Space News
Universe Today
391
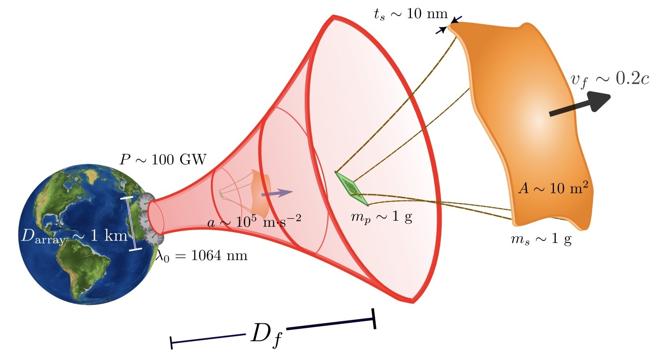
Image Credit: Universe Today
Photonic Lightsails are our Best Shot at Reaching Another Star
- Photonic lightsails offer a potential solution for interstellar travel due to their ability to propel spacecraft using beams of energy.
- A recent paper explores the principles of lightsail technology and identifies the best materials and designs for interstellar travel.
- Finding the right materials like molybdenum disulfide and nano-structured designs like diffraction gratings are crucial for the success of lightsails.
- However, the technology is still in its early stages and further progress is needed in material science, metalenses, and high-powered lasers.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Armaghplanet
86

Image Credit: Armaghplanet
Lord of Ether and Light – Earliest Astronomical Drawings on display at Armagh Planetarium
- The Armagh Planetarium is currently hosting an exhibition of the earliest astronomical drawings, called 'The Lord of Ether and Light'.
- The exhibition showcases the sketches of the Orion Nebulae, made by the 3rd Earl of Rosse and his team using the Great Telescope.
- The Great Telescope, built in 1845, used a 6-foot mirror made of Speculum, a copper and tin alloy, to gather light. It was a breakthrough instrument at the time.
- The drawings, which were later vindicated by astrophotography, have had a significant impact on our understanding of the universe.
Read Full Article
5 Likes
Universe Today
77

Image Credit: Universe Today
DARPA Wants to Build Structures in Orbit, Without Needing a Launch from Earth
- DARPA is partnering with universities to develop 3D printing technology and in-orbit assembly of satellite components.
- DARPA's NOM4D program aims to send lightweight materials to space for on-site construction, enabling the building of larger and more mass-efficient structures in orbit.
- Partnerships with Caltech and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign are progressing to in-space testing of the assembly process for smaller satellites.
- DARPA is exploring the possibility of growing large biological structures in space to enable new construction possibilities.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Earthsky
159

Image Credit: Earthsky
What’s a supermoon? Here are the supermoons in 2025
- In 2025, there will be five new supermoons, followed by three full supermoons in a row at the end of the year.
- A supermoon occurs when the new or full moon coincides closely with the moon's closest point to Earth, known as perigee.
- The new supermoons in 2025 will occur on February 28, March 29, April 27, May 27, and June 25 at varying distances from Earth.
- One of the supermoons in March 2025 will cause a partial solar eclipse.
- The closest full supermoons in 2025 will be on October 7, November 5, December 4, and starting in January 2026.
- Supermoons appear brighter than ordinary full moons, as they exceed the average brightness and size of the moon.
- The term 'supermoon' originated in 1979 by astrologer Richard Nolle and has gained popularity in recent years.
- Supermoons can cause higher-than-usual tides known as perigean spring tides, which may lead to localized flooding under certain conditions.
- The cycle of supermoons repeats every 14 lunar months, with variations in distance and brightness compared to micromoons, which occur when the moon is farthest from Earth.
- In 2025, there will also be three full micromoons, with the most distant full moon occurring on April 13.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Discover more
Digitaltrends
72

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
The space station is too darn clean, research suggests
- New research suggests that the International Space Station (ISS) might benefit from having a more diverse microbial community.
- The excessive cleanliness of the ISS may be contributing to health issues experienced by astronauts including immunity problems and skin rashes.
- The study found that the ISS has a lower diversity of microbes compared to human-built environments on Earth, with most species introduced by visiting astronauts.
- Adding more Earth microbes to the ISS could potentially improve astronaut health without compromising hygiene.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
Medium
27

Image Credit: Medium
Exploring Mars — The Red Planet
- Mars, also known as the Red Planet, continues to be explored by various missions from NASA, ESA, and other space agencies.
- Key features of Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano in the solar system, Valles Marineris, a vast canyon system, and the polar ice caps composed of water and carbon dioxide ice.
- Mars has a thin atmosphere consisting mainly of carbon dioxide, making it uninhabitable for humans without artificial environments.
- Scientists are still searching for answers regarding the possibility of past or current life on Mars, while plans for human missions and potential terraforming projects are being discussed.
Read Full Article
1 Like
The Verge
1.1k

Image Credit: The Verge
Jeff Bezos is sending Katy Perry to space
- Katy Perry will fly to space during Blue Origin’s next crewed mission.
- The pop star will join CBS host Gayle King and Bezos’s fiancé Lauren Sánchez aboard the New Shepard rocket this spring.
- Blue Origin’s most recent human spaceflight took place earlier this week, with a six-person crew reaching the edge of space and experiencing zero gravity for a few minutes before returning to Earth.
- Since 2021, Blue Origin has taken 52 people to space aboard its New Shepard rocket, including Star Trek’s William Shatner and Bezos himself.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Guardian
268
Image Credit: Guardian
Planetary parade: Mercury falls into line for rare seven-planet alignment
- A rare seven-planet alignment, known as a planetary parade, will occur on the last day of February.
- The visibility of the planets in the parade depends on their proximity to the horizon.
- Mercury, Neptune, and Saturn will be hard to see, while Venus, Jupiter, and Mars will be easily visible to the naked eye.
- Planetary parades with more than four or five planets are rare, with the next predicted alignment set to occur in 2040.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Medium
314

Image Credit: Medium
"The 2025 Planetary Alignment: A Cosmic Turning Point?"
- The planets will align in a rare celestial formation on February 28, 2025.
- Throughout history, planetary alignments have coincided with moments of profound change.
- Events such as the Black Death and World War I were preceded by planetary alignments.
- The upcoming alignment in 2025 raises the question of what kind of change it will bring.
Read Full Article
18 Likes
Arstechnica
414
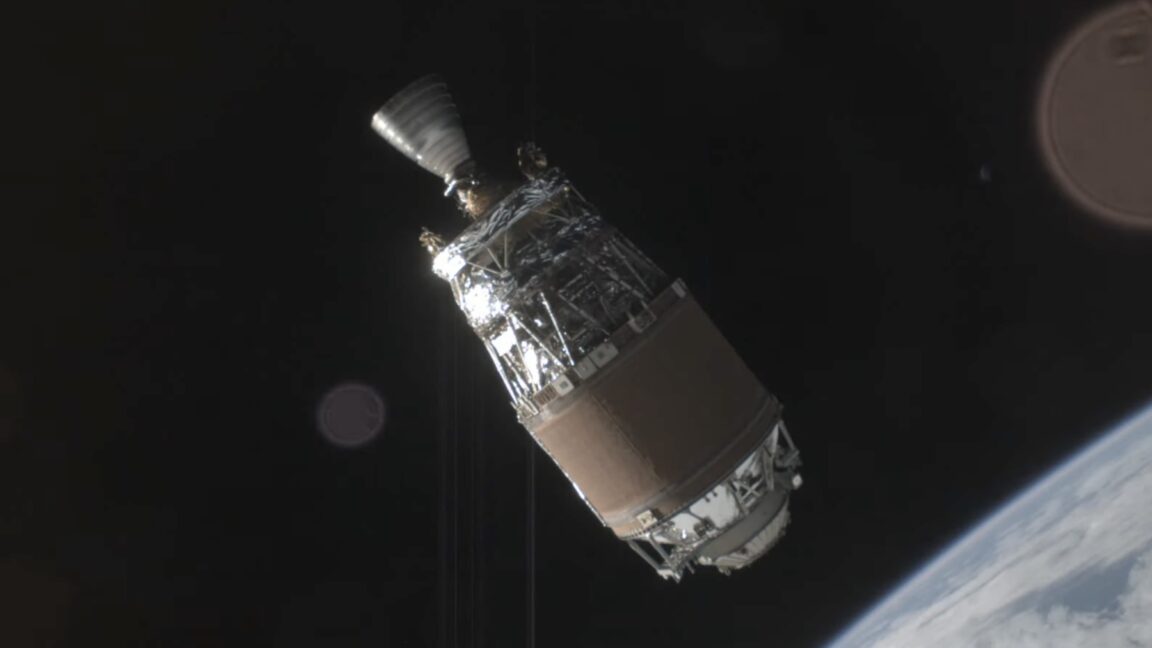

Image Credit: Arstechnica
Astroscale aced the world’s first rendezvous with a piece of space junk
- Astroscale's ADRAS-J mission successfully approached a piece of space junk in low-Earth orbit.
- The particular object, a derelict upper stage from a Japanese H-IIA rocket, has been in orbit since 2009.
- Astroscale's achievement is an impressive feat of engineering and orbital dynamics.
- It is the world's first spacecraft mission to rendezvous with space debris in a classified environment.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Universe Today
414

Image Credit: Universe Today
Lucy Sees its Next Target: Asteroid Donaldjohanson
- NASA's spacecraft Lucy captured an image of its next flyby target, the asteroid Donaldjohanson.
- Lucy will pass within 960 km of the asteroid on April 20th and will continue to image it for the next two months.
- The asteroid Donaldjohanson is a main-belt, carbonaceous C-type asteroid, about 4 km in diameter.
- Lucy's flyby of Donaldjohanson will allow mission personnel to test and calibrate the spacecraft's navigation system and instruments.
Read Full Article
24 Likes
Nasa
200

Image Credit: Nasa
Progress Cargo Mission Lifts Off to Station for Saturday Arrival
- The Progress 91 cargo craft successfully launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
- The unpiloted spacecraft is on its way to the International Space Station (ISS).
- It will automatically dock to the ISS Zvezda Service module in two days.
- The spacecraft carries approximately three tons of food, fuel, and supplies.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Nasa
237

Image Credit: Nasa
Progress Cargo Craft Counts Down to Launch Today on NASA+
- The Progress 88 cargo craft launches from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on May 30, 2024, during Expedition 71.
- The unpiloted Progress 91 spacecraft is scheduled to launch at 4:24 p.m. EST (2:24 a.m. Baikonur time) on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It will carry about three tons of food, fuel, and supplies for the Expedition 72 crew aboard the International Space Station.
- NASA’s live coverage is underway on NASA+, providing multiple platforms to watch NASA content, including social media.
- The spacecraft will dock to the aft port of the orbiting laboratory’s Zvezda Service module at 6:03 p.m., Saturday, March 1, after a two-day in-orbit journey. NASA’s rendezvous and docking coverage will begin at 5:15 p.m. on NASA+.
Read Full Article
14 Likes
Brighter Side of News
22
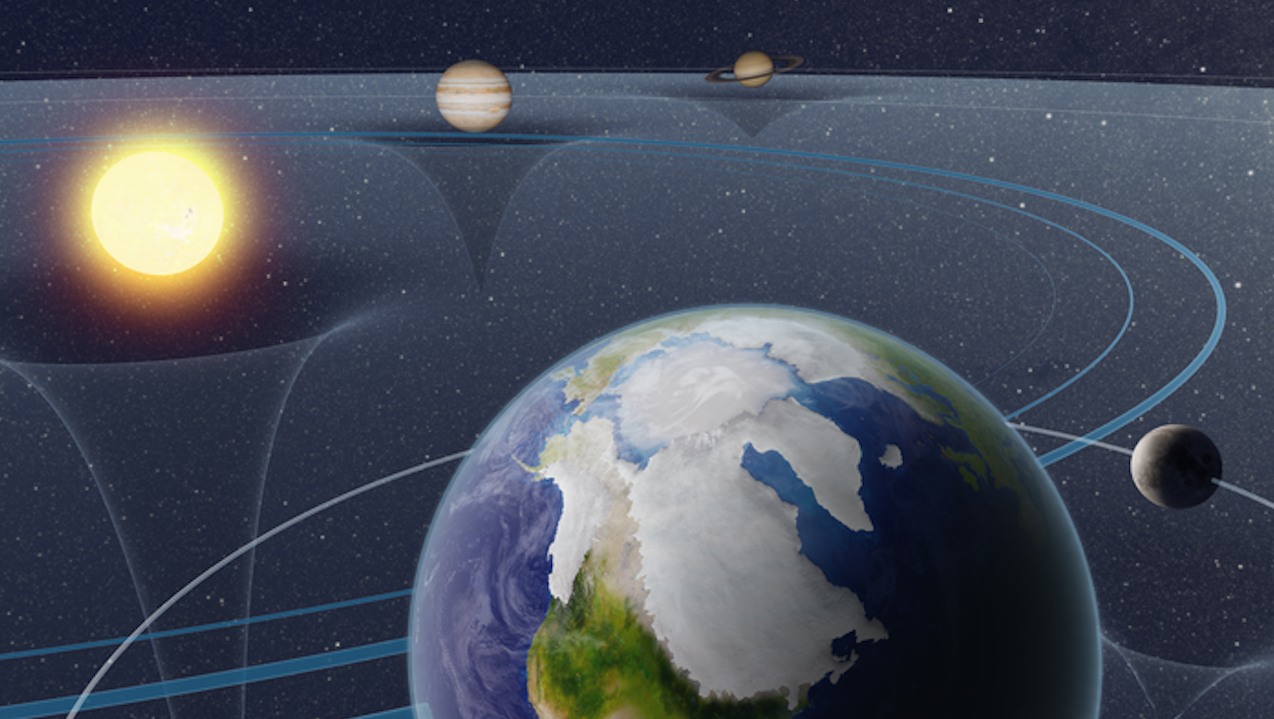
Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
New research links ice ages to shifts in the Earth’s orbit
- Research suggests that the next ice age would likely begin in about 10,000 years without human influence, based on Earth's orbital shifts and Milankovitch theory.
- Milankovitch theory explains how variations in Earth's orbit and axial tilt impact climate through changes in sunlight distribution.
- Orbital factors like axial tilt, precession, and eccentricity influence sunlight reaching high latitudes, shaping global climate.
- Recent study in Science reanalyzed a million years of climate history, highlighting a predictable pattern in Earth's glacial cycles.
- The study revealed a consistent correlation between Earth's orbital shifts and transitions between ice ages and interglacial periods.
- While Earth would be on track for a stable warm period in 10,000 years, human-induced greenhouse gas emissions have disrupted this natural cycle.
- Understanding past climate shifts helps refine climate models and predict future trends, offering insights into the impact of human activities.
- The delicate balance of Earth's climate system emphasizes the significance of predicting and understanding natural climate rhythms.
- By calibrating past changes, scientists aim to inform future climate predictions and address the long-term effects of human influence.
- This research provides a clearer understanding of how human activities are altering Earth's climate over long timescales.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Universe Today
218
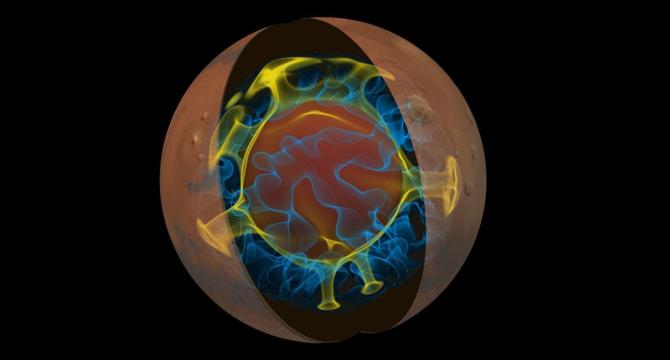
Image Credit: Universe Today
Mars’s Northern Ice Cap is Surprisingly Young
- Researchers have found that Mars's northern polar ice cap is quite young, providing insights into the planet's interior.
- The team used techniques to measure glacial isostatic adjustment, revealing ongoing deformation in response to the weight of the ice.
- The Martian ice cap measures approximately 1000 kilometers in diameter and up to three kilometers thick, causing depression in the underlying rocky crust.
- By studying glacial isostatic rebound on Mars, researchers concluded that the planet's north polar cap is relatively young and deforms the ground beneath it.
- The small deformation rates suggest that Mars's upper mantle is cold, highly viscous, and stiffer compared to Earth's upper mantle.
- Understanding how ice affects planetary surfaces helps scientists probe deep beneath the surfaces of rocky planets like Mars and Earth.
- Measurements of depression and rebound provide insights into the viscosity of the mantle rocks and the characteristics of planetary construction.
- The team estimated that Mars's north pole surface area is subsiding at rates of up to 0.13 millimeters per year, indicating a cold Martian interior.
- The age of Mars's north polar ice cap is estimated to be between 2 and 12 million years, making it one of the youngest large-scale features on the planet.
- The findings highlight the presence of local melt zones in the mantle near the equator, contrasting with the cold mantle underneath the north pole.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app