Space News
Knowridge
90
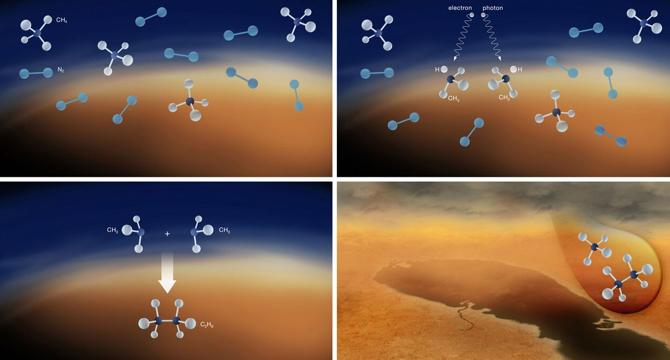
Image Credit: Knowridge
Astronomers spot rising methane clouds on Saturn’s moon Titan
- Astronomers have observed cloud convection in the northern hemisphere of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, for the first time using the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaiʻi.
- Titan's weather is powered by methane, creating weather patterns resembling those on Earth, with methane evaporating, forming clouds, and sometimes falling as rain on the moon's surface.
- Using the Keck Observatory and the James Webb Space Telescope, researchers observed methane clouds rising and moving in Titan's atmosphere, revealing insights into cloud convection in the northern region of the moon.
- These observations could provide deeper insights into Titan's methane cycle, weather patterns, and potential to support organic chemistry, with upcoming observations anticipated after the moon's next equinox in May 2025.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Brighter Side of News
258

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Subatomic wormholes could be responsible for universal expansion
- Scientists have discovered that the universe's expansion is speeding up, a phenomenon unexplained by general relativity.
- Dark energy, a mysterious force, makes up about 68% of the universe's total energy, surpassing all other known components.
- The nature of dark energy, including its origin and behavior, remains highly debated and poorly understood.
- Microscopic wormholes have been proposed as a potential driver of the universe's accelerated expansion.
- Quantum field theory predicts a significant discrepancy in the value of the cosmological constant, posing a fundamental challenge.
- Research is exploring alternative explanations for dark energy, such as dynamic forces and holographic dark energy.
- A new theory suggests subatomic-size wormholes created and destroyed in the vacuum of space may be responsible for universal expansion.
- Experimental verification of the wormholes driving dark energy theory remains a challenge but could provide significant insights into quantum gravity.
- The research team is refining calculations to determine the rate of wormhole formation and hopes to publish results soon.
- Understanding dark energy and potential confirmation of wormholes as drivers of cosmic expansion could revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Nasa
107

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Welcomes Norway as 55th Nation to Sign Artemis Accords
- Norway has become the 55th nation to sign the Artemis Accords, joining the commitment to peaceful and responsible space exploration.
- The signing ceremony held at the Norwegian Space Agency saw Minister of Trade and Industry Cecilie Myrseth signing the accords on behalf of the country.
- The Artemis Accords aim to establish guidelines for nations to enhance safety and reduce risks in civil space exploration, building on existing agreements and best practices.
- The accords are based on the Outer Space Treaty and include provisions for responsible behavior, such as the public release of scientific data.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
314

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Satellite Images Could Provide Early Volcano Warnings
- NASA satellites monitoring changes in vegetation near volcanoes could provide early warnings for eruptions, as seen with the Chaitén Volcano eruption in southern Chile in 2008 after 9,000 years of dormancy.
- The collaboration between NASA and the Smithsonian Institution aims to utilize NASA satellite images like Landsat 8 to detect changes in tree leaves, indicating increased volcanic activity from the release of carbon dioxide as magma ascends through the Earth's crust.
- Early detection of volcanic gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide is crucial for public safety, especially considering that ten percent of the world's population resides in areas vulnerable to volcanic hazards.
- While sulfur dioxide emissions are detectable from orbit, distinguishing volcanic carbon dioxide emissions that precede eruptions is a challenge, prompting the need for innovative methods like monitoring changes in vegetation.
- Scientists are exploring using trees as proxies to monitor volcanic carbon dioxide emissions, with satellites like Landsat 8, NASA's Terra satellite, and ESA's Sentinel-2 being potential resources for detecting changes in tree leaf color, indicative of magma-generated carbon dioxide.
- Despite limitations such as varying climatic conditions and interpretations influenced by factors like fires and plant diseases, using trees as indicators for volcanic carbon dioxide emissions could offer valuable early warning signals for eruptions.
- Early success stories like the Philippines' Mayon volcano, where carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide sensors aided in mass evacuations prior to a major eruption, highlight the potential lifesaving benefits of improved early warning systems for volcanoes.
- Continuing research aims to refine methods of monitoring volcanic activity through tree proxies and satellite imagery to enhance early warning systems and minimize casualties from volcanic events.
- By utilizing advancements in technology and interdisciplinary collaborations, scientists are working towards enhancing volcano early warning systems for improved public safety and disaster preparedness.
- The methods involving NASA satellites and tree monitoring could revolutionize how we detect and respond to volcanic activity, offering earlier insights and potential life-saving measures for populations at risk.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Nasa
51

Image Credit: Nasa
Let’s Bake a Cosmic Cake!
- To celebrate Dr. Nancy Grace Roman's 100th birthday, NASA is baking a cosmic cake representing the universe and the Roman Space Telescope's discoveries.
- The cake is designed to show the universe's components: dark energy, dark matter, and normal matter, each with different layers and ingredients.
- Dark matter, making up 25% of the universe, is represented by a layer with dark-colored batter, while dark energy, 68% of the cosmos, has a distinct layer.
- The cosmic candy mix for the cake symbolizes stars, galaxies, supernovae, neutron stars, black holes, and distant planets that the Roman telescope will observe.
- The telescope aims to map galaxies, study dark matter and dark energy, and reveal hidden cosmic objects, providing insights into the universe's mysteries.
- After baking and layering the cake, the final product, called the 'Roman Cosmic Cake,' is frosted in black with edible glitter, resembling the night sky.
- The cake's cutting symbolizes Roman's exploration of cosmic objects, inspiring wonder about the universe and its intricate components.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Popsci
197

Image Credit: Popsci
US Mint releases Space Shuttle $1 gold coin
- The US Mint has released a new $1 gold coin commemorating the NASA Space Shuttle program as part of the American Innovation $1 Coin series.
- The coin features the shuttle launching above plumes of exhaust and is the 28th coin in the 15-year project.
- The Space Shuttle played a significant role in space exploration from 1981 to 2011, transporting astronauts on missions and delivering components for projects like the Hubble Space Telescope and International Space Station.
- The ongoing American Innovation series has previously featured space-related themes, with the Florida coin following coins representing Delaware, Maryland, and Alabama.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Nasa
427

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Selects Student Teams for Drone Hurricane Response and Cybersecurity Research
- NASA has selected two university student teams to address real-world aviation challenges through projects involving drones for hurricane relief and cybersecurity for air traffic systems protection.
- The research awards were granted through NASA’s University Student Research Challenge (USRC) to allow student-led teams to contribute novel ideas to advance NASA’s Aeronautics research priorities.
- Each selected team receives a NASA grant up to $80,000 and is required to raise additional funds through student-led crowdfunding to develop skills in entrepreneurship and public communication.
- The chosen university teams and their research topics focus on developing advanced Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) for hurricane relief and implementing network authentication systems for cybersecurity threats in drone traffic control systems.
Read Full Article
26 Likes
Livescience
172

Image Credit: Livescience
The sun just spat out the strongest solar flares of 2025 — and more could be headed toward Earth
- The sun has recently released strong solar flares, including X1.2, M5.3, X2.7, and M7.7 flares, causing radio blackouts in various regions.
- Solar flares are sudden bursts of electromagnetic radiation from intense magnetic activity on the sun's surface, often linked to sunspots.
- The intensity of solar flares is categorized by NOAA as A, B, C, M, or X-class, with X-class being the most potent.
- X-class flares like the recent X1.2 and X2.7 can cause radio blackouts and impact communication and navigation systems on Earth.
- The solar flares also released a coronal mass ejection (CME), a massive explosion of charged solar plasma.
- CMEs travel slower than flares and can lead to geomagnetic storms, affecting power grids, satellites, and causing auroras.
- Recent CMEs from the flares have been directed towards Mars and are not expected to impact Earth directly.
- There is a possibility of more solar flares, potentially leading to radio blackouts and geomagnetic storms in the next few days.
- NOAA predicts a high chance of M-class solar flares hitting Earth in the coming days, with a smaller chance of X-class flares.
- The sun's activity may continue, with sunspot AR4087 potentially posing a threat as it moves across the sun's surface towards Earth.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
107

Image Credit: Nasa
Ongoing ISS Operations: Training, Research, Outreach, and Station Maintenance
- The International Space Station crew focused on critical tasks such as training, cargo handling, research, outreach, and maintenance.
- Crew members addressed physiological effects of microgravity by training for two hours daily using exercise equipment like ARED and CEVIS.
- Activities included cargo stowage in SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft, engaging with students through HAM radio, conducting experiments in material science and life sciences, and working with the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace.
- In the Russian segment, cosmonauts conducted maintenance tasks like auditing storage areas, regeneration of the Micropurification System, and reconfiguring the ventilation system.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Nasa
103

Image Credit: Nasa
Space Cloud Watch Needs Your Photos of Night-Shining Clouds
- The Space Cloud Watch project is calling for photos and observations of noctilucent or night-shining clouds, which glow with a blue silvery hue at dusk or dawn.
- These rare high-altitude clouds are typically found near the poles but are now being seen at mid- and low latitudes, prompting scientists to study how human activities may impact the atmosphere.
- By submitting photos and observations of these clouds, individuals can contribute to understanding why noctilucent clouds are appearing in new locations where temperatures are usually too warm for their formation.
- The collected data will be used in conjunction with satellite data and model simulations to analyze these phenomena, with opportunities for volunteers to assist in examining and identifying cloud structures.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Futurity
142

Image Credit: Futurity
Listen: ‘Planet Hunter’ searches for alien life on distant worlds
- Jacob Bean, known as the 'Planet Hunter,' discusses his work on searching for alien life in a Big Brains podcast episode.
- University of Chicago astrophysicist Jacob Bean was part of a team that detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a distant planet, using the James Webb Space Telescope.
- Bean utilizes cutting-edge tools and discoveries to explore planet habitability, biosignatures, and humanity's position in the universe.
- The podcast episode delves into the significance of studying the atmospheres of exoplanets like K2-18b in answering the question of whether we are alone in the universe.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Knowridge
303

Image Credit: Knowridge
Water ice found in another star system
- Water ice plays a significant role in shaping the outer regions of the Solar System, contributing to the composition of moons, planets, comets, and Kuiper Belt objects.
- A recent study published in Nature confirms the presence of crystalline water ice within a debris disk of a young star located 155 light-years away, observed using the James Webb Space Telescope.
- The debris disk around the star HD 181327 bears similarities to our own Kuiper Belt and offers insights into planetary formation processes, showcasing uneven distribution of water ice across different regions.
- The discovery provides valuable information on the distribution of water ice in planetary systems, aiding in understanding the evolution of habitable zones and potential conditions for life in the Galaxy.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Knowridge
426

Image Credit: Knowridge
New studies reveal hidden secrets of the Moon and asteroid Vesta
- New studies have revealed fascinating details about the internal structures of the moon and asteroid Vesta using gravity data collected from orbiting spacecraft.
- The research, published in Nature and Nature Astronomy, offers insights into the formation and composition of these celestial bodies without requiring landing on their surfaces.
- Scientists, led by Ryan Park from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, used a unique gravity analysis technique to create detailed maps of the moon and Vesta's gravitational fields.
- The findings suggest that the moon's near side is warmer and more flexible than the far side, possibly due to past volcanic activity, while Vesta's internal structure appears more uniform than previously thought.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app