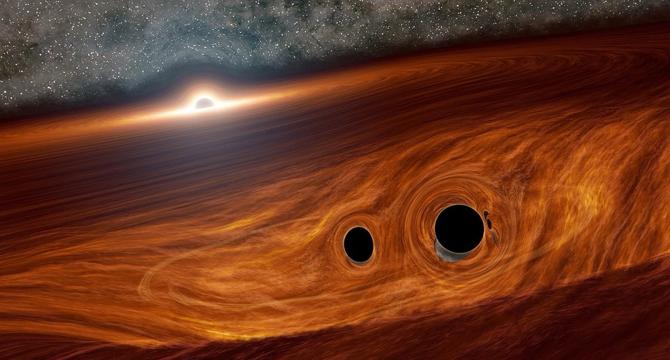
Image Credit: Medium
Black Hole Collision May Have Exploded With Light
- When two black holes collide, they send out gravitational waves that can be detected on Earth.
- Black hole mergers are typically invisible as they do not emit light visible to telescopes.
- Scientists using Caltech's Zwicky Transient Facility may have observed a possible light signal from a black hole collision.
- The potential light flare was linked to an event detected by gravitational wave detectors in 2019 known as GW190521g.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Livescience
162

Image Credit: Livescience
Did astronomers just discover the smallest galaxy in the universe?
- UMa3/U1, a recently discovered astronomical object, poses a challenge in defining whether it is a small galaxy or a star cluster.
- The distinction between Ultra-Faint Dwarfs (UFDs) and star clusters is blurred due to the significant presence of dark matter in UFDs.
- UMa3/U1 is exceptionally small, measuring only 20 light-years across with around 60 stars and a visible mass equivalent to 16 Suns.
- Based on current evidence, UMa3/U1 is likely a stable star cluster, although more observations are needed to confirm its classification.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Knowridge
333

Image Credit: Knowridge
NASA peers into a blazar’s heart and solves a 30-year-old mystery
- NASA's Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) has helped scientists uncover the mystery behind how X-rays are generated in powerful jets from supermassive black holes, specifically focusing on a blazar called BL Lacertae (BL Lac).
- The study revealed that X-rays in these jets are produced by electrons through Compton Scattering, not protons, as scientists previously debated, and the X-rays showed low polarization compared to optical polarization.
- IXPE, launched in December 2021, collaborated with radio and optical telescopes to observe BL Lac, leading to groundbreaking findings that shed light on the mechanisms of X-ray generation in extreme environments.
- The discovery not only solved a longstanding mystery about supermassive black hole jets but also highlighted the importance of IXPE in challenging scientific assumptions and exploring new possibilities in the study of blazars.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Earthsky
333

Image Credit: Earthsky
Magnetars’ strong flares forge gold and other heavy elements
- Powerful flares from magnetars, compact, dead stars with intense magnetic fields, have been found to create heavy elements like gold and platinum.
- A single flare from magnetar SGR 10.18106–20 in 2004 is believed to have produced a significant amount of heavy elements, potentially equal to a third of Earth’s mass.
- Magnetar flares now join neutron star mergers and supernovas as major sources of heavy elements in the universe.
- Astronomers discovered that powerful flares from magnetars can generate up to 10% of heavy elements in our galaxy.
- Neutron stars, magnetars with intense magnetic fields, have been identified as a new mechanism for creating heavy elements like gold and platinum.
- Astronomers are now able to directly observe the creation of heavy elements in magnetar flares, expanding understanding of element production in extreme environments.
- Magnetar flares present a third way to create heavy elements, in addition to neutron capture processes in stars and neutron star mergers.
- The study provides evidence that magnetar flares, through the rapid neutron capture process, contribute significantly to the production of heavy elements.
- Further observations of magnetar flares are crucial to determine the exact contribution of these events to heavy element creation in the universe.
- The launch of the Compton Spectrometer and Imager mission in 2027 by NASA aims to gather more data on magnetar flares and their role in element formation.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app