Space News
Nasa
189

Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Toxic Substance Exposure
- Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
- Toxic exposure to chemical contaminants can originate from various sources, including environmental system leaks, payload leaks, pyrolysis of polymeric materials, off-gassing of polymeric materials, and more.
- The risks of toxic exposure in space are mitigated through preventive measures and monitoring to ensure crew safety and reduce impacts on their health and performance.
- Safe, breathable air is crucial for crew health, and efforts are made to minimize toxic exposure events in space missions.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Nasa
342

Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome
- Exposure to altered gravity can cause ocular and brain structural changes to develop during spaceflight; these changes could lead to vision alterations, cognitive effects, or other deleterious health effects.
- Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome (SANS) is a syndrome unique to humans that fly in space and is not present in terrestrial diseases.
- Over half of crewmembers experience one or more symptoms of SANS, indicating brain structural changes.
- Determining intracranial pressure during spaceflight could improve understanding of SANS mechanisms and the ability to target countermeasures for future missions.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Nasa
144

Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Renal Stone Formation
- Exposure to microgravity induces bone atrophy/bone loss which increases circulating calcium, impacting the renal stone risk.
- Risk mitigation strategies including exercise and hydration are well-defined although the ability to treat a renal stone during exploration missions is not yet available.
- Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
- ISS Expedition 13 Flight Engineer, Thomas Reiter, on board ISS processes samples for the Renal Stone investigation.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Nasa
283
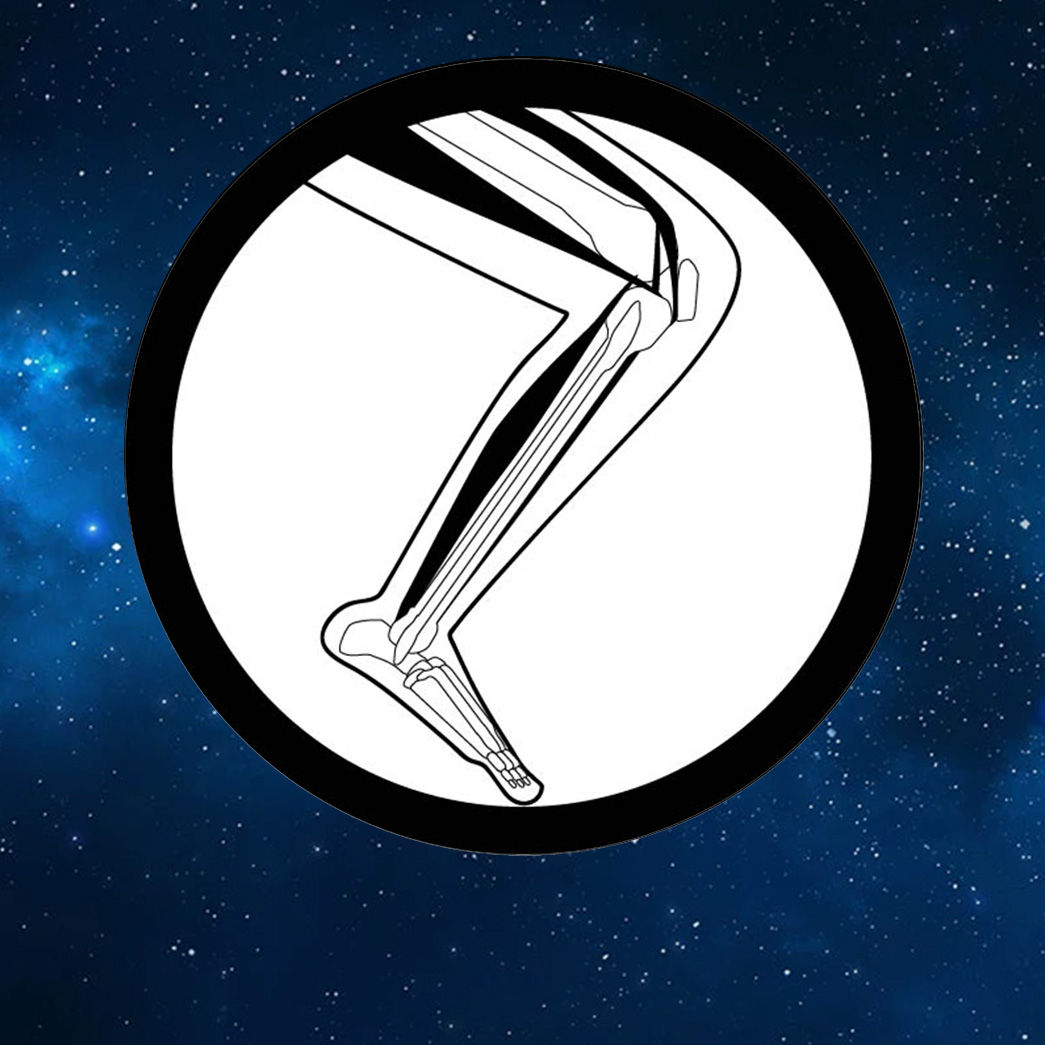
Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Reduced Physical Performance Capabilities Due to Reduced Muscle Size, Strength, and Endurance (Muscle Risk)
- Exposure to microgravity causes a decline in muscle size, strength, and endurance.
- Astronauts on the International Space Station (ISS) have minimal losses in muscle size, strength, and endurance if they adhere to the exercise schedule.
- New exploration countermeasure systems may not be able to support exercise as required to maintain human performance.
- NASA is conducting research to mitigate the risk of reduced physical performance capabilities due to reduced muscle size, strength, and endurance.
Read Full Article
17 Likes
Discover more
Nasa
184

Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Reduced Physical Performance Capabilities Due to Reduced Aerobic Capacity (Aerobic Risk)
- Spaceflight can cause a decline in maximum aerobic capacity, resulting in impaired mission task performance.
- Existing exercise schedules and countermeasure systems on the International Space Station (ISS) minimize losses in aerobic fitness.
- New exploration countermeasures systems may not be able to support exercise as required to maintain human performance.
- Reduced aerobic capacity poses a risk for reduced physical performance capabilities.
Read Full Article
11 Likes
Nasa
153

Image Credit: Nasa
Risk of Reduced Crew Health and Performance Due to Hypoxia
- Extravehicular Activity (EVA) architecture protocols for human exploration missions may lead to compromised health and performance due to exposure to mild hypobaric hypoxia.
- Concerns include potential effects on intracranial pressure, visual impairment, cognitive performance, sensorimotor dysfunction, oxidative damage, and sleep quality.
- Additional factors contributing to hypoxic exposure include cabin depressurization, system failures, toxic exposure, and crewmember illness/injury.
- NASA is researching the risks of reduced crew health and performance due to hypoxia in order to develop effective countermeasures.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Livescience
378

Image Credit: Livescience
Evidence for Stephen Hawking's unproven black hole theory may have just been found — at the bottom of the sea
- Researchers believe they may have observed an exploding black hole at the bottom of the sea.
- In 2025, underwater detectors discovered a highly energetic neutrino in the European collaboration KM3NeT.
- Scientists propose that the observed neutrino is the signature of an evaporating black hole.
- The discovery may provide insights into the existence of primordial black holes and dark matter.
Read Full Article
22 Likes
Brighter Side of News
355
Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Astronomers discover cosmic water source 140 trillion times larger than Earth’s oceans combined
- Astronomers have uncovered the largest and most distant water reservoir ever detected in the universe, enveloping a quasar more than 12 billion light-years away.
- The water reservoir is equal to 140 trillion times the volume of Earth’s oceans and surrounds the quasar APM 08279+5255, which hosts a black hole 20 billion times the mass of the sun.
- Water vapor plays a crucial role in understanding the conditions around the quasar, heating gas to unusual levels and making it far denser than typical interstellar environments.
- The discovery offers insights into the future of the quasar, with the available gas potentially sustaining the black hole's growth until it becomes larger or collapsing into new stars.
- Astronomers detected the water reservoir using instruments like Z-Spec and the Plateau de Bure Interferometer, revealing the vast quantity of water in the region.
- Water in the universe can be found in interstellar clouds, protoplanetary disks, comets, asteroids like Ceres, planetary atmospheres, surfaces, and even exoplanets like K2-18b.
- The formation of water primarily occurs through chemical reactions between hydrogen and oxygen, leading to water ice in space that eventually coalesces into larger bodies containing water.
- This remarkable discovery showcases the pervasiveness of water throughout the universe and provides valuable insights into the extreme environments surrounding quasars.
- Understanding the presence of water in various cosmic objects enhances our knowledge of planetary formation processes and the distribution of water in different regions of the universe.
- The immense scale of the water reservoir around the quasar APM 08279+5255 challenges previous assumptions about the distribution of water in deep space and highlights the unique conditions in that region.
- The research team's observations shed light on the role of water vapor in shaping the environment around quasars and contribute to the ongoing exploration of water sources across the cosmic landscape.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Insider
328

Image Credit: Insider
Photo taken on the moon shows what went wrong with an American space company's latest mission
- Intuitive Machines' lunar lander Athena landed on its side in a crater 820 feet away from the intended landing site and is no longer functioning.
- The craft landed in the Mons Mouton region on the moon's south pole.
- Athena's batteries will not recharge due to the direction of the sun, the orientation of its solar panels, and the frigid temperatures in the crater.
- Despite the unsuccessful landing, Intuitive Machines' teams are analyzing the collected data to gain insights for further space exploration.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Nasa
162

Image Credit: Nasa
The NASA DC-8 Retires: Reflections on its Contributions to Earth System Science
- The NASA DC-8, a key player in NASA's Airborne Science Program since 1987, has been retired after its last science flight in April 2024.
- It has been succeeded by a refurbished Boeing 777 aircraft, offering increased capabilities for Earth system science research.
- A workshop titled 'Contributions of the DC-8 to Earth System Science at NASA' was held in October 2024, reflecting on the aircraft's role in Earth science and beyond.
- The DC-8 was pivotal in missions like the Antarctic Airborne Ozone Expedition, which provided evidence for human impact on the ozone layer.
- The aircraft was also involved in various atmospheric research campaigns, contributing significantly to stratospheric and tropospheric chemistry studies.
- The DC-8 fostered a strong community of scientists, engineers, and professionals over its 37-year history, showcasing international collaborations and student involvement.
- Student programs like the Student Airborne Research Program (SARP) provided hands-on research opportunities on the DC-8, impacting many young scientists.
- The retirement of the DC-8 signifies a shift towards the future with the introduction of the Boeing 777, aiming to continue the legacy of airborne scientific research.
- NASA aims to carry forward the remarkable contributions of the DC-8 while embracing new possibilities with the Boeing 777.
- The DC-8's retirement marks the end of an era but highlights the ongoing commitment to advancing Earth system science through airborne observations.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Nasa
409

Image Credit: Nasa
Cardiovascular Health and Space Botany Day Before Crew-10 Launch
- The Expedition 72 crew on the International Space Station conducted space research while preparing for the SpaceX Crew-10 mission.
- Doctors are researching the cardiovascular risk for astronauts in space, particularly the aging-like changes in crewmember's arteries.
- The Vascular Aging investigation aims to decrease health risks for astronauts and treat aging conditions on Earth.
- The crew performed blood work for the glucose tolerance study and tended to lettuce plants in the Advanced Plant Habitat to study space botany.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Nasa
207

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Astronaut Jonny Kim to Discuss Upcoming Launch, Mission
- NASA astronaut Jonny Kim will launch on April 8 aboard the Roscosmos Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft for an eight-month mission to the International Space Station.
- During his time in orbit, Kim will conduct scientific investigations and technology demonstrations to benefit future space missions and people on Earth.
- Kim, a U.S. Navy lieutenant commander, holds a bachelor's degree in Mathematics and a medical degree from Harvard Medical School.
- The International Space Station serves as a testbed for long-duration spaceflight and enables NASA to focus on deep space missions to the Moon and Mars.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Knowridge
139

Image Credit: Knowridge
Webb Telescope discovers surprisingly complex chemistry in early galaxy
- Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have discovered a highly chemically complex galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, which formed when the universe was just 300 million years old.
- The properties of this early galaxy challenge our understanding of how galaxies formed after the Big Bang.
- The amount of oxygen found in JADES-GS-z14-0 suggests that stars may have started forming earlier than previously thought.
- The discovery highlights the potential of JWST in reshaping our knowledge of the cosmos and understanding the early history of the universe.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Livescience
207

Image Credit: Livescience
The universe's water is billions of years older than scientists thought — and may be nearly as old as the Big Bang itself
- Water likely appeared 100 million to 200 million years after the Big Bang, billions of years earlier than previously predicted.
- Oxygen forged in supernovas combined with hydrogen to create water.
- The amount of water in early gas clouds was small, but concentrated in regions where planets and stars formed.
- The presence of water early in the Universe suggests conditions for life formation were in place earlier than imagined.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app