Space News
Guardian
310
Image Credit: Guardian
Passing probe captures images of mysterious Mars moon
- The European spacecraft Hera has captured images of Mars's second moon, Deimos.
- Hera took the photos as it passed Mars on its way to a pair of asteroids.
- The images show the far side of Deimos, which is usually not visible.
- Hera's mission is to study asteroids and understand their potential threat to Earth.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Knowridge
184

Image Credit: Knowridge
Whoa! Astronomers found 128 new moons orbiting Saturn
- An international team of astronomers discovered 128 new moons orbiting Saturn, confirmed by the Minor Planet Center.
- Observations between 2019 and 2021 led to the discovery of 64 new moons initially.
- The new moons are irregular, likely captured objects that broke apart due to collisions.
- Saturn's moons follow wide, elliptical orbits compared to Earth's Moon.
- The small moons are suspected to be fragments of larger captured moons in Saturn's system.
- The ratio of small moons to large ones indicates a significant past collision in the Saturn system.
- Most of the 128 moons have retrograde orbits, hinting at their captured origins.
- The moons are near the Mundilfari group, suggesting a significant past collision in that region.
- Saturn's moon population is connected to its rings, shaping and influencing them.
- The IAU has assigned temporary designations for the new moons until they are officially named.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Insider
305
Image Credit: Insider
An 18-year-old won $250,000 for discovering over a million objects in space. Some could help unravel one of the universe's biggest mysteries
- Matteo Paz, an 18-year-old high school student from Pasadena, won $250,000 for discovering 1.5 million new space objects using an AI algorithm he built to sift through NASA data.
- Paz's discoveries include variable objects like supernovae and supermassive black holes, which could offer key insights into mysteries of the universe, such as the rate of expansion from the Big Bang.
- His work was recognized in the Regeneron Science Talent Search, where he was awarded first place among nearly 2,500 participants.
- Using the NASA NEOWISE space telescope data, Paz's AI algorithm identified a large number of variable space objects, some of which had never been cataloged before.
- Paz's catalog, named VarWISE, is being utilized by an infrared research group at Caltech to study dual-star systems and distant alien planets.
- By dividing the vast amount of data into smaller parts, Paz's algorithm successfully identified 1.5 million new space objects, contributing to astronomical research.
- The catalog is expected to be submitted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal, showcasing Paz's significant contributions to the field of astrophysics.
- Paz's ambition extends to using his discoveries to study the expansion rate of the universe from the Big Bang, potentially shedding light on fundamental cosmological mysteries.
- Apart from his scientific achievements, Paz also showed resilience during the LA fires, gaining a new perspective and considering applications of his research to benefit Earth monitoring.
- His dedication, talent, and groundbreaking work have positioned Paz as a promising young scientist with the potential to make significant contributions to astrophysics and cosmology.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Earthsky
274
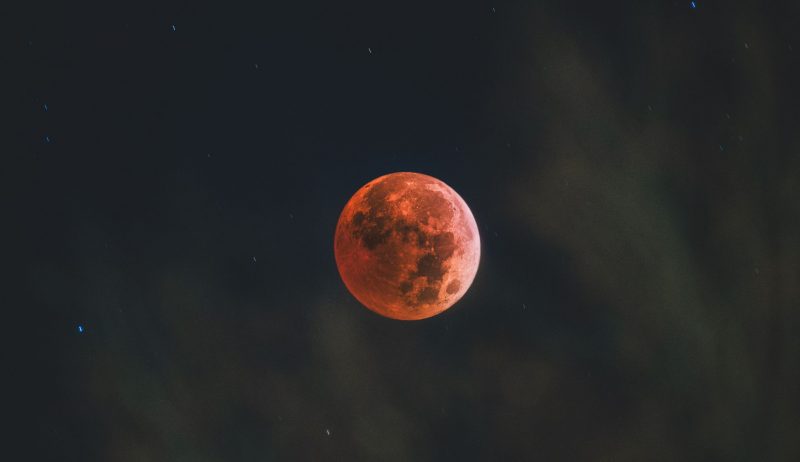

Image Credit: Earthsky
A total lunar eclipse looks red. Why?
- During a total lunar eclipse, the Earth's shadow causes the moon to appear red, rusty orange, or copper-colored.
- The Earth's atmosphere plays a key role in making the moon look red during a lunar eclipse.
- Sunlight passing through the Earth's atmosphere results in filtering out green to violet light, allowing the reddish spectrum to prevail.
- The reddish light is bent and refracted towards the moon, creating the red hue during a total lunar eclipse.
- Factors like dust, humidity, smoke, and temperature influence the brightness and color of the moon during an eclipse.
- The appearance of the moon during a total lunar eclipse can vary from copper-colored to deep red.
- The brightness of the moon during totality can differ based on atmospheric conditions.
- Uncertainty prevails regarding how red or dark the moon will appear during a lunar eclipse, adding to the allure of observing eclipses.
- A blue band of light along the limb of the moon, caused by light passing through the ozone layer, may also be visible during a lunar eclipse.
- The upcoming total lunar eclipse of March 13-14, 2025, offers another opportunity to witness the moon turning red due to Earth's atmosphere.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Discover more
TechBullion
422

Image Credit: TechBullion
Wiley and Pi School Join Forces to Boost ESA’s EVE Project with AI Innovation.
- Wiley and Pi School have joined forces to boost the European Space Agency’s AI-Powered Earth Virtual Expert (EVE) Project.
- Wiley will provide access to a curated collection of Earth science research materials to enhance the training and capabilities of the EVE project.
- Pi School, leading the development of the EVE project, has signed an agreement with Wiley.
- The collaboration aims to make authoritative scientific knowledge more accessible in Earth Observation research.
Read Full Article
25 Likes
Digitaltrends
4

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
Cool space video shows star trails stretching over city lights
- NASA astronaut Don Pettit has shared a video clip from the International Space Station showing star trails and city lights.
- The surreal footage demonstrates the expanding star trail and the trailing city lights across the frame.
- Pettit's space photography skills have captivated many, leading to the sharing of breathtaking photos during his orbital mission.
- Other astronauts, such as Thomas Pesquet and Matthew Dominick, have also shown great talent for capturing stunning shots of Earth from space.
Read Full Article
Like
Medium
1.3k
Image Credit: Medium
Why Elon Musk Plans to Take Humanity to Space
- Elon Musk plans to take humanity to space to mitigate existential risks and ensure the survival of the human species.
- Musk sees space colonization as the greatest engineering challenge in history and believes solving these problems can drive innovation on Earth.
- Apart from the existential motivation, there is an economic incentive to space development, with potential trillion-dollar industries like resource extraction and space-based solar power.
- Musk considers space exploration to provide a greater purpose and inspire humanity beyond day-to-day concerns, marking a new chapter in human evolution.
Read Full Article
28 Likes
Arstechnica
40
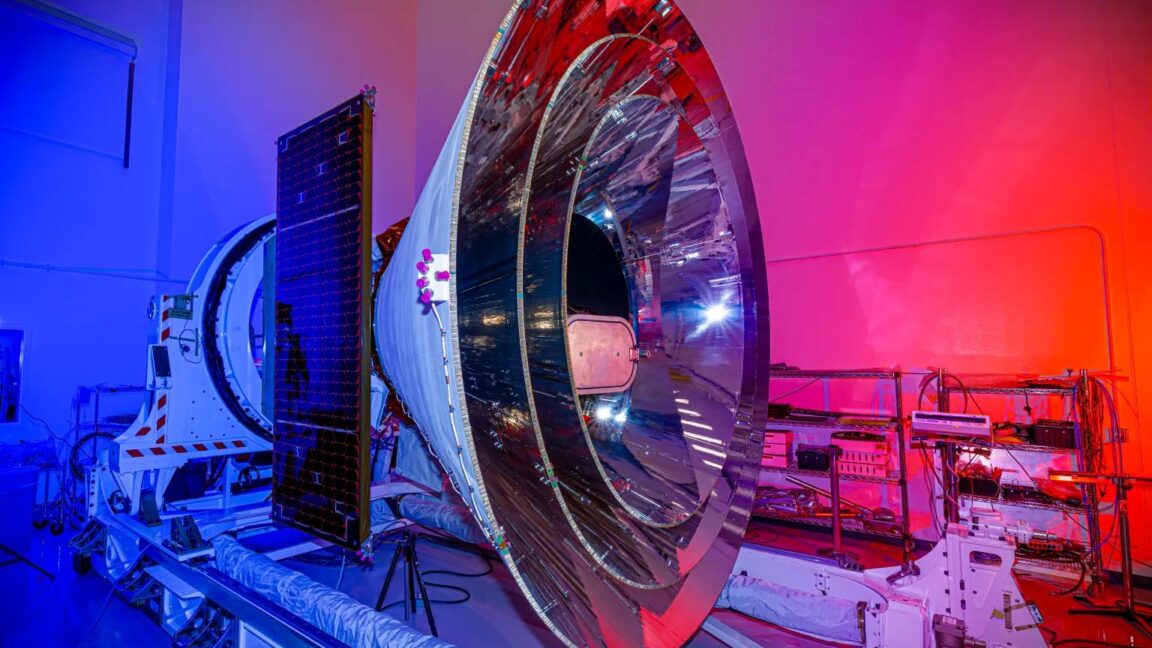
Image Credit: Arstechnica
No, that’s not a cosmic cone of shame—it’s NASA’s newest space telescope
- NASA has launched SPHEREx, an infrared observatory, on a mission to answer questions about the origins of the Universe and life.
- SPHEREx was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
- The observatory will conduct a two-year science mission surveying the sky in 102 colors invisible to the human eye.
- SPHEREx's infrared detectors will collect data on the chemical composition of asteroids, star-forming clouds, and distant galaxies.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
Earthsky
301

Image Credit: Earthsky
Powerful supernovas led to at least 2 mass extinctions
- At least two mass extinction events in Earth’s history were likely caused by the devastating effects of nearby supernova explosions, stripping the protective ozone layer, sparking acid rain, and exposing life to harmful radiation.
- The late Devonian and Ordovician extinctions, occurring 372 and 445 million years ago respectively, led to the decimation of 70% and 85% of earthly life.
- Researchers at Keele University in England published a study in March 2025 linking supernovas to these mass extinctions, highlighting the destructive power of massive star explosions.
- Supernovas spread heavy elements essential for life across the universe but can also have devastating effects if occurring near a planet, as seen in past extinctions on Earth.
- The research by the scientists involved studying massive stars within a kiloparsec of the sun to analyze the rate of supernovas and their potential impact on planets like Earth.
- Lead author Alexis Quintana emphasized the dual role of massive stars as creators and destructors of life due to their explosive nature when reaching the end of their lifecycle.
- Co-author Nick Wright warned of the catastrophic consequences of a massive star exploding as a supernova near Earth, potentially leading to significant harm to life on the planet.
- A supernova rate study within 20 parsecs of the sun supported the theory that supernovas were responsible for the late Devonian and Ordovician mass extinction events, contributing to Earth's history of catastrophic events.
- Although astronomers estimate 1-2 supernovas per century in galaxies like the Milky Way, the likelihood of nearby stars, such as Antares and Betelgeuse, affecting Earth in the near future is minimal due to their distance.
- The study sheds light on the impact of violent supernovas on mass extinctions and underlines the importance of understanding cosmic events that could potentially threaten life on Earth.
- Understanding the past link between supernovas and extinctions helps in preparing for potential future cosmic events and their impact on Earth and its biodiversity.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Knowridge
346

Image Credit: Knowridge
Is Europa alive? A laser could detect biosignatures from space
- Europa is a moon of Jupiter with a subsurface ocean of liquid water beneath its frozen exterior.
- Hydrothermal vents on Europa's ocean floor could create hydrogen and organic molecules, potentially supporting life.
- New research suggests laser-induced ultraviolet fluorescence could detect biosignatures in newly exposed ice on Europa.
- Aromatic amino acids surviving in Europa's surface ice could be a possible sign of life.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Digitaltrends
107

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
SpaceX scrubs Crew-10 launch attempt 40 minutes from liftoff
- SpaceX and NASA have scrubbed the launch attempt of Crew-10 due to a technical issue on the ground.
- The issue is related to the hydraulic system that controls a clamp arm that links the rocket to the launch tower.
- The next launch opportunity is scheduled on Thursday, March 13, if the issue gets resolved.
- The four Crew-10 astronauts will return to crew quarters and await confirmation of the new launch time.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
The Verge
170

Image Credit: The Verge
NASA plans to launch SpaceX Crew-10 tonight to help bring the Starliner astronauts home
- NASA's SpaceX Crew-10 mission is set to launch tonight to bring the Starliner astronauts back home.
- The Dragon spacecraft, flying atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will dock with the ISS on March 13th.
- The Crew-10 mission includes NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams, who have been stranded aboard the ISS for nine months.
- The astronauts will return on the Crew-9 capsule tentatively scheduled for March 16th, 2025.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
265

Image Credit: Nasa
Sols 4477-4478: Bumping Back to Business
- The Curiosity rover is winding between the Gould mesa and Texoli butte to analyze and characterize an interesting rock.
- Mastcam imaged troughs along the sand ridge to understand their formation, while ChemCam analyzed bedrock and loose rock for geochemistry.
- The science team selected the face of Gould mesa and upper Texoli butte for long-distance RMI imaging.
- The environmental theme group conducted activities to study clouds, atmospheric opacity, and aerosol scattering properties.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app