Space News
Knowridge
50

Image Credit: Knowridge
Scientists witness birth of a super star cluster in a nearby galaxy
- A super star cluster has been observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), offering insight into the early stages of massive star formation.
- Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers confirmed the presence of a second super star cluster in the LMC.
- The super star cluster in the LMC, named H72.97-69.39, is only 100,000 years old, allowing scientists to witness its birth in real-time.
- The collision of two massive clouds of dust and gas in the N79 region of the LMC is believed to have triggered the formation of the super star cluster.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Nasa
137

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA University Research Program Makes First Award to a Community College Project
- NASA's University Student Research Challenge awarded its first grant to a community college project led by students from Cerritos Community College in California.
- The Project F.I.R.E. team is researching the use of drones to extinguish fires with eco-friendly pellets, aiming to address the challenge of wildfires.
- This award marks a milestone as USRC has previously only selected participants from four-year institutions, showcasing NASA's commitment to inclusivity and innovation.
- Project F.I.R.E.'s research involves dropping biodegradable pellets into fires from autonomous drones, creating a foam-like fire retardant solution.
- The team aims to support firefighters and enhance safety during natural disasters, collaborating with stakeholders to refine their technology.
- Having won the 'Future Game-Changer' award at NASA's Gateway to Blue Skies competition, the team secured the USRC grant to further develop their idea.
- The community college students expressed gratitude for the opportunity to contribute to cutting-edge research and highlighted the value of community colleges in innovation.
- Through USRC support, the Project F.I.R.E. team plans to turn their concept into a tangible solution for fire suppression, building on their prior achievements.
- The innovative approach of using drones and eco-friendly materials in firefighting demonstrates a proactive response to the pressing issue of wildfires.
- NASA's recognition and support of community college students like those from Cerritos Community College signify a dedication to fostering diverse talent in aeronautics research.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Guardian
320
Image Credit: Guardian
Starwatch: a gloriously brilliant Venus and a young crescent moon
- This week, the western sky will offer a beautiful sight of Venus and a young crescent moon.
- On the evening of 2 March, the crescent moon will be just over three days old with 10% illumination.
- Venus will remain gloriously brilliant, situated in the Pisces constellation.
- Mercury, although fainter, can also be spotted above the western horizon after sunset.
Read Full Article
19 Likes
Nasa
397

Image Credit: Nasa
Simulation Tools
- The Simulation and Graphics Branch offers various software tools to facilitate simulation building and operation.
- Trick Simulation Environment streamlines domain-specific model building by providing common simulation capabilities.
- General-Use Nodal Network Solver (GUNNS) combines nodal analysis and hydraulic-electric analogy for medium-fidelity, real-time simulations.
- TrickHLA software supports the IEEE 1516 High Level Architecture standard for the Trick Simulation Environment.
- TrickFMI provides a Functional Mockup Interface implementation for Trick Base Models and Simulations.
- TrickCFS synchronizes core Flight Software system with the Trick simulation executive for proper interfacing.
- Input Device Framework (IDF) offers an infrastructure for software to interact with physical input devices.
- Displays and Controls Software (DCApp) is designed for UNIX platforms, employing technologies like OpenGL and libxml2.
- Koviz is a simulation data visualization tool offering real-time analysis report for Trick real-time data recordings.
- JSC Engineering Orbital Dynamics (JEOD) facilitates vehicle trajectory generation and spacecraft simulations for various missions.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Discover more
Medium
214
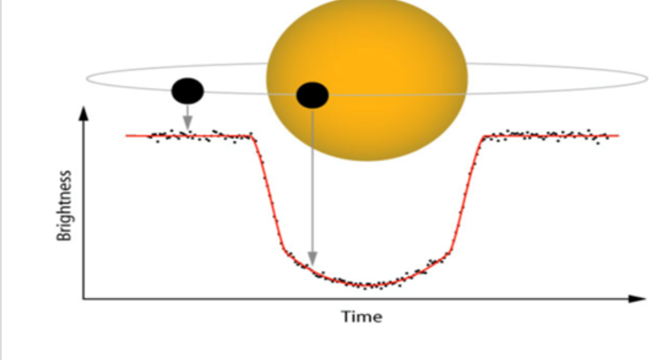
Image Credit: Medium
My Journey to creating an AI Model to Detect Exoplanets
- Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing space exploration and aiding in the discovery of exoplanets orbiting stars other than the Sun.
- AI models analyze light curves to detect transit dips, suggesting the presence of exoplanets by observing fluctuations in brightness over time.
- Flux quantifies light from celestial objects, helping determine the period of a planet's orbit and its size relative to the star.
- Various AI models like KNeighbors Classifier, Logistic Regression, Neural Networks, and Convolutional Neural Networks are used for exoplanet detection.
- KNeighbors Classifier achieved 99.12% accuracy, Logistic Regression had 63.68%, Neural Networks had 98.95%, and Convolutional Neural Networks had 99.18% accuracy in predicting exoplanets.
- AI systems can extend beyond space exploration to analyze FLUX data for sound, liquid, and music generation based on text input.
- AI advancements have practical applications in various fields like biology, chemistry, and video enhancement, showcasing the potential for innovative discoveries.
- AI's role in enabling groundbreaking research, such as detecting exoplanets and enhancing scientific instruments, underscores its importance in future discoveries.
- Artificial intelligence serves as a catalyst for progress and promising advancements in multiple domains, offering vast potential for future developments.
- Efficient AI systems, like those used in space exploration, hold promises for diverse applications that can impact numerous areas of human life and scientific exploration.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
Digitaltrends
27

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
SpaceX will launch its Starship megarocket this week
- SpaceX will launch its Starship megarocket for the eighth time on February 28.
- This upcoming test flight aims to achieve controlled landings for both the Super Heavy booster and the Starship spacecraft.
- NASA plans to use the Starship for crew and cargo missions to the moon and Mars.
- Elon Musk expressed his desire to prioritize the first crewed mission to Mars over NASA's moon-focused Artemis program.
Read Full Article
1 Like
Knowridge
4

Image Credit: Knowridge
Cosmic radiation altered virus evolution in Africa, study finds
- A nearby supernova may have influenced the evolution of life on Earth approximately 2.5 million years ago, according to astronomers from UC Santa Cruz.
- The radiation from the supernova is believed to have broken apart the DNA of living creatures in Lake Tanganyika in Africa, leading to an increase in viruses in the region.
- The study, led by recent graduate Caitlyn Nojiri and her team, found evidence of iron-60 isotopes from the supernova in samples retrieved from Lake Tanganyika.
- The team traced the origin of the iron isotopes back to a nearby supernova that occurred between 2 and 3 million years ago.
- Simulation of a near-Earth supernova suggested that cosmic rays bombarded Earth for 100,000 years after the blast, potentially damaging DNA.
- The researchers observed an increased diversification of viruses in the Rift Valley lakes at a similar timeframe to the supernova event.
- Caitlyn Nojiri, the lead researcher, was the first UCSC undergraduate invited to give a seminar at CCAPP at Ohio State and plans to pursue a career in astrophysics.
- Nojiri participated in programs like UC LEADS and Lamat, which inspired her to apply for graduate school in astrophysics.
- Enrico Ramirez-Ruiz, the UCSC Professor of astronomy, emphasized the importance of diverse perspectives in solving scientific problems.
- The study sheds light on how cosmic events like supernovae can impact the evolution of life on Earth and highlights the interdisciplinary nature of scientific research.
Read Full Article
Like
Universe Today
114

Image Credit: Universe Today
We Know How Much Radiation Astronauts Will Receive, But We Don’t Know How to Prevent it
- The journey to Mars will subject astronauts to extended periods of exposure to radiation during their months-long travel through space.
- Space radiation includes high-energy galactic cosmic rays and solar particle events that can damage DNA, increase cancer risk, and weaken the immune system.
- NASA estimates that a mission to Mars could expose astronauts to radiation levels that exceed current career exposure limits.
- Traditional shielding approaches are largely ineffective against galactic cosmic rays, and radiation levels vary depending on location and shielding configurations.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Universe Today
279
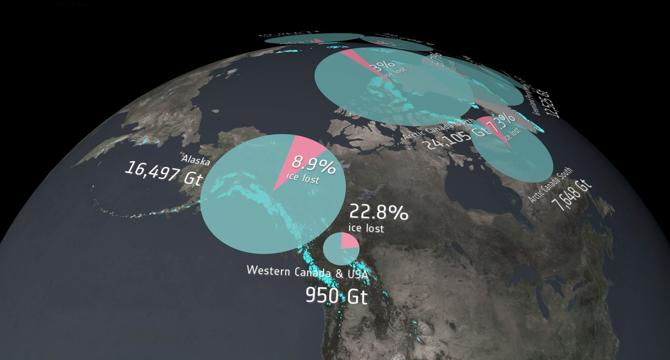
Image Credit: Universe Today
Glaciers Worldwide are Melting Faster Causing Sea Levels to Rise More
- Rising temperatures due to anthropogenic climate change are causing glaciers to melt at a faster rate, leading to various consequences like rising sea levels, coastal flooding, and drought risk.
- Research by the Glacier Mass Balance Intercomparison Exercise (GlaMBIE) team shows an alarming increase in glacier loss over the last decade.
- The study, published in Nature, utilized data from various satellite missions to track global glacier mass changes from 2000 to 2023.
- Glaciers lost 273 billion tonnes of ice annually, with regional losses ranging from 2% in the Antarctic to 39% in Central Europe.
- The rate of ice loss accelerated in the second half of the study, with glaciers contributing significantly to global sea-level rise.
- Glaciers collectively lost 6,542 tonnes of ice, leading to an 18 mm rise in global sea levels.
- The research provides a new observational baseline for studying the impact of glacier melt on water availability and sea-level rise.
- These findings are crucial for understanding the effects of climate change and developing strategies aligning with IPCC recommendations.
- The study aligns with the UN's focus on glacier preservation and highlights the need for collective action to address climate change.
- This research underlines the urgent need to address climate change and its impacts on glaciers and sea levels.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Universe Today
36

Image Credit: Universe Today
A Chinese Satellite Tests Orbital Refuelling
- China has launched the Shijian-25 satellite to test orbital refuelling operations, with the aim of extending the life of satellites and developing a network of orbital refuelling stations.
- Satellites require fuel for maneuvering and maintaining their desired orbits; once they run out of propellant, they become space debris.
- Orbital refuelling technology can extend satellite lifespans and transform space operations.
- Various companies and space agencies are developing orbital refuelling systems, which could make satellite operations more sustainable and cost-effective.
Read Full Article
2 Likes
The Verge
343

Image Credit: The Verge
The Space Force shares a photo of Earth taken by the X-37B space plane
- The Space Force shared a photo taken by the X-37B space plane of Earth.
- The photo was taken during experimental aerobraking maneuvers to safely change the orbit of the space plane using minimal fuel.
- This is the seventh mission of the X-37B, with previous missions having lasted up to two-and-a-half years.
- The mission of the X-37B includes operating in new orbital regimes and testing space domain awareness technologies.
Read Full Article
20 Likes
Universe Today
224
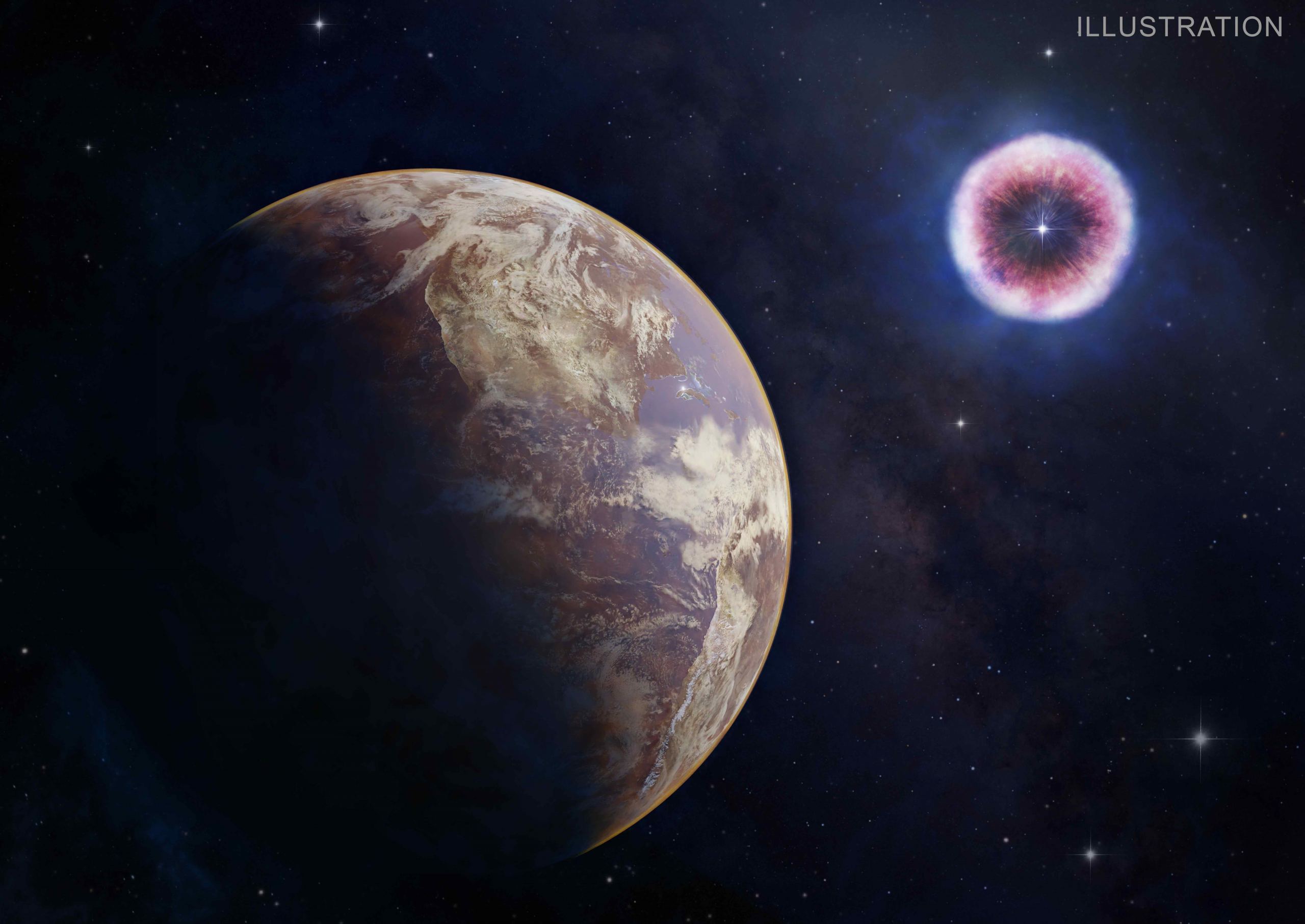

Image Credit: Universe Today
New Study Proposes that Cosmic Radiation Altered Virus Evolution in Africa
- A recent study by astronomers from UC Santa Cruz suggests that Earth was affected by radiation from a nearby supernova 2.5 million years ago, potentially leading to an increase in virus diversity in Africa.
- Scientists analyzed iron-60 samples from Lake Tanganyika, dating them to 2.5 and 6.5 million years old, indicating supernova activity near Earth during those times.
- They traced the origin of iron isotopes back to our Solar System passing through the Local Bubble in the Milky Way, and a nearby star going supernova between 2 and 3 million years ago.
- Simulations showed that cosmic rays from the supernova bombarded Earth for 100,000 years post-blast, potentially impacting DNA and leading to evolutionary changes and increased virus diversification.
- Lead author Caitlyn Nojiri is now pursuing a Ph.D. in astrophysics after her groundbreaking research was published.
- The findings suggest a link between cosmic radiation events and biological changes on Earth, highlighting the interconnectedness of astronomical events and life on our planet.
- Nojiri's research has garnered attention and recognition, with her being the first UCSC undergraduate to present at the Center for Cosmology and AstroParticle Physics.
- The study emphasizes the significance of diversity in scientific research and the importance of varied perspectives in understanding complex phenomena like supernova effects on Earth.
- This groundbreaking study sheds light on the potential impact of cosmic events on Earth's biological evolution and showcases the interdisciplinary nature of astrophysics research.
- The study opens up new avenues for exploring the connections between astronomical phenomena and biological evolution, highlighting the vast influence of the cosmos on life on Earth.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Brighter Side of News
155

Image Credit: Brighter Side of News
Scientists detect the most energetic neutrino ever recorded
- The most energetic neutrino ever recorded, with an estimated energy of 220 peta-electron volts (PeV), was detected by the ARCA detector of the KM3NeT neutrino telescope deep in the Mediterranean Sea.
- This groundbreaking discovery surpasses any previous observations and offers new insights into extreme astrophysical events.
- The detection marks a significant milestone in neutrino astronomy, shedding light on the universe's most energetic phenomena.
- Neutrinos, elusive subatomic particles, play a crucial role in revealing the origins of cosmic events like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- The KM3NeT deep-sea neutrino telescope employs advanced optical sensors in the Mediterranean Sea to capture elusive neutrino interactions with matter.
- KM3NeT's detectors, ARCA and ORCA, provide a vantage point to study high-energy cosmic neutrinos and neutrino oscillations, enhancing our understanding of the universe.
- The recently detected high-energy neutrino, KM3-230213A, likely has an extraterrestrial origin, hinting at powerful cosmic accelerators or unique cosmic phenomena.
- As KM3NeT expands and refines its capabilities, more high-energy neutrinos will be detected, aiding in identifying their sources and advancing particle physics.
- This discovery fuels the field of multi-messenger astronomy, integrating data from neutrinos, gravitational waves, and electromagnetic signals for a comprehensive view of cosmic events.
- KM3NeT's collaborative efforts demonstrate the dedication to advancing neutrino astronomy and unraveling the mysteries of the universe.
Read Full Article
9 Likes
Livescience
9

Image Credit: Livescience
NASA supercomputer reveals strange spiral structure at the edge of our solar system
- The Oort cloud, located at the edge of our solar system, may have a pair of spiral arms resembling a miniature galaxy.
- Researchers have developed a new model that suggests the inner structure of the Oort cloud resembles a spiral disk.
- The Oort cloud is a shell of icy objects that formed from the remnants of the solar system's giant planets.
- Further observations are needed to confirm the spiral structure and understand the origin and impact of comets in the Oort cloud.
Read Full Article
Like
Popsci
77

Image Credit: Popsci
Unistellar Odyssey Pro smart telescope review: Approachable in every way but the price
- The Unistellar Odyssey Pro smart telescope offers an easy and flexible viewing experience, solving many astrophotography complaints but comes with a steep price of $3,999.
- The telescope is compact, lightweight, and easy to set up, featuring an Alt-Azimuth mount for full tracking capabilities and a sturdy tripod for stability.
- Connectivity is reliant on the Unistellar app for functions such as orientation. The telescope has a five-hour battery life, USB-C charging, and 64GB storage for imaging.
- The Odyssey Pro uses an 85mm mirror diameter and a 4.1-megapixel sensor for viewing, with an eyepiece for a more traditional experience and OLED micro-display for immersive viewing.
- The Unistellar app simplifies the astronomy process with tools like a catalog of celestial objects, motorized mount tracking, image processing, and manual controls.
- Astrophotography with the Odyssey Pro is made easy with Deep Dark Technology, reducing light pollution effects and producing quality images with minimal fuss.
- While the telescope excels in simplifying stargazing and providing impressive results, drawbacks include limited Wi-Fi range, app dependence, and the high price point.
- The Odyssey Pro's portability, intuitive design, and ability to connect multiple apps make it suitable for social stargazing events, despite some drawbacks.
- Overall, the Unistellar Odyssey Pro offers an approachable astronomy experience but may not justify its high cost for all users, making the more affordable Odyssey a viable alternative.
- Key specs include a focal length of 320mm, 85mm mirror diameter, f/3.9 focal ratio, 4.1-megapixel image resolution, motorized Alt-Az mount, 5000+ object database, and 5-hour battery life.
Read Full Article
4 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app