Space News
Livescience
169

Image Credit: Livescience
Scientists made fake Martian dust — and found a big surprise about what makes Mars red
- The characteristic red hue of Mars may be due to ferrihydrite instead of rusted iron minerals, as previously believed.
- New research suggests that Mars' red color is better matched by ferrihydrite, an iron oxide that contains water.
- This indicates that Mars may have been a cool ocean world in the past, challenging the assumption that it turned red after losing its water.
- Further research is needed to determine the original source of ferrihydrite and its timing and composition in Mars' history.
Read Full Article
10 Likes
Nasa
228

Image Credit: Nasa
Science in Orbit: Results Published on Space Station Research in 2024
- NASA and its partners have conducted over 4,000 research investigations on the International Space Station, leading to 4,400 research publications, with 361 published in 2024 alone.
- Research on the space station advances technology on Earth and prepares for future space exploration missions.
- Key findings include the Microgravity Investigation of Cement Solidification, JAXA Colloidal Clusters, and Optical Imaging of Bubble Dynamics on Nanostructured Surfaces.
- The Microgravity Investigation of Cement Solidification uses AI to analyze cement samples formed in microgravity for potential applications in civil engineering and manufacturing.
- The JAXA Colloidal Clusters research focuses on pyramid-shaped clusters with applications in optical and laser communications systems.
- NASA's study on bubble dynamics reveals insights into bubble growth in microgravity that can improve thermal cooling systems and sensors.
- ESA's Cytoskeleton investigation explores cellular responses to space, providing insights into aging processes and potential countermeasures for astronaut health.
- The Canadian Space Agency's Wayfinding study examines spatial awareness in astronauts, revealing impacts of microgravity on spatial processing regions of the brain.
- The Mini-EUSO telescope project by Roscosmos-ESA-Italian Space Agency aids in detecting space debris and meteors to enhance space activity safety.
- Research on the ISS in 2024 has led to significant contributions in various fields, offering insights into space-based technology and human health in space.
Read Full Article
13 Likes
Eu-Startups
132

From space junk to interplanetary travel: Magdrive’s €9.9 million funding for spacecraft propulsion
- Oxfordshire-based startup Magdrive has raised €9.9 million in a seed funding round to develop spacecraft propulsion technology.
- The funding round was led by Redalpine and saw participation from Founders Fund, Balerion, Alumni Ventures, Outsized Ventures, 7percent, and Entrepreneur First.
- Magdrive's propulsion system offers unrivaled thrust and efficiency, enabling spacecraft to travel farther and maneuver with greater precision.
- The funding will support Magdrive's research and development, construction of a manufacturing facility, and establishment of a US office.
Read Full Article
7 Likes
Discover more
TechCrunch
105
Image Credit: TechCrunch
Redalpine, Founders Fund back Magdrive’s electric thruster business
- UK-based startup Magdrive has secured $10.5 million in funding to develop its electric propulsion system for satellites.
- Magdrive's electric propulsion system offers higher thrust, smaller form factor, and high specific impulse compared to traditional systems.
- The scalable technology allows for sustained rendezvous and proximity operations, stochastic movements, and satellite servicing missions.
- The funding round was led by redalpine and included participation from Founders Fund and other investors.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Universe Today
397

Image Credit: Universe Today
China’s Tianwen-2 Is About to Launch. Here’s What We Know About Its Target Kamo’oalewa
- China is preparing to launch the Tianwen-2 mission to explore asteroid 469219 Kamo’oalewa and Comet 311P/PanSTARRS in a first-ever asteroid-comet exploration mission.
- A rare quasi-satellite of Earth, asteroid Kamo’oalewa fluctuates between quasi-satellite and horseshoe orbits, potentially posing a future impact risk.
- Researchers suggest Kamo’oalewa may be ejecta from the Moon's Giordano Bruno crater, showing a spectral resemblance to Apollo 14 and Luna 24 soil returns.
- A recent study by the European Space Agency aims to refine Kamo’oalewa's orbit and study the Yarkovsky and YORP effects affecting its rotation.
- Kamo’oalewa's fast rotation poses challenges for sample collection, with an expected return of approximately 100 grams of material on the Tianwen-2 mission.
- Comparison to lunar S-type asteroids suggests Kamo’oalewa may have regolith on its surface, hinting at unexpected features for such fast rotators.
- Tianwen-2's mission timeline includes a rendezvous with Kamo’oalewa in 2026, sample collection, and exploration of periodic comet 311/P PanSTARRS in 2034.
- China's CNSA has embarked on incremental space exploration, with plans for a Mars sample return mission in 2028 following the success of previous missions.
- The launch of Tianwen-2 signifies China's continued advancements in space exploration, aiming to unravel the mysteries of asteroid Kamo’oalewa and beyond.
- The mission's goal is to expand our understanding of asteroid and comet compositions, shedding light on the origins of celestial bodies in our solar system.
Read Full Article
23 Likes
Nasa
0

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA Prepares Gateway Lunar Space Station for Journey to Moon
- NASA is preparing Gateway lunar space station for its journey to the Moon.
- The Power and Propulsion Element, assembled by Maxar Space Systems in California, will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
- Gateway will allow NASA to conduct unique science and exploration while preparing astronauts to go to Mars.
- Artemis IV mission astronauts will be the first to inhabit the lunar space station.
Read Full Article
Like
Metro
54

Image Credit: Metro
New update on chance of ‘city killer’ asteroid hitting Earth in 2032
- The chance of the 'city killer' asteroid hitting Earth in 2032 has been calculated to be 0.0027%.
- Nasa has concluded that there is no significant potential for this asteroid to impact our planet for the next century.
- Even though there is still a small chance of it hitting the Moon on December 22, 2032.
- Improved observations and early detection give us a better chance to deflect or avoid potential asteroid impacts.
Read Full Article
3 Likes
Earthsky
105
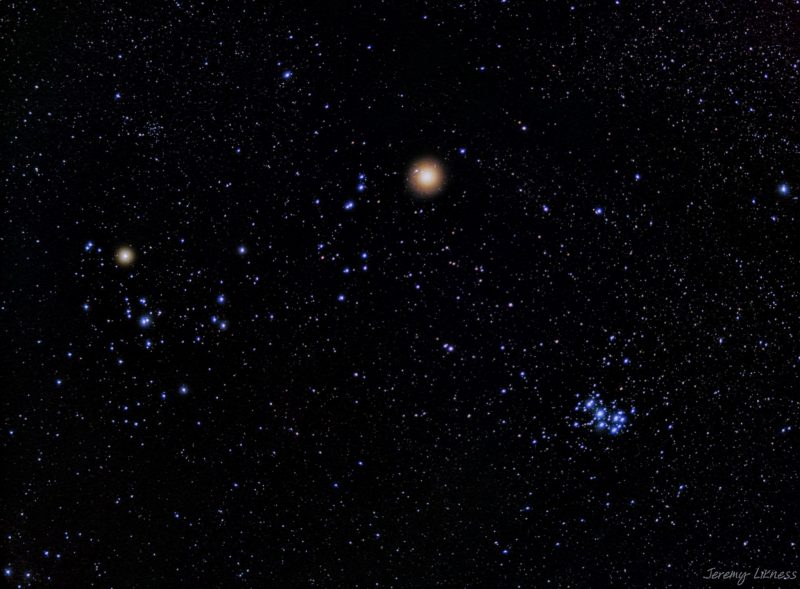

Image Credit: Earthsky
Look for the colors of the stars
- In January 2023, Jeremy Likness captured a photo of Mars and Aldebaran in the Hyades star cluster in Monroe, Washington.
- Observing stars in the dark sky allows one to appreciate the variations in their colors, from red to yellow to blue-white.
- In 2025, Jupiter and Mars will be prominent among the stars of Taurus and Gemini.
- Capella, a golden star in Auriga, contrasts with reddish Aldebaran and bluish Pleiades in Taurus.
- Sirius appears white, whereas Betelgeuse in Orion is red and Rigel is blue.
- A star's color indicates its spectral type, with Capella being a G star, Aldebaran a K star, and Betelgeuse an M star.
- Surface temperature determines a star's color, with yellow stars like Capella having mid-range temperatures and blue stars like Rigel being hot.
- Stars with high surface temperatures appear blue, while those with lower temperatures appear red in color.
- Winter offers a great opportunity to appreciate the colors of stars, with Orion being a standout constellation for observing various colored stars.
- Understanding the relationship between a star's color and its spectral class can provide insights into their temperatures.
Read Full Article
6 Likes
Livescience
146
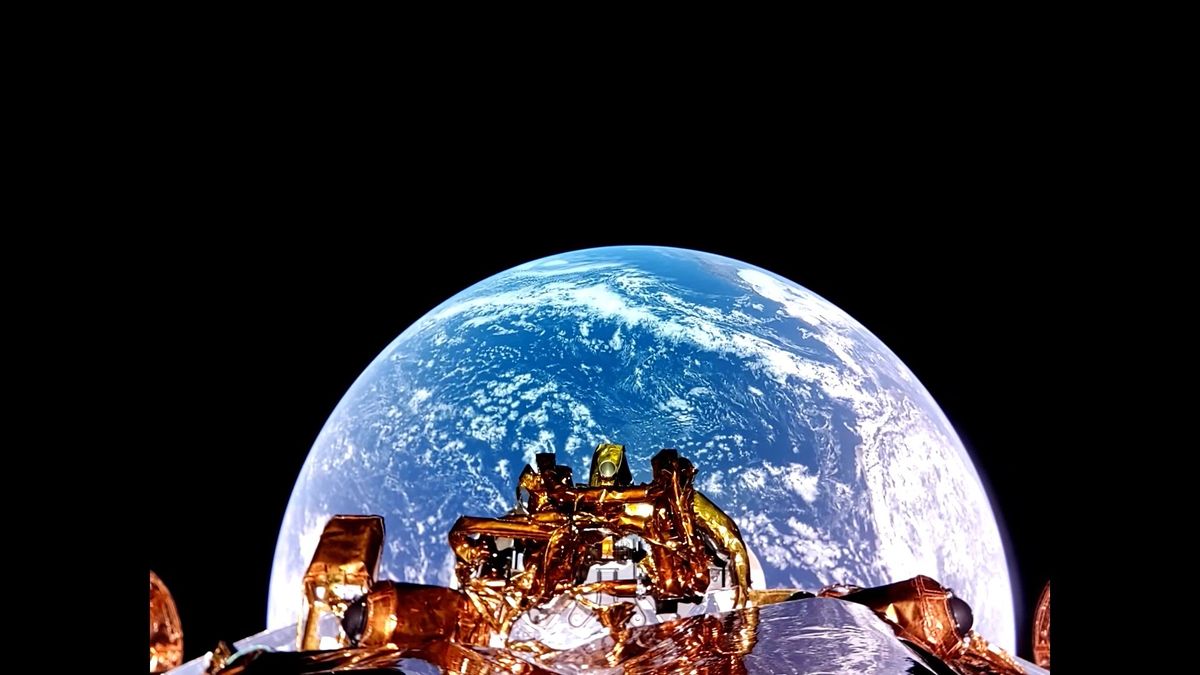

Image Credit: Livescience
Blue Ghost spacecraft captures rare, stunnning views of Earth eclipsing the moon
- The Blue Ghost lunar lander, part of Blue Ghost Mission 1, captured stunning images of Earth eclipsing the moon.
- The mission, led by Firefly Aerospace and NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services program, aims to learn about the moon and demonstrate new technology.
- Blue Ghost launched on Jan 15, circled Earth, and will attempt a lunar landing on March 2.
- The lander filmed the lunar far side and will conduct experiments exploring the moon's formation and test new technologies.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
Nasa
278

Image Credit: Nasa
NASA: New Study on Why Mars is Red Supports Potentially Habitable Past
- A new study funded by NASA provides evidence that Mars may have had a cool, wet, and potentially habitable climate in the past.
- Research suggests that Mars' red dust is likely due to the presence of water-rich iron mineral ferrihydrite.
- Ferrihydrite formation indicates Mars could have sustained liquid water before transitioning to a dry environment billions of years ago.
- The study highlights coordinated research between NASA and international partners in exploring Mars' habitable past.
- Data from Mars missions and laboratory experiments support the theory of ferrihydrite's role in Mars' coloration.
- The study aims to understand ancient Martian climate, chemical processes, and potential habitability for life.
- Future Mars samples could conclusively test the proposed formation model for Mars' reddish dust.
- The return of samples from Mars, such as those collected by the Perseverance rover, will provide valuable insights.
- The study opens doors for applying mineral formation principles, awaiting confirmation from Mars samples analysis.
- Laboratory experiments and spectral measurements help researchers explore Mars' environmental history and conditions.
Read Full Article
16 Likes
Metro
210

Image Credit: Metro
Why is Mars red? Scientists think they’ve found answer to mystery
- Scientists believe they have discovered the reason behind the red color of Mars.
- A study suggests that ferrihydrite, a water-rich iron mineral, could be the main cause.
- The theory is based on the recreation of Martian dust in a lab and observational data.
- This finding not only explains the color but also provides insights into Mars' past environment.
Read Full Article
12 Likes
COSMOS
255

Image Credit: COSMOS
The Red Planet slowly gives up its oceanic secrets
- Recent research indicates Mars may have once had cool water in large volumes, potentially supporting microbial life.
- Using radar data from the Chinese Zhurong rover, scientists identified geological formations on Mars resembling coastlines from an ancient ocean.
- Chemists studying the Red Planet's rusty hue suggest Mars's red color is likely due to the presence of a mineral called ferrihydrite, formed in cool, wet conditions.
- The discovery of ferrihydrite implies Mars rusted earlier than previously thought, highlighting the planet's watery past.
- A team of researchers has developed a miniature laser-powered mass spectrometer to detect traces of microbial life in gypsum, a mineral found on Mars.
- Gypsum is known for its fossilization potential, preserving biological structures and chemical biosignatures, making it an important target for life detection.
- Detecting fossils of alien life on Mars would be a groundbreaking scientific discovery with implications for future rover missions.
- The innovative detection method could aid in locating potential sites for future exploration, although researchers emphasize the need for additional validation methods.
- Understanding Mars's watery history and the presence of potential biosignatures is crucial for exploring the possibility of past microbial life on the Red Planet.
Read Full Article
15 Likes
Popsci
351

Image Credit: Popsci
Why is Mars red? Our old understanding might be wrong.
- A new study published in Nature Communications challenges the old understanding of how Mars got its red color.
- The hypothesis focuses on ferrihydrite, which might have formed when Mars still had water, potentially during a habitable period.
- Mars acquired its red color from rusted iron minerals reacting with water and oxygen, similar to rust formation on Earth.
- Iron in Mars' rocks reacted with oxygen and water in its wetter past, creating rust that was washed into rivers and seas.
- Volcanic activity and ice-melting events further contributed to the rust formation on Mars.
- New analysis suggests that Mars' red color is better matched by ferrihydrite, an iron oxide containing water, rather than hematite.
- Ferrihydrite likely formed when Mars still had water on its surface, preserving a watery signature for billions of years.
- Comprehensive proof of ferrihydrite in Martian dust was obtained through a study combining space mission data and lab experiments.
- ESA's Mars Express and Trace Gas Orbiter, along with NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and rovers, contributed to the research.
- Future missions like NASA's Perseverance rover and ESA's Rosalind Franklin rover aim to deepen the understanding of Mars' red color.
Read Full Article
21 Likes
Digitaltrends
138

Image Credit: Digitaltrends
How to watch SpaceX’s 8th Starship flight test this week
- SpaceX is targeting Friday, February 28, for the eighth test of the Starship rocket.
- The mission will include the deployment of four Starlink simulators and experiments focused on enabling the upper stage to return to the launch site.
- The test flight will be livestreamed on SpaceX's website or on its X account starting about 40 minutes before liftoff.
- The schedule is subject to change, so it is advised to check for updates on SpaceX's website or X account.
Read Full Article
8 Likes
For uninterrupted reading, download the app